Abstract
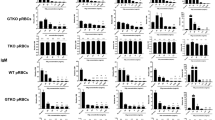
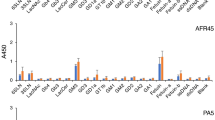
MANY assays for alloantibody depend on functional activities of the Fc portion of the immunoglobulin molecule. These functional activities are acquired when the antibody binds to its target cell. Complement binding, as demonstrated by lysis or complement fixation, has been the most widely used of these activities. In man, alloantibody can also be detected by its ability to mediate cell-dependent lysis of target cells1–3. In this system, effector cells (human peripheral blood leukocytes) lyse allogeneic chromium 51Cr-labelled target cells (lymphocytes) in the presence of the appropriate alloantibody, providing a sensitive, complement-independent assay for alloantibody. In contrast, we have found that mouse alloantisera do not usually mediate lysis of mouse target cells (lymph node lymphocytes, phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) blast cells, and tumour cells) by mouse effector cells (spleen cells). Data supporting this conclusion will be presented elsewhere.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wunderlich, J. R., Rosenberg, E. B., and Connolly, J. M., in Progress in Immunology (edit. by Amos, B.), 1, 473 (Academic Press, New York, 1971).
Hersey, P., Cullen, P., and Maclennan, I. C. M., Transplantation 16, 9 (1973).
McConnachie, P. R., and Dossetor, J. B., Tissue Antigens, 3, 303 (1973).
Perlmann, P., and Perlmann, H., Cell. Immun., 1, 300 (1970).
Van Boxel, J. A., Stobo, J. D., Paul, W. E., and Green, I., Science 175, 194 (1972).
Snell, G. D., Cherry, M., and Demant, P., Transpln Rev., 15, 3 (1973).
Chia, E., and Festenstein, H., Eur. J. Immun., 3, 438 (1973).
Maclennan, I. C. M., Transpln Rev., 13, 67 (1972).
Perlmann, P., Perlmann, H., and Wigzell, H., Transpln Rev., 13, 91 (1972).
Perlmann, P., Perlmann, H., and Biberfield, P., J. Immun., 108, 558 (1972).
Greenberg, A. H., and Shen, L., Nature new Biol., 145, 282 (1973).
Kiessling, R., and Klein, E., J. exp. Med., 137, 527 (1973).
Festenstein, H., and Demant, P., Transpln Proc., 5, 1321 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HALLORAN, P., FESTENSTEIN, H. Inhibition of cell-dependent cytotoxicity as an assay for mouse alloantibody. Nature 250, 52–54 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/250052a0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/250052a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.