Abstract
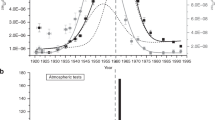
Nuclear weapons tests at oceanic sites during the 1950s produced a large amount of 36Cl (t1/2 = 3.0 × 105 yr) through neutron capture of 35Cl in seawater. Part of this anthropogenic 36Cl was injected into the stratosphere from where it was redistributed throughout the Earth. This pulse of 36Cl was first detected in rainfall by Schaeffer et al.1. The global deposition rates are several orders of magnitude larger than the natural pre-and post-bomb 36Cl production rate that reflects cosmic-ray spallation of atmospheric 40Ar. Because 36Cl is not a fission product, the anthropogenic 36Cl is produced mainly in marine tests carried out on small islands and barges where a large amount of seawater chlorine is present to serve as a target. This target element requirement leads to a temporal dependence different from the other bomb produced isotopes2–4. We have determined the temporal dependence of 36Cl fallout by measuring the depth profile of 36Cl in an ice core from Dye 3 Greenland (65° 11′ N, 43° 50′ W) using tandem accelerator mass spectrometry5. We show here that the results agree well with a calculation of the 36Cl produced and injected into the stratosphere by the tests.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schaeffer, O. A., Thompson, S. O. & Lark, N. L. J. geophys. Res. 65, 4013–4016 (1960).
Koide, M., Michel, R., Goldberg, E. D., Herron, M. M. & Langway, C. C. Jr Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 44, 205–223 (1979).
Koide, M., Michel, R., Goldberg, E. D., Herron, M. M. & Langway, C. C. Jr Nature 296, 544–547 (1982).
Koide, M., Goldberg, E. D., Herron, M. M. & Langway, C. C. Jr Nature 269, 137–139 (1977).
Elmore, D. et al. Nature 277, 22–25, 246 (1979).
Hammer, C. U. J. Glaciol 25, 359–372 (1980).
Nishiizumi, K. et al. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 45, 285–292 (1979).
Finkel, R. C., Nishiizumi, K., Elmore, D., Ferraro, R. D. & Gove, H. E. Geophys. Res. Lett. 7, 983–986 (1980).
Purser, K. H., Schneider, R. J., Dobbs, J. M. & Post, R. Proc. Symp. Accel. Mass. Spect., 431–462 (Argonne National Laboratory, 1981).
Reeh, N. et al. J. Glaciol. 20, 27–30 (1978).
Glasstone, S. (ed.) The Effects of Nuclear Weapons (Appendix B, USAEC Rep. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1964).
Zander, I. & Araskog, R. Nuclear Explosions 1945–1972: Basic Data (FOA-4 Report A-4505-A, 1973).
Carter, M. W. & Moghissi, A. A. Hlth Phys. 33, 55–71 (1977).
Machta, L. Radioactive Fallout from Nuclear Weapons Tests, 369–391 (USAEC, Oak Ridge, 1963).
Dyrssen, D. & Nyman, P. O. Acta radiol. 43, 421–427 (1955).
Joseph, A. B. et al. in Radioactivity in the Marine Environment 6–41 (National Academy of Science, Washington DC, 1971).
Bentley, H. W. et al. Nature 300, 737–740 (1982).
Lal, D. & Peters, B. in Handbuch der Physik Vol. 46/2 (ed. K. Sitte) 551–612 (Springer, Berlin, 1967).
Oeschger, H., Houtermans, J., Loosli, H. & Wahlen, M. Proc. XII Nobel Symp. (Wiley, New York, 1970).
Peterson, K. R. Hlth Phys. 18, 357–378 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elmore, D., Tubbs, L., Newman, D. et al. 36Cl bomb pulse measured in a shallow ice core from Dye 3, Greenland. Nature 300, 735–737 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/300735a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/300735a0
This article is cited by
-
36Cl, a new tool to assess soil carbon dynamics
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Recent measurements of 36Cl in Yucca Mountain rock, soil and seepage
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry (2008)
-
Application of the chlorine-36 method for the delineation of groundwater infiltration of large river systems: example of the Danube River in western Hungary (Szigetk�z area)
Environmental Geology (2004)
-
Records of climatic changes and volcanic events in an ice core from Central Dronning Maud Land (East Antarctica) during the past century
Journal of Earth System Science (2002)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.