Abstract
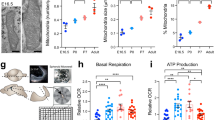
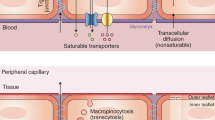
HIGH levels of alpha foetoprotein (AFP), albumin and IgG have been detected in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of six human foetuses between 16.5 and 25 weeks old1. The levels of AFP were found to decline from 1,200 µg ml−1 in a foetus of 16.5 weeks to 52 and 60 µg ml−1 in the older ones tested. During this period of foetal life, the ratios between albumin and AFP in CSF were shown to increase. The levels of IgG ranged between 60 and 117 µg ml−1 and were higher than those detected in CSF from normal adult subjects (20–40 µg ml−1)2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seller, M., and Adinolfi, M., Archs Dis. Childh., 50, 454–485 (1975).
Laterre, E. C., Ric. Clin. Lab., 3, 736–763 (1973).
Hochwald, G. M., and Thorbecke, G. J., Proc. Soc. exp. Biol., 109, 91–95 (1962).
Penny, R., and Osserman, E. F., Aust. J. exp. Biol. Med., 49, 111–120 (1971).
Peterson, P. A., Ervin, P. F., and Beggard, I., J. clin. Invest., 48, 1189–1198 (1969).
Osserman, E. F., and Lawlor, D. P., J. exp. Med., 124, 921–952 (1966).
Weir, D. M., Handbook of Experimental Immunology, second ed. (Blackwell, Oxford, 1973).
Nellhaus, G., Archs Neurol., 24, 441–448 (1971).
Harms, D., Eur. Neurol., 13, 54–64 (1975).
Thorley, J. D., Holmes, R. K., Kaplan, J. M., McCraken, G. H., and Sanford, J. P., Lancet, i, 651–653 (1975).
Brock, D. J. H., and Sutcliffe, R. G., Lancet, ii, 197–199 (1972).
Adinolfi, A., Adinolfi, M., and Lessof, M. H., J. med. Genet., 12, 138–151 (1975).
Sonoda, S., and Schlamowitz, M., Immunochemistry, 7, 885–898 (1970).
Adinolfi, A., Adinolfi, M., and Cohen, S., Biochim. biophys. Acta, 251, 197–207 (1971).
Carp, R. I., Davidson, A. L., and Merz, P. A., Res. vet. Sci., 12, 499 (1971).
Dawson, H., Physiology of the Cerebrospinal Fluid (Churchill, London, 1967).
Dobbing, J., and Smart, J. L., Br. med. Bull., 30, 164–168 (1974).
Balazs, R., Br. med. Bull., 30, 126–134 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ADINOLFI, M., BECK, S., HADDAD, S. et al. Permeability of the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier to plasma proteins during foetal and perinatal life. Nature 259, 140–141 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1038/259140a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/259140a0
This article is cited by
-
Characteristics of passive immunity against hantavirus infection in rats
Archives of Virology (1989)
-
Permeability of blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier during foetal and perinatal life
Nature (1976)
-
Permeability of blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier during foetal and perinatal life (reply)
Nature (1976)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.