Abstract
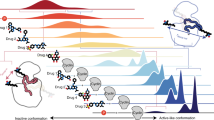
The crystal structure of the cyclin D-dependent kinase Cdk6 bound to the p19INK4d protein has been determined at 1.9 Å resolution. The results provide the first structural information for a cyclin D-dependent protein kinase and show how the INK4 family of CDK inhibitors bind. The structure indicates that the conformational changes induced by p19INK4d inhibit both productive binding of ATP and the cyclin-induced rearrangement of the kinase from an inactive to an active conformation. The structure also shows how binding of an INK4 inhibitor would prevent binding of p27Kip1, resulting in its redistribution to other CDKs. Identification of the critical residues involved in the interaction explains how mutations in Cdk4 and p16INK4a result in loss of kinase inhibition and cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sherr, C. J. Cancer cell cycles. Science 274, 1672–1677 (1996).
Morgan, D. O. Principles of CDK regulation. Nature 374, 131–134 (1995).
Parker, L. L., Sylvestre, P. J., Brynes, M. J., Liu, F. & Piwnicaworms, H. Identification of a 95 Kda WEE1-like tyrosine kinase in Hela-cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci .USA 92, 9638–9642 (1995).
Kumagai, A. & Dunphy, W. G. The Cdc25 protein controls tyrosine dephosphorylation of the Cdc2 protein in a cell-free system. Cell 64, 903–914 (1991).
Sherr, C. & Roberts, J. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 9, 1149–1153 (1995).
Harper, J. W. in Checkpoint Control and Cancer(ed Kastan, M. B.) Vol. 29, 91–107 (CSHL Press, New York, 1997).
Soos, T. J. et al. Formation of p27-CDK complexes during the human mitotic cell cycle. Cell Growth Differ. 7, 135–146 (1996).
Poon, R. Y. C., Toyoshima, H. & Hunter, T. Redistribution of the CDK inhibitor p27 between different cyclin-CDK complexes in the mouse fibroblast cell cycle and in cells arrested with lovastatin or ultraviolet irradiation. Mol. Biol. Cell 6, 1197–1213 (1995).
Serrano, M., Hannon, G. J. & Beach, D. Anew regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature 366, 704–707 (1993).
Hannon, G. J. & Beach, D. p15INK4B is a potential effector of TGF-β-induced cell cycle arrest. Nature 371, 257–261 (1994).
Hirai, H., Roussel, M. F., Kato, J-Y., Ashmun, R. A. & Sherr, C. J. Novel INK4 proteins, p19 and p18, are specific inhibitors of the cyclin D-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 2672–2681 (1995).
Chan, F. K. M., Zhang, J., Cheng, L., Shaprio, D. N. & Winoto, D. A. Identification of human and mouse p19, a novel CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitor with homology to p16INK4. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 2682–2688 (1995).
Guan, K. et al. Isolation and characterization of p19INK4d, a p16 related inhibitor specific to CDK6 and CDK4. Mol. Biol. Cell 7, 57–70 (1996).
Weinberg, R. A. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell 81, 323–330 (1995).
De Bondt, H. L. et al. Crystal structure of cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature 363, 595–602 (1993).
Jeffrey, P. D. et al. Mechanism of CDK activation revealed by the structure of a cyclin-CDK2 complex. Nature 376, 313–320 (1995).
Russo, A. A., Jeffrey, P. D. & Pavletich, N. P. Structural basis of cyclin-dependent kinase activation by phosphorylation. Nature Struct. Biol. 3, 696–700 (1996).
Bork, P. Hundreds of ankyrin-like repeats in functionally diverse proteins: mobile modules that cross phyla horizontally. Proteins Struct. Funct. and Genet. 17, 363–374 (1993).
Luh, F. Y. et al. Structure of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p19INK4d. Nature 389, 999–1003 (1997).
Venkataramani, R., Swaminathan, K. & Marmorstein, R. Crystal structure of the CDK4/6 inhibitory protein p18INK4c provides insights into ankyrin-like repeat structure/function and tumor-derived p16INK4 mutations. Nature Struct. Biol. 5, 74–81 (1998).
Byeon, I.-J. L. et al. Tumor suppressor p16INK4a: Determination of solution structure and analyses of its interaction with cyclin-dependent kinase 4. Mol. Cell 1, 421–431 (1998).
Reynisdottir, I. & Massagué, J. The subcellular locations of p15INK4b and p27Kip1 coordinate their inhibitory interactions with Cdk4 and Cdk2. Genes Dev. 11, 492–503 (1997).
Yang, R., Gombart, A. F., Serrano, M. & Koeffler, H. P. Mutational effects on the p16INK4a tumour-suppressor protein. Cancer Res. 55, 2503–2506 (1995).
Gorina, S. & Pavletich, N. P. Structure of the p53 tumor suppressor bound to the ankyrin and SH3 domains of 53BP2. Science 274, 1001–1005 (1996).
Batchelor, A. H., Piper, D. E., de la Brousse, F. C., McKnight, S. L. & Wolberger, C. The structure of GABPα/β: an ETS domain-ankyrin repeat heterodimer bound to DNA. Science 279, 1037–1041 (1998).
Zhang, B. & Peng, Z.-Y. Defective folding of mutant p16INK4a proteins encoded by tumor-derived alleles. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 28734–28737 (1996).
Wölfel, T. et al. Ap16INK4A-insensitive CDK4 mutant targeted by cytolytic T-lymphocytes in a human-melanoma. Science 269, 1281–1284 (1995).
