Abstract
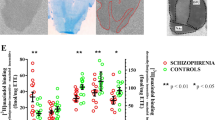
THE neuroleptic or antipsychotic drugs, introduced in 19521, effectively prevent relapse and rehospitalisation of schizophrenic patients. These drugs provide a strategy2 for localising possible abnormalities in the brain in schizophrenia. The hypothesis that schizophrenia might be associated with abnormally sensitive dopamine synapses3–6 evolved from the suggestion that neuroleptics block dopamine receptors and thus accelerate the turnover of dopamine7,8. The hypothesis received additional support from the observations that dopamine-mimetic drugs (for example d-amphetamine, L-dopa) elicit or exacerbate psychotic symptoms9–12, that neuroleptics produce supersensitivity to dopamine13–15, that the neuroleptic and antipsychotic actions are enhanced by drugs which block the synthesis of catecholamines16, that neuroleptics all have conformations that match that of dopamine17, and that dopamine is the most potent neurotransmitter to inhibit the specific binding of 3H-haloperidol to dopamine-rich regions of the brain18–20. Although all this evidence for the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia is circumstantial, we have now obtained direct evidence for some abnormalities in brain dopamine receptors in schizophrenia by measuring the specific binding of 3H-apomorphine and 3H-haloperidol or 3H-spiperone to four regions of postmortem brains from schizophrenic patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delay, J., Deniker, P. & Harl, J.-M. Ann. Méd.-Psychol. 110, 267–273 (1952).
Seeman, P. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 9, 145–221 (1966).
Randrup, A. & Munkvad, I. Orthomolec. Psychiat. 1, 2–7 (1972).
Matthysse, S. & Lipinski, J. A. Rev. Med. 551–565 (1975).
Matthysse, S. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmac. 16, 667–669 (1977).
Hornykiewicz, O. A. Rev. Pharmac. Toxic. 17, 545–559 (1977).
Van Rossum, J. M. Archs Int. Pharmacodyn. 160, 492–494 (1966).
Carlsson, A. & Lindqvist, M. Acta pharmac. toxic. 20, 140–144 (1963).
Yaryura-Tobias, J. A., Diamond, B. & Merlis, S. Curr. Ther. Res. 12, 528–531 (1970).
Snyder, S. H. Am. J. Psychiat. 133, 197–202 (1976).
Angrist, B., Thompson, H., Shopsin, B. & Gershon, S. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 44, 273–280 (1975).
Janowsky, D. S. & Davis, J. M. Archs gen. Psychiat. 33, 304–308 (1976).
Tarsy, D. & Baldessarini, R. J. Neuropharmacology 13, 927–940 (1974).
Sayers, A. C., Bürki, H. R., Ruch, W. & Asper, H. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 41, 97–104 (1975).
Jackson, D. M., Andén, N.-E., Engel, J. & Liljequist, S. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 45, 151–155 (1975).
Carlsson, A., Persson, T., Roos, B.-E. & Wålinder, J. J. Neural Trans. 33, 83–90 (1972).
Horn, A. S., Post, M. L. & Kennard, O. J. Pharm. Pharmac. 27, 553–563 (1975).
Seeman, P., Lee, T., Chau-Wong, M. & Wong, K. Nature 261, 717–719 (1976).
Seeman, P. Biochem. Pharmac. 26, 1741–1748 (1977).
Burt, D. R., Creese, I. & Snyder, S. H. Molec. Pharmac. 12, 800–812 (1976).
Seeman, P., Lee, T., Chau-Wong, M., Tedesco, J. & Wong, K. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 4354–4358 (1976).
Laduron, P. & Leysen, J. Biochem. Pharmac. 26, 1003–1007 (1977).
Bird, E. D. et al. Lancet ii, 1157–1159 (1977).
Muller, P. & Seeman, P. Soc. Neurosci. 6, 874 (1976).
Burt, D. R., Creese, I. & Snyder, S. H. Science 196, 326–328 (1976).
Muller, P. & Seeman, P. Life Sci. 21, 1751–1758 (1977).
Nagy, J. I., Lee, T., Seeman, P. & Fibiger, H. C. Nature 274, 278–281 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LEE, T., SEEMAN, P., TOURTELLOTTE, W. et al. Binding of 3H-neuroleptics and 3H-apomorphine in schizophrenic brains. Nature 274, 897–900 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/274897a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/274897a0
This article is cited by
-
Antagonist and partial agonist at the dopamine D2 receptors in drug-naïve and non-drug-naïve schizophrenia: a randomized, controlled trial
European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience (2015)
-
Calculating Occupancy when One does not have Baseline: A Comparison of Different Options
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (2011)
-
The use of healthy volunteers instead of patients to inform drug dosing studies: a [11C]raclopride PET study
Psychopharmacology (2011)
-
D2-Receptor Upregulation is Dependent upon Temporal Course of D2-Occupancy: A Longitudinal [11C]-Raclopride PET Study in Cats
Neuropsychopharmacology (2009)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.