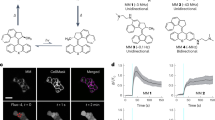
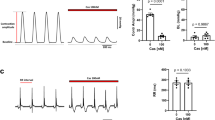
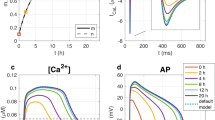
Abstract
DURING the past three years calcium ionophores have been increasingly used to study calcium-dependent mechanisms, for example, excitation–contraction coupling1 and stimulus–secretion coupling2–5. They seem to act by increasing the cytoplasmic ionised calcium concentration, but the mechanism of action does not seem to be identical in the different tissues studied. The calcium ionophore A23187 transports calcium from the extracellular space and intracellular sources towards the cytosol2,3 whereas another ionophore X537A (Lasalocid) seems to release calcium from intracellular binding sites only1,5. In addition, X537A does not seem to affect all the tissues studied so far—possibly because it does not readily penetrate cell membranes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levy, J. V., Cohen, J. A., and Inesi, G., Nature, 242, 461–463 (1973).
Foreman, J. C., Mongar, J. L., and Comperts, B. D., Nature, 245, 249–251 (1973).
Van Sande, J., and Dumont, J. E., Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun., 62, 168–175 (1975).
Nakazato, Y., and Douglas, W. W., Nature, 249, 497–481 (1974).
Nordmann, J. J., and Currell, G. A., Nature, 253, 646–647 (1975).
Mikiten, T. M., and Douglas, W. W., Nature, 207, 302 (1965).
Douglas, W. W., and Poisner, A. M., J. Physiol., Lond., 172, 19–30 (1964).
Dreifuss, J. J., Grau, J. D., and Nordmann, J. J., J. Physiol., Lond., 231, 96–98P (1973).
Nordmann, J. J., thesis, Univ. Geneva (1973).
Dreifuss, J. J., and Nordmann, J. J., J. Physiol., Lond., 240, 46–47P (1974).
Bisset, G. W., et al., Br. J. Pharmac., 31, 537–549 (1967).
Neilands, J. B., in Methods in Enzymology, 1 (edit. by Colowick, S. P., and Kaplan, N. O.) 449–454 (Academic, New York and London, 1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
NORDMANN, J., DYBALL, R. New calcium-mobilising agent. Nature 255, 414–415 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/255414a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/255414a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.