Abstract
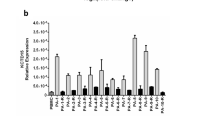
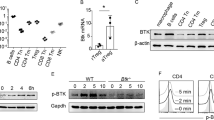
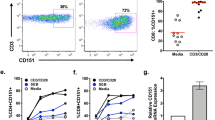
The Syk family tyrosine kinase ZAP-70 is essential for normal T-cell development and signaling. Recently, leukemic cells from some patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) were shown to express ZAP-70. Owing to the prognostic value of B-CLL ZAP-70 expression, this phenotype may reflect intrinsic biological differences between the two subsets of disease. However, it remains unclear whether CLL-B cells aberrantly acquire ZAP-70 expression during the transformation process or whether ZAP-70 may be expressed under certain conditions in normal human B-lymphocytes. To discriminate between these two possibilities, we assessed ZAP-70 expression in normal human B-lymphocytes. Our data demonstrate that ZAP-70 is expressed in a subpopulation of tonsillar and splenic normal B-lymphocytes that express an activated phenotype. Furthermore, ZAP-70 expression can be induced in vitro upon stimulation of blood and tonsillar B cells. Finally, we show that phosphorylation of ZAP-70 occurs in tonsillar B cells with stimulation through the B-cell receptor. These results provide new insight into normal human B-cell biology as well as provide clues about the transformed cell in B-CLL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Oers NSC, Weiss A . The Syk/ZAP-70 protein tyrosine kinase connection to antigen receptor signalling processes. Semin Immunol 1995; 7: 227–236.
Chan AC, Iwashima M, Turck CW, Weiss A . ZAP-70: a 70 kd protein-tyrosine kinase that associates with the TCR zeta chain. Cell 1992; 71: 649–662.
Chan AC, van Oers NS, Tran A, Turka L, Law CL, Ryan JC et al. Differential expression of ZAP-70 and Syk protein tyrosine kinases, and the role of this family of protein tyrosine kinases in TCR signaling. J Immunol 1994; 152: 4758–4766.
Wiestner A, Rosenwald A, Barry TS, Wright G, Davis RE, Henrickson SE et al. ZAP-70 expression identifies a chronic lymphocytic leukemia subtype with unmutated immunoglobulin genes, inferior clinical outcome, and distinct gene expression profile. Blood 2003; 101: 4944–4951.
Crespo M, Bosch F, Villamor N, Bellosillo B, Colomer D, Rozman M et al. ZAP-70 expression as a surrogate for immunoglobulin-variable-region mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1764–1775.
Bosch F, Villamor N . ZAP-70 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a new parameter for an old disease. Haematologica 2003; 88: 724–726.
Orchard JA, Ibbotson RE, Davis Z, Wiestner A, Rosenwald A, Thomas PW et al. ZAP-70 expression and prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet 2004; 363: 105–111.
Rosenwald A, Alizadeh AA, Widhopf G, Simon R, Davis RE, Yu X et al. Relation of gene expression phenotype to immunoglobulin mutation genotype in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Exp Med 2001; 194: 1639–1647.
Rassenti LZ, Huynh L, Toy TL, Chen L, Keating MJ, Gribben JG et al. ZAP-70 compared with immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene mutation status as a predictor of disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 893–901.
Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1840–1847.
Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, Oscier DG, Stevenson FK . Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1848–1854.
Krober A, Seiler T, Benner A, Bullinger L, Bruckle E, Lichter P et al. V(H) mutation status, CD38 expression level, genomic aberrations, and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 1410–1416.
Oscier DG, Gardiner AC, Mould SJ, Glide S, Davis ZA, Ibbotson RE et al. Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in CLL: clinical stage, IGVH gene mutational status, and loss or mutation of the p53 gene are independent of prognostic factors. Blood 2002; 100: 1177–1184.
Dürig J, Nuckel H, Cremer M, Führer A, Halfmeyer K, Fandrey J et al. ZAP-70 expression is a prognostic factor in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2426–2434.
Schweighoffer E, Vanes L, Mathiot A, Nakamura T, Tybulewicz VLJ . Unexpected requirement for ZAP-70 in pre-B cell development and allelic exclusion. Immunity 2003; 18: 523–533.
