Abstract
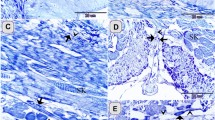
NEUROTENSIN, originally isolated from bovine hypothalamus1, was shown to be a peptide of 13 amino acids2. It has been synthesised3 and its pharmacological actions shown to include effects on small intestine motility, blood vessel tone, enhancement of glycogenolysis, release of glucagon and inhibition of insulin release5–7. Immunoreactive neurotensin has been detected in mammalian hypothalamus and a few other areas of the brain8–10 but much larger quantities occur in the intestine11. Neurotensin has been shown in discrete cells in the ileal mucosa of various birds and mammals including man12–15. The cell type has recently been fully characterised and its identity internationally accepted (see ref. 16). The distribution of the peptide in man is unknown. Using a combination of radioimmunoassay (RIA) and immunocytochemistry (IC) we have found large amounts of neurotensin-like reactivity in human ileum with less in the jejunum. The immunoreactive cells are restricted to the mucosa. Neurotensin thus joins the growing group of peptides which are common to brain and gut17. The effect of such peptides may differ according to their location. Neurotensin has been reported in rat blood11 and may therefore act as a circulating hormone. In addition, its location in the brain suggests a possible role as a peptidergic neuro-transmitter.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carraway, R. & Leeman, S. E. . J. biol. Chem. 248, 6854–6861 (1973).
Carraway, R. & Leeman, S. E. J. biol. Chem. 250, 1907–1911 (1975).
Carraway, R. & Leeman, S. E. J. biol. Chem. 250, 1912–1918 (1975).
Brown, M., Villarreal, J. & Vale, W. Metabolism 25, 1459–1461 (1976).
Nagai, K. & Frohman, L. A. Life Sci. 19, 273–280 (1976).
Carraway, R., Demers, L. & Leeman, S. E. Endocrinology 99, 1452–1462 (1976).
Brown, M. & Vale, W. Endocrinology 98, 819–822 (1976).
Carraway, R. & Leeman, S. E. J. biol. Chem. 251, 7035–7044 (1976).
Uhl, G. R. & Snyder, S. H. Life Sci. 19, 1827–1832 (1976).
Kobayashi, R. M., Brown, M. & Vale, W. Brain Res. (in the press).
Carraway, R. & Leeman, S. E. J. biol. Chem. 251, 7045–7052 (1976).
Orci, L. et al. Life Sci. 19, 559–562 (1976).
Sundler, F., Alumets, J., Håkanson, R., Carraway, R. & Leeman, S. E. Histochemistry 53, 25–34 (1977).
Helmstaedter, V., Taugner, C., Feurle, G. E. & Forssman, W. G. Histochemistry 53, 35–41 (1977).
Buchan, A. M. J. et al. in Gut Hormones (ed. Bloom, S. R.) (Churchill-Livingstone, London, in the press).
Bloom, S. R. (ed.) Gut Hormones (Churchill-Livingstone, London, in the press).
Pearse, A. G. E. Nature 262, 92–94 (1976).
Pearse, A. G. E. & Polak, J. M. Histochemie 27, 96–102 (1971).
Polak, J. M., Sullivan, S. N., Bloom, S. R., Facer, P. & Pearse, A. G. E. Lancet i, 972–974 (1977).
Pearse, A. G. E., Polak, J. M. & Bloom, S. R. Gastroenterology 72, 746–761 (1977).
Solcia, E., Capella, C., Vassallo, G. & Buffa, R. Int. Rev. Cytol. 45, 223–286 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
POLAK, J., SULLIVAN, S., BLOOM, S. et al. Specific localisation of neurotensin to the N cell in human intestine by radioimmunoassay and immunocytochemistry. Nature 270, 183–184 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/270183a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/270183a0
This article is cited by
-
Individuals with type 2 diabetes have higher density of small intestinal neurotensin-expressing cells
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2023)
-
Neurotensin-induced miR-133α expression regulates neurotensin receptor 1 recycling through its downstream target aftiphilin
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
An obligatory role for neurotensin in high-fat-diet-induced obesity
Nature (2016)
-
Neurotensin prevents intestinal mucosal hypoplasia in rats fed an elemental diet
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (1992)
-
Physiology and pathophysiology of colonic motor activity
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (1991)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.