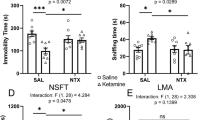
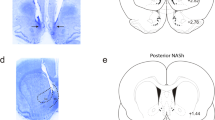
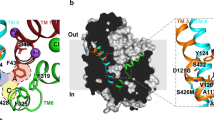
Abstract
At least three different families of endogenous opioid peptides, the enkephalins, endorphins and dynorphins, are present in the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). Immuno-cytochemical studies have demonstrated their localization in neurones1–8, which supports the view that these peptides may have a role as neurotransmitters or neuromodulators. However, the target cells and cellular processes acted upon by the opioid peptides are still largely unknown. One possible function of neuropeptides, including the opioid peptides, may be presynaptic modulation of neurotransmission in certain neuronal pathways, for example, by inhibition or promotion of neurotransmitter release from the nerve terminals9–12. Here we report that dynorphin and some benzomorphans potently and selectively inhibit the release of (radiolabelled) dopamine from slices of rat corpus striatum, by activating κ-opioid receptors. In contrast, [Leu5]enkephalin and [D-Ala2, D-Leu5]enkephalin selectively inhibit acetylcholine release by activating δ-opioid receptors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloom, F. E. et al. Adv. biochem. Psychopharmac. 18, 89–109 (1978).
Snyder, S. H. & Childers, S. R. A. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 35–64 (1979).
Watson, S. J. et al. Science 216 85–87 (1982).
Vincent, S. R., Hökfelt, T., Christensson, I. & Terenius, L. Neurosci. Lett. 33, 185–190 (1982).
Khachaturian, H. et al. Peptides 3, 941–954 (1982).
Watson, S. J. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80 891–894 (1983).
Weber, E. & Barchas, J. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 1125–1129 (1983).
Cuello, A. C. Br. med. Bull. 39, 11–16 (1983).
Iwamoto, E. T. & Way, E. L. Adv. biochem. Psychopharmac. 20, 357–407 (1979).
Vaughan, P. F. T. Cell. molec. Biol. 28, 369–382 (1982).
Langer, S. Z. Pharmac. Rev. 32, 337–362 (1980).
Starke, K. A. Rev. Pharmac. Toxicol. 21, 7–30 (1981).
Martin, W. R., Eades, C. G., Thompson, J. A., Huppler, R. E. & Gilbert, P. E. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 197, 517–532 (1976).
Lord, J. A. H., Waterfield, A. A., Hughes, J. & Kosterlitz, H. W. Nature 267, 495–499 (1977).
Wüster, M., Schultz, R. & Herz, A. Biochem. Pharmac. 30, 1883–1887 (1981).
Wood, P. L. Neuropharmacology 21, 487–497 (1982).
Paterson, S. J., Robson, L. E. & Kosterlitz, H. W., Br. med. Bull. 39, 31–36 (1983).
Chavkin, C., James, I. F. & Goldstein, A. Science 215, 413–415 (1982).
Yoshimura, K., Huidobro-Toro, J. P. & Way, E. L. Eur. J. Pharmac. 84, 17–24 (1982).
Dray, A. Neuroscience 4, 1407–1439 (1979).
Hattori, T., Singh, U. K. & McGeer, P. L. Brain Res. 102, 164–173 (1976).
Bartholini, G., Stadler, H., Gadea Civia, M. & Lloyd, K. G. Neuropharmacology 15, 515–519 (1976).
Garattini, S., Pujol, J.F. & Samanin, R.S. (eds) Interactions Between Putative Neurotransmitters in the Brain 3–38 (Raven, New York, 1978).
Stoof, J. C., Horn, A. S. & Mulder, A. H. Brain Res. 196, 276–281 (1980).
Hertting, G., Zumstein, A., Jackish, R., Hoffmann, I. & Starke, K. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 315, 111–117 (1980).
Hughes, J., Kosterlitz, H. W. & Smith, T. W. Br. J. Pharmac. 61, 639–647 (1977).
Yang, H. Y., Hong, J. S. & Costa, E. Neuropharmacology 16, 303–307 (1977).
Simantov, R., Kuhar, M. J., Uhl, G. R. & Snyder, S. H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 2167–2171 (1977).
Goldstein, A. & Ghazarossian, V. E. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 6207–6210 (1980).
Höllt, V., Haarmann, I., Bovermann, K., Jericz, M. & Herz, A. Neurosci. Lett. 18, 149–153 (1980).
Schoffelmeer, A. N. M., Wemer, J. & Mulder, A. H. Neurochem. Int. 3, 129–136 (1981).
Mulder, A. H. Prog. Brain Res. 55, 135–156 (1982).
Frankhuyzen, A. L. & Mulder, A. H. Eur. J. Pharmac. 78, 91–97 (1982).
Lubetzki, C., Chesselet, M. F. & Glowinski, J. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 222, 435–440 (1982).
Szerb, J. C. Eur. J. Pharmac. 29, 192–194 (1974).
Arbilla, S. & Langer, S. Z. Nature 271, 559–561 (1978).
Starr, M. J. pharm. Pharmac. 30, 359–363 (1978).
Beani, L., Bianchi, C. & Siniscalchi, A. Br. J. Pharmac. 76, 393–401 (1982).
Celsen, B. & Kuschinsky, K. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 284, 159–165 (1974).
Taube, H. D., Starke, K. & Borowski, E. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 299, 123–141 (1977).
Göthert, M., Pohl, I. M. & Wehking, E. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 307, 21–27 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mulder, A., Wardeh, G., Hogenboom, F. et al. κ and δ-opioid receptor agonists differentially inhibit striatal dopamine and acetylcholine release. Nature 308, 278–280 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/308278a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/308278a0
This article is cited by
-
Molecular Adaptations in the Rat Dorsal Striatum and Hippocampus Following Abstinence-Induced Incubation of Drug Seeking After Escalated Oxycodone Self-Administration
Molecular Neurobiology (2019)
-
Characterization of the decrease of extracellular striatal dopamine induced by intrastriatal morphine administration
British Journal of Pharmacology (1999)
-
Reversion of muscarinic autoreceptor agonist‐induced acetylcholine decrease and learning impairment by dynorphin A (1–13), an endogenous κ‐opioid receptor agonist
British Journal of Pharmacology (1998)
-
Effects of kappa receptor agonists on D1 and D2 dopamine agonist and antagonist-induced behaviors
Psychopharmacology (1996)
-
Postsynaptic and extrasynaptic localization of ?-opioid receptor in selected brain areas of young rat and chick using an anti-receptor monoclonal antibody
Journal of Neurocytology (1995)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.