Abstract
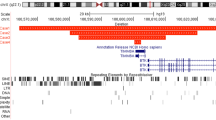
The Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) locus has been localized to the short arm of the human X chromosome (Xp21) by detection of structural abnormalities1–5 and by genetic linkage studies6–8. A library highly enriched for human DNA from Xp21 was constructed9 using DNA isolated from a male patient who had a visible deletion and three X-linked disorders (DMD, retinitis pigmentosa and chronic granulomatous disease)5. Seven cloned DNA probes from this library and the probe 754 (refs 5,8) are used in the present study to screen for deletions in the DNA isolated from 57 unrelated males with DMD. Five of these DMD males are shown to exhibit deletions for one of the cloned DNA segments and at least 38 kb of surrounding DNA. In addition, two subclones from the same region detect four restriction fragment length polymorphisms which exhibit no obligate recombination with DMD in 34 meiotic events. These new DNA segments will complement the existing Xp21 probes4–9 for use in carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis of DMD. Elucidation of the end points of the five deletions will help delineate the extent of the DMD locus and ultimately lead to an understanding of the specific sequences involved in DMD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacobs, P. A., Hunt, P. A. & Bart, R. D. Am. J. hum. Genet. 33, 531–538 (1981).
Greenstein, R. M. et al. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 27, 268 (1980).
Worton, R. G. et al. Science 224, 1447–1449 (1984).
de Martinville, B. et al. Am. J. hum. Genet. 37, 235–249 (1985).
Francke, U. et al. Am. J. hum. Genet. 37, 250–267 (1985).
Davies, K. E. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 11, 2303–2312 (1983).
Aldridge, J. et al. Am. J. hum. Genet. 36, 546–564 (1984).
Bakker, E. et al. Lancet i, 655–658 (1985).
Kunkel, L. M., Monaco, A. P., Middlesworth, W., Ochs, H. D. & Latt, S. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 4778–4782 (1985).
Langes, K. et al. Am. J. hum. Genet. (in the press).
Benton, W. D. & Davis, R. W. Science 196, 180–182 (1977).
Loenan, W. A. M. & Blattner, F. R. Gene 26, 171–179 (1983).
Frischauf, A. M. et al. J. molec. Biol. 170, 827–842 (1983).
Southern, E. M. J. molec. Biol. 98, 503–517 (1975).
Pearce, J. M. S. et al. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 27, 181–185 (1964).
Emery, A. E. H. & Holloway, S. Hum. Hered. 27, 118–126 (1977).
Yang, T. P. et al. Nature 310, 412–414 (1984).
Rozen, R., Fox, J., Fenton, W. A., Horwich, A. L. & Rosenberg, L. E. Nature 313, 815–817 (1985).
Conneally, P. M. & Rivas, M. L. in Advances in Human Genetics (eds Harris, H. & Hirschhorn, K.) 209–266 (Plenum, New York, 1980).
Kunkel, L. M. et al. Gene 33, 251–258 (1985).
Appel, S. H. & Roses, A. D. in The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease (ed. Stanbury, J. B.) 1470–1495 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1983).
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F. & Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monaco, A., Bertelson, C., Middlesworth, W. et al. Detection of deletions spanning the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus using a tightly linked DNA segment. Nature 316, 842–845 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/316842a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/316842a0
This article is cited by
-
Molecular and cellular basis of genetically inherited skeletal muscle disorders
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2021)
-
Therapeutic strategies to address neuronal nitric oxide synthase deficiency and the loss of nitric oxide bioavailability in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2017)
-
Attempting to Compensate for Reduced Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase Protein with Nitrate Supplementation Cannot Overcome Metabolic Dysfunction but Rather Has Detrimental Effects in Dystrophin-Deficient mdx Muscle
Neurotherapeutics (2017)
-
Simultaneous mutation scanning for gross deletions, duplications and point mutations in the DMD gene
European Journal of Human Genetics (2008)
-
Molecular characterization of a novel translocation t(5;14)(q21;q32) in a patient with congenital abnormalities
Journal of Human Genetics (2006)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.