Abstract
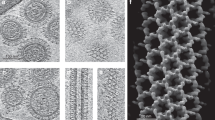
THE plasma membrane of the smooth muscle cell presents characteristic rows of micro-invaginations or caveolae arranged parallel to the longitudinal axis of the cell1–4. Previous studies have demonstrated that the plasma membrane in the rows contains a much higher density of intramembranous particles than the intervening membrane zones2,4. The polyene antibiotic, filipin, by specifically interacting with cholesterol5–7, produces distinctive alterations in freeze-fractured membranes8–11, and the addition of filipin to aldehyde fixatives has been recently introduced as a cytochemical technique for the freeze-fracture localisation of cholesterol in cell membranes12,13. By applying this technique to smooth muscle cells, we have now obtained morphological evidence that the invaginated, particle-rich bands of the plasma membrane react with filipin to a far greater extent than does the non-invaginated membrane. The two membrane zones may thus differ in cholesterol content.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Devine, C. E., Simpson, F. O. & Bertaud, W. S. J. Cell Sci. 8, 427–443 (1971).
Wells, G. S. & Wolowyk, M. W. J. Physiol., Lond. 218, 11P–13P (1971).
Müggli, R. & Baumgartner, H. R. Experientia 28, 1212–1214 (1972).
Orci, L. & Perrelet, A. Science 181, 868–869 (1973).
Kinsky, S. C. A. Rev. Pharmac. 10, 119–142 (1970).
Norman, A. W., Demel, R. A., De Kruijff, B. & Van Deenen, L. L. M. J. biol. Chem. 247, 1918–1929 (1972).
De Kruijff, B., Gerritsen, W. J., Oerlemans, A., Demel, R. A. & Van Deenen, L. L. M. Biochim. biophys. Acta 339, 30–43 (1974).
Verkleij, A. J. et al. Biochim. biophys. Acta 291, 577–581 (1973).
Tillack, T. W. & Kinsky, S. C. Biochim. biophys. Acta 323, 43–54 (1973).
Kitajima, Y., Takashi, S. & Nozawa, Y. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 445, 452–465 (1976).
Andrews, L. D. & Cohen, A. I. J. Cell Biol. 81, 215–228 (1979).
Elias, P. M., Friend, D. S. & Goerke, J. J. Cell Biol. 79, 232a (1978).
Friend, D. S. & Elias, P. M. J. Cell Biol. 79, 216a (1978).
Branton, D. et al. Science 190, 54–56 (1975).
Norman, A. W., Spielvogel, A. M. & Wong, R. G. Adv. Lipid Res. 14, 127–170 (1976).
Burnstock, G. in Smooth Muscle (ed. Bülbring, E., Brading, A., Jones, A. & Tomita, T.) 1–69 (Arnold, London, 1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MONTESANO, R. Inhomogeneous distribution of filipin–sterol complexes in smooth muscle cell plasma membrane. Nature 280, 328–329 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/280328a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/280328a0
This article is cited by
-
Spatiotemporal analysis of endocytosis and membrane distribution of fluorescent sterols in living cells
Histochemistry and Cell Biology (2008)
-
Caveolae — from ultrastructure to molecular mechanisms
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2003)
-
Freeze-fracture cytochemistry of sympathetic ganglia
Histochemistry (1985)
-
Failure of filipin to detect cholesterol-rich domains in smooth muscle plasma membrane
Nature (1983)
-
?-Hydroxysterol distribution as determined by freeze-fracture cytochemistry
The Histochemical Journal (1981)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.