Coleman, K. G. et al. Identification of Cdk4 sequences involved in Cyclin D1 and p16 binding. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18869–18874 (1997).
Zuo, L. et al. Germline mutations in the p16INK4a binding domain of CDK4 in familial melanoma. Nature Genet. 12, 97–99 (1996).
Tsao, H., Benoit, E., Sober, A. J., Thiele, C. & Haluska, F. G. Novel mutation in the p16/CDKN2A binding region of cyclin-dependent kinase-4 gene. Cancer Res. 58, 109–113 (1998).
Soufir, N. et al. Prevalence of p16 and CDK4 germline mutations in 48 melanoma-prone families in France. Hum. Mol. Genet. 7, 209–216 (1998).
Zhang, F., Strand, A., Robbins, D., Cobb, M. H. & Goldsmith, E. J. Atomic structure of the MAP kinase ERK2 at 2.3 Å resolution. Nature 367, 704–710 (1994).
Taylor, S. S. & Radzio-Andzelm, E. Three protein kinase structures define a common motif. Structure 2, 345–355 (1994).
Zheng, J. H. et al. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase complexed with MgATP and peptide inhibitor. Biochemistry 32, 2154–2161 (1993).
Parry, D., Bates, S., Mann, D. J. & Peters, G. Lack of cyclin D-Cdk complexes in Rb-negative cells correlates with high levels of p16INK4/4MTS1 tumour suppressor gene product. EMBO J. 14, 503–511 (1995).
DellaRagione, F. et al. Biochemical characterisation of p16INK4- and p18-containing complexes in human cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 15942–15949 (1996).
Russo, A. A., Tong, L., Lee, J.-O., Jeffrey, P. D. & Pavletich, N. P. Structural basis for inhibition of the cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk6 by the tumour suppressor p16INK4a. Nature 395, 237–244 (1998).
Reynisdottir, I., Polyak, A., Iavarone, A. & Massagué, J. Kip/Cip and INK4D CDK inhibitor cooperate to induce cell cycle arrest in response to TGF-β. Genes Dev. 9, 1831–1845 (1995).
Sandhu, C. et al. TGFβ stabilizes p15INK46 protein, increases p15INK46/CDK4 complexes, and inhibits cycD1/CDK4 association in human mammary epithelial cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 2458–2467 (1997).
Russo, A. A., Jeffrey, P. D., Patten, A. K., Massagué, J. & Pavletich, N. P. Crystal structure of the p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor bound to the cyclin A-Cdk2 complex. Nature 382, 325–331 (1996).
Vlach, J., Hennecke, S. & Amati, B. Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1. EMBO J. 16, 5334–5344 (1997).
Collaborative computing project, Number 4. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 (1994).
Brünger, A. T. X-PLOR, Version 3.1, A System for X-Ray Crystallography and NMR(Yale Univ. Press, New Haven and London, 1992).
Murshudov, G. N., Vagin, A. A. & Dodson, E. J. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr. D 53, 240–255 (1997).
Read, R. J. Improved Fourier coefficients for maps using phases from partial structures with errors. Acta Crystallogr. A 42, 140–149 (1986).
Jones, T. A., Zou, J. Y., Cowan, S. W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron-density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A 47, 110–119 (1991).
Kraulis, P. J. MOLSCRIPT: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Merrit, E. A. & Murphy, M. E. Raster3D. A program for photorealistic molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 869–873 (1994).
Hubbard, S. J. & Thornton, J. M. ‘NACCESS’ computer program(Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Univ. College London, 1993).
Foulkes, W. D., Flanders, T. Y., Pollock, P. M. & Hayward, N. K. The CDKN2A (p16) gene and human cancer. Mol. Med. 3, 5–20 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. J. Sherr (Howard Hughes Medical Institute) for the plasmid expressing GST–p19INK4d; A. Raine for computer programming; M. Nilges for X-PLOR scripts; I. Tickle for advice; F. Luh for the selectively protonated p19INK4d; J. Eckstein for help with molecular graphics; and E. Duke, W. Burmeister and R. C. Kehoe for help with data collection. This work was supported by grants from the BBSRC and the Wellcome Trust. D.H.B. is supported by a studentship from the MRC. M.S. is supported by a grant from DGICYT, Spain, and by a core grant to the Department of Immunology and Oncology from Pharmacia-Upjohn and the Spanish Research Council. The Cambridge Centre for Molecular Recognition is supported by the BBSRC and the Wellcome Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brotherton, D., Dhanaraj, V., Wick, S. et al. Crystal structure of the complex of the cyclin D-dependent kinase Cdk6 bound to the cell-cycle inhibitor p19INK4d. Nature 395, 244–250 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/26164
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/26164
This article is cited by
-
Mechanisms of Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Hormone Receptor-Positive (HR +) Breast Cancer: Spotlight on Convergent CDK6 Upregulation and Immune Signaling
Current Breast Cancer Reports (2022)
-
Clinical CDK4/6 inhibitors induce selective and immediate dissociation of p21 from cyclin D-CDK4 to inhibit CDK2
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Targeting cell cycle and hormone receptor pathways in cancer
Oncogene (2013)
-
Simultaneous downregulation of CDK inhibitors p18Ink4c and p27Kip1 is required for MEN2A-RET-mediated mitogenesis
Oncogene (2007)
-
Biochemical and cellular mechanisms of mammalian CDK inhibitors: a few unresolved issues
Oncogene (2005)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.