Abstract
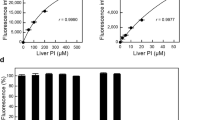
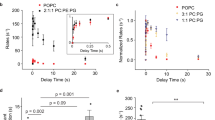
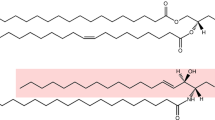
PHOSPHOLIPID and protein are the major components of biological membranes, and much is known about their organisation in various cell membranes1,2. An important question concerns the existence and significance of specific protein–phospholipid interactions in membranes. Among the methods used to elucidate these interactions is the study of the regulatory function of specific phospholipids in intact cells. Phosphatidylserine (PS) enhances the secretory response of the mast cell3 in a highly specific manner. Other diacyl phospholipids, phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidic acid, are ineffective3–5 and several N-substituted derivatives of PS are competitive inhibitors of the effect of PS on mast cells6. Furthermore, PS selectively enhances the response of cells to IgE-dependent secretagogues7,8 without increasing the response of the cells to IgE-independent agents such as polymyxin B9, chymotrypsin3, compound 48/80 (refs 3, 9), or A23187 (D. L. and T. W. M., unpublished). As histamine secretion involves a major alteration in the organisation of membrane components10, the effect of PS on secretion makes it possible to study a complex membrane event with an established phospholipid specificity. Previously, we have used PS of various fatty acid compositions11: dimyristoyl PS, dipalmitoyl PS, and distearoyl PS. We now provide evidence that lysophosphatidyl-serine (lyso-PS) generated from bovine brain PS by the action of phospholipase A2 activates mast cell secretion induced by concanavalin A (Con A) at 1/30th to 1/50th the concentration of PS required for an equivalent response. Although some characteristics of the activation of mast cell secretion by lyso-PS resemble those observed with PS, its mode of interaction with the cell may be different; PS acts on mast cells in a micellar state12, but lyso-PS acts to potentiate secretion well below its critical micelle concentration (CMC).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steck, T. L. J. Cell Biol. 62, 1–19 (1974).
Rothman, J. E. & Lenard, J. Science 195, 743–753 (1977).
Goth, A., Adams, H. R. & Knoohuizen, M. Science 173, 1034–1035 (1971).
Baxter, J. H. & Adamik, R. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med. 152, 266–271 (1976).
Mongar, J. L. & Svec, P. Br. J. Pharmac. 46, 741–752 (1972).
Martin, T. W. & Lagunoff, D. Science (in the press).
Stechschulte, D. J. & Austen, K. F. J. Immun. 112, 970–978 (1974).
Sullivan, T. J., Greene, W. C. & Parker, C. W. J. Immun. 115, 278–282 (1975).
Read, G. W., Knoohuizen, M. & Goth, A. Eur. J. Pharmac. 42, 171–177 (1977).
Lagunoff, D. & Chi, E. Y. J. invest. Derm. 71, 81–84 (1978).
Martin, T. W. & Lagunoff, D. J. Cell Biol. 79, 243a (1978).
Martin, T. W. & Lagunoff, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 4997–5000 (1978).
Sanders, H. Biochim. biophys. Acta 144, 485–487 (1967).
Hanahan, D. J., Dittmer, J. C. & Warashina, E. J. biol. Chem. 228, 685–700 (1957).
Barenholz, Y. et al. Biochemistry 16, 2806–2810 (1977).
Tanford, C. The Hydrophobic Effect: Formation of Micelles and Biological Membranes (Wiley, New York, 1973).
Sydbom, A. & Uvnäs, B. Acta physiol. scand. 97, 222–232 (1976).
Patai, S. (ed.) The Chemistry of Amidines and Imidates (Wiley, New York, 1975).
Lagunoff, D. in Techniques of Biochemical and Biophysical Morphology, Vol. 2 (eds Glick, D. & Rosenbaum, R.) 283–305 (Wiley, New York, 1975).
Kremzner, L. T. & Wilson, I. B. Biochim. biophys. Acta 50, 364–367 (1961).
Schrock, H. L. & Gennis, R. B. J. biol. Chem. 252, 5990–5995 (1977).
Ko, L. & Lagunoff, D. Expl Cell Res. 100, 313–321 (1976).
Lowry, O. H., Roberts, N. R. & Kapphahn, J. I. J. biol. Chem. 224, 1047–1064 (1957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MARTIN, T., LAGUNOFF, D. Interactions of lysophospholipids and mast cells. Nature 279, 250–252 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/279250a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/279250a0
This article is cited by
-
Current Knowledge on the Biology of Lysophosphatidylserine as an Emerging Bioactive Lipid
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2021)
-
Possible involvement of PS-PLA1 and lysophosphatidylserine receptor (LPS1) in hepatocellular carcinoma
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
The Lysophosphatidylserines—An Emerging Class of Signalling Lysophospholipids
The Journal of Membrane Biology (2020)
-
GPR34 in spinal microglia exacerbates neuropathic pain in mice
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2019)
-
Gpr174-deficient regulatory T cells decrease cytokine storm in septic mice
Cell Death & Disease (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.