Abstract
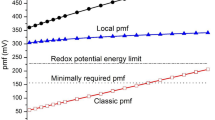
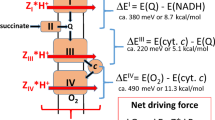
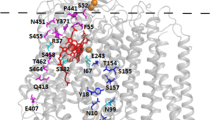
The stoichiometry and mechanism of redox-linked proton translocation by the mitochondrial respiratory chain is a major issue of debate in membrane bioenergetics. The function of cytochrome oxidase is a focal point of disagreement. In 1977 it was suggested that the terminal component of the respiratory chain, cytochrome oxidase, functions as a redox-linked proton pump1. That and subsequent studies were based mainly on measurements of proton ejection from mitochondria or from vesicles reconstituted with isolated cytochrome oxidase, or on measurements of translocation of electrical charge equivalents across mitochondrial and vesicle membranes2–6. This proton-translocating function of cytochrome oxidase is confirmed here by a quantitative determination of proton uptake from the inside (matrix) of intact mitochondria.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wikström, M. Nature 266, 271–273 (1977).
Wikström, M. & Krab, K. Biochim. biophys. Acta 549, 177–222 (1979).
Casey, R. P., Chappell, J. B. & Azzi, A. Biochem. J. 182, 149–156 (1979).
Sigel, E. & Carafoli, E. Eur. J. Biochem. 111, 299–306 (1980).
Penttilä, T. Eur. J. Biochem. 133, 355–361 (1983).
Wikström, M., Krab, K. & Saraste, M. A. Rev. Biochem. 50, 623–655 (1981).
Mitchell, P. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 341, 564–584 (1980).
Lorusso, M., Capuano, F., Boffoli, D., Stefanelli, R. & Papa, S. Biochem. J. 182, 133–147 (1979).
Papa, S. et al. Biochem. J. 192, 203–218 (1980).
Papa, S., Guerrieri, F. & Izzo, G. Biochem. J. 216, 259–272 (1983).
Azzone, G. F., Pozzan, T. & Di Virgillio, F. J. biol Chem. 254, 10206–10212 (1979).
Reynafarje, B., Alexandre, A., Davies, P. & Lehninger, A. L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 7218–7222 (1982).
Junge, W., Ausländer, W., McGeer, A. & Runge, T. Biochim. biophys. Acta 546, 121–141 (1979).
Hong, Y. Q. & Junge, W. Biochim. biophys. Acta 722, 197–208 (1983).
Appelberg, B. G. & Saris, N.-E. Abstr. 10th int. Congr. Biochem., Hamburg, 345 (International Union of Biochemistry, 1976).
Pick, U. & Avron, M. FEBS Lett. 65, 348–353 (1976).
Mitchell, P., Moyle, J. & Mitchell, R. Meth. Enzym. 55, 627–640 (1979).
Wikström, M. & Saraste, M. in New Comprehensive Biochemistry; Bioenergetics (ed. Ernster, L.) (Elsevier, Amsterdam, in the press).
Moyle, J. & Mitchell, P. FEBS Lett. 88, 268–272 (1978).
Wikström, M. & Krab, K. FEBS Lett. 91, 8–14 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wikström, M. Pumping of protons from the mitochondrial matrix by cytochrome oxidase. Nature 308, 558–560 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/308558a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/308558a0
This article is cited by
-
Salt stress and respiration inAspergillus repens
Current Microbiology (1993)
-
Resonance electroconformational coupling: A proposed mechanism for energy and signal transductions by membrane proteins
Bioscience Reports (1989)
-
Variable stoichiometry of proton pumping by the mitochondrial respiratory chain
Nature (1987)
-
On the role of subunit III in proton translocation in cytochromec oxidase
Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes (1987)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.