Meade J, Tybulewicz VL, Turner M . The tyrosine kinase Syk is required for light chain isotype exclusion but dispensable for the negative selection of B cells. Eur J Immunol 2004; 34: 1102–1110.
Chen L, Widhopft G, Huynh L, Rassenti L, Rai KR, Weiss A et al. Expression of ZAP-70 is associated with increased B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 4609–4614.
Chen L, Apgar J, Huynh L, Dicker F, Giago-McGahan T, Rassenti L et al. ZAP-70 directly enhances IgM signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2005; 105: 2036–2041.
Admirand JH, Rassidakis GZ, Abruzzo LV, Valbuena JR, Jones D, Jeffrey Medeiros L . Immunohistochemical detection of ZAP-70 in 341 cases of non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma. Mod Pathol 2004; 14: 954–961.
Jelinek DF, Tschumper RC, Stolovitzky GA, Iturria SJ, Tu Y, Lepre J et al. Identification of a global gene expression signature of B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Mol Cancer Res 2003; 1: 346–361.
Bernasconi NL, Traggiai E, Lanzavecchia A . Maintenance of serological memory by polyclonal activation of human memory B cells. Science 2002; 298: 2199–2202.
Walters DK, French JD, Arendt BK, Jelinek DF . Atypical expression of ErbB3 in myeloma cells: cross-talk between ErbB3 and the interferon-α signaling complex. Oncogene 2003; 22: 3598–3607.
Williams BL, Schreiber KL, Zhang W, Wange RL, Samelson LE, Leibson PJ et al. Genetic evidence for differential coupling of Syk family kinases to the T-Cell receptor: reconstitution studies in a ZAP-70 deficient Jurkat T-cell line. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 1388–1399.
Liu YJ, Arpin C . Germinal center development. Immunol Rev 1997; 156: 111–126.
Liu YJ, Arpin C, de Bouteiller O, Guret C, Banchereau J, Martinez-Valdez H et al. Sequential triggering of apoptosis, somatic mutation, and isotype switch during germinal center development. Semin Immunol 1996; 8: 169–177.
Sup SJ, Domiati-Saad R, Kelley TW, Steinle R, Zhao X, Hsi ED . ZAP-70 expression in B-cell hematologic malignancy is not limited to CLL/SLL. Am J Clin Pathol 2004; 122: 582–587.
Kong GH, Bu JY, Kurosaki T, Shaw AS, Chan AC . Reconstitution of Syk function by the ZAP-70 protein tyrosine kinase. Immunity 1995; 5: 485–492.
Ibrahim S, Keating M, Do KA, O'Brien S, Huh YO, Jilani I et al. CD38 expression as an important prognostic factor in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2001; 98: 181–186.
Lin K, Sherrington PD, Dennis M, Matrai Z, Cawley JC, Pettitt AR . Relationship between p53 dysfunction, CD38 expression, and IgV(H) mutation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 1404–1409.
Zupo S, Isnardi L, Megna M, Massara R, Malavasi F, Dono M et al. CD38 expression distinguishes two groups of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias with different responses to anti-IgM antibodies and propensity to apoptosis. Blood 1996; 88: 1365–1374.
Latour S, Veillette A . Proximal protein tyrosine kinases in immunoreceptor signaling. Curr Opin Immunol 2001; 13: 299–306.
Kolanus W, Romeo C, Seed B . T cell activation by clustered tyrosine kinases. Cell 1993; 74: 171–183.
Futterer K, Wong J, Grucza RA, Chan AC, Waksman G . Structural basis for Syk tyrosine kinase ubiquity in signal transduction pathways revealed by the crystal structure of its regulatory SH2 domains bound to a dually phosphorylated ITAM peptide. J Mol Biol 1998; 281: 523–537.
Steinberg M, Adjali O, Swainson L, Merida P, Di Bartolo V, Pelletier L et al. T-cell receptor-induced phosphorylation of the zeta chain is efficiently promoted by ZAP-70 but not Syk. Blood 2004; 104: 760–767.
Latour S, Chow LML, Veillette A . Differential intrinsic enzymatic activity of Syk and ZAP-70 protein-tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 22782–22790.
Thien CB, Bowtell DD, Langdon WY . Perturbed regulation of ZAP-