Abstract
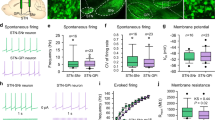
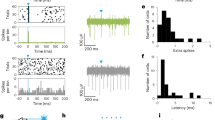
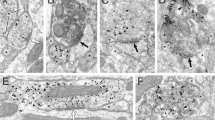
USING cats implanted with push–pull cannulae, we have previously demonstrated a reciprocal regulation of the activity of the two nigro-striatal dopaminergic pathways. Asymmetric fluctuations in the spontaneous release of dopamine(DA) were simultaneously seen in the two caudate nuclei (CN)1. As revealed by the changes in DA release from nerve terminals, the unilateral nigral application of DA1 or of drugs enhancing the dendritic release of DA, such as amphetamine or benztropine (2), reduced the activity of ipsilateral dopaminergic neurones and induced an opposite effect in the contralateral side. Conversely, the unilateral nigral blockade of dopaminergic transmission by local application of neuroleptics enhanced the release of DA in the ipsilateral CN and decreased the transmitter release in the contralateral structure2. Opposite changes in the release of DA were also seen in the two CN under unilateral delivery of sensory stimuli3 or during unilateral electrical stimulation of the cerebellar dentate nucleus4. These latter effects were associated with asymmetric changes in the dendritic release of DA in the two substantia nigrae (SN) which were in an opposite direction to those seen in the two CN (an increased release of DA from nerve terminals corresponded to a decreased release of the transmitter from dendrites and vice versa). These experiments indicated that DA which is released from dendrites in one SN regulates the activity of the ipsilateral dopaminergic neurones; they also suggested that it contributes to the control of the contralateral dopaminergic neurones by influencing the dendritic release of DA in the contralateral SN. This hypothesis was confirmed in the present study by measuring the changes in DA release from nerve terminals and dendrites of the two pathways under pharmacological blockade or facilitation of dopaminergic transmission in one SN.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nieoullan, A., Chéramy, A. & Glowinski, J. Science 198, 416–418 (1977).
Nieoullon, A., Chéramy, A., Leviel, V. & Glowinski, J. Eur. J. Pharmac. 53, 289–296 (1979).
Nieoullan, A., Chéramy, A. & Glowinski, J. Nature 269, 340–342 (1977).
Nieoullon, A., Chéramy, A. & Glowinski, J. Brain Res. 148, 143–152 (1978).
Nieoullon, A., Chéramy, A. & Glowinski, J. J. Neurochem. 28, 819–828 (1977).
Bunney, B. S., Aghajanian, G. K. & Roth, R. H. Nature new Biol. 245, 123–125 (1973).
Groves, P. M., Wilson, C. J., Young, S. J. & Rebec, G. V. Science 190, 522–529 (1975).
Prémont, J. et al. FEBS Lett. 68, 99–104 (1976).
Gale, K., Guidotti, A. & Costa, E. Science 195, 503–505 (1977).
Carlsson, A. & Lindqvist, M. Acta pharmac. tox. 20, 140–144 (1963).
Dray, A., Gonye, T. J., Oakley, N. R. & Tanner, T. Brain Res. 113, 45–57 (1976).
Reubi, J. C., Iversen, L. L. & Jessell, T. M. Nature 268, 652–654 (1977).
Llamas, A. & Reinoso-Suares, F. in 3rd Symp. on Parkinson Disease (eds Gillingham, F.J. & Donaldson, IL.LM.) 82–87 (Livingstone, London, 1969).
Rinvik, E. Brain Res. 91, 313–318 (1975).
Royce, G. J. Brain Res. 153, 465–475 (1978).
Sakai, K., Touret, M., Salvert, D. & Jouvet, M. in Interaction between Putative Neurotransmitters in the Brain (eds Garattini, S., Pujol, J. F. & Samanin, R.) 319–342 (Raven, New York, 1978).
Chan-Palay, V. Cerebellar Dentate Nucleus: Organization, Cytology and Transmitters, 202 (Springer, Berlin, 1977).
Chéramy, A. et al. Brain Res. 155, 404–408 (1978).
Michelot, R., Leviel, V., Giorguieflf-Chesselet, M. F., Chéramy, A. & Glowinski, J. Life Sci. 24, 715–724 (1979).
Hökfelt, T., Kellerth, J. O., Nilsson, G. & Pernow, B. Science 190, 889–890 (1975).
Jessel, T. M., Emson, P. C., Paxinos, C. & Cuello, A. C. Brain Res. 152, 487–498 (1978).
Gauchy, C. et al. Neurosci. Lett. 12, 127–131 (1979).
Davies, J. & Dray, A. Brain Res. 107, 623–627 (1976).
Walker, R. J., Kemp, J. A., Yazima, H., Kitagawa, K. & Woodruf, G. N. Experientia 32, 214–215 (1976).
Leviel, V., Chéramy, A., Nieoullon, A. & Glowinski, J. Brain Res. (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LEVIEL, V., CHÉRAMY, A. & GLOWINSKI, J. Role of the dendritic release of dopamine in the reciprocal control of the two nigro-striatal dopaminergic pathways. Nature 280, 236–239 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/280236a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/280236a0
This article is cited by
-
Lateral differences in the GABAergic system of the rat striatum
The Italian Journal of Neurological Sciences (1985)
-
Electrophysiological evidence for the existence of crossed nigrostriatal fibers
Experientia (1982)
-
Dendritic release of dopamine in the substantia nigra
Nature (1981)
-
In vivo release of acetylcholinesterase in cat substantia nigra and caudate nucleus
Nature (1980)
-
Influence of monoamine oxidase inhibition on the release of 3H-dopamine elicited by potassium and by amphetamine from the rat substantia nigra and corpus striatum
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (1980)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.