Abstract
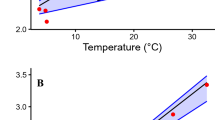
MEASUREMENTS of the oxygen consumption of two common benthopelagic fishes, Coryphaenoides acrolepis and Eptatretus deani, made in situ at 1,230 m in the San Diego Trough1 have indicated low respiration rates. The metabolic measurements reported here for the rattail, Coryphaenoides (Nematonurus) armatus (Hector), at 3,650 m support the earlier findings of low respiration rates in deep-sea rattails. They also support the physiological axiom that respiration increases as a fractional power of body weight in animals2–4. Both the metabolic rate and chemical composition of C. armatus suggest an adaptation to a food-limited deep-sea environment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith, K. L. & Messier, R. R. Science 184, 72–73 (1974).
Zeuthen, E. C. r Lab. Carlsb. Ser. Chim. 26, 15–161 (1947); Q. Rev. Biol. 28, 1–12 (1953).
Hemmingsen, A. M. Rep. Steno Hasp. Copenhagen 4, 7–58 (1950); 9 (1960).
Prosser, C. L. Comparative Animal Physiology (Saunders, Philadelphia, 1973).
Iwamoto, T. & Stein, D. L. Occas. Pap. Calif. Acad. Sci. 111, 1–79 (1974).
Marshall, N. B. & Iwamoto, T. in Fishes of the Western North Atlantic (Sears Foundation for Marine Research, 1973).
Haedrich, R. L. & Rowe, G. T. Nature 269, 141–142 (1977).
Haedrich, R. L. & Henderson, N. R. Deep-Sea Res. 21, 739–744 (1974).
Pearcy, W. G. & Ambler, J. W. Deep-Sea Res. 21, 745–759 (1974).
Smith, K. L., Jr, White, G. A., Laver, M. B., McConnaughey, R. R. & Meador, J. P. Deep-Sea Res. (in the press).
Smith, K. L. et al. Limnol Oceanogr, 21, 164–170 (1976).
Smith, K. L., White, G. A., Laver, M. B. & Haugsness, J. A. Limnol. Oceanogr. (in the press).
Kanwisher, J. Limnol. Oceanogr. 4, 210–217 (1959).
Strickland, J. D. H. & Parsons, T. R. A Practical Handbook of Sea Water Analysis (Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Ottawa, 1972).
Shibko, S., Koivistoinen, P., Tratnyek, C. A., Newhall, A. R. & Friedman, L. Analyt. Biochem. 19, 514–528 (1967).
Smith, K. L., Harbison, G. R., Rowe, G. T. & Clifford, C. H. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 32, 1607–1612 (1975).
Patton, S. & Thomas, A. J. J. Lipid Res. 12, 331–335 (1971).
Saunders, R. L. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 20, 373–386 (1963).
Poulson, T. L. Am. Midl. Nat. 70, 257–290 (1963).
Forster, R. P. & Goldstein, L. in Fish Physiology (eds Hoar, W. S. & Randall, D. J.) (Academic, New York, 1969).
Wood, J. D. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 36, 1237–1242 (1958).
Love, R. M. The Chemical Biology of Fishes (Academic, New York, 1970).
Dambergs, N. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 20, 909–918 (1963).
Bligh, E. G. & Scott, M. A. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 23, 1025–1036 (1966).
Beamish, F. W. H. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 25, 837–851 (1968).
Childress, J. J. & Nygaard, M. H. Deep-Sea Res. 20, 1093–1109 (1973).
McLellan, T. Deep-Sea Res. 24, 1019–1036 (1977).
Childress, J. J. & Nygaard, M. H. Mar. Biol. 27, 225–238 (1974).
Black, E. C., Robertson, A. C. & Parker, R. R. in Comparative Physiology of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Heterothermic Animals (ed. Martin, A. W.), University of Washington Press, Seattle, 1961).
Tomlinson, N. & Geiger, S. E. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 19, 997–1003 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SMITH, K. Metabolism of the abyssopelagic rattail Coryphaenoides armatus measured in situ. Nature 274, 362–364 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/274362a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/274362a0
This article is cited by
-
Comparison of serum enzyme activity in great sturgeon, Huso huso, cultured in brackish and freshwater earth ponds in Iran
Comparative Clinical Pathology (2010)
-
Seasonal variation in the white muscle biochemical composition of deep-sea macrourids in the North-east Atlantic
Marine Biology (2008)
-
Life in a warm deep sea: routine activity and burst swimming performance of the shrimp Acanthephyra eximia in the abyssal Mediterranean
Marine Biology (2005)
-
Photographic and acoustic tracking observations of the behaviour of the grenadier Coryphaenoides (Nematonurus) armatus the eel Synaphobranchus bathybius, and other abyssal demersal fish in the North Atlantic Ocean
Marine Biology (1992)
-
Direct measurement of active dispersal of food-falls by deep-sea demersal fishes
Nature (1991)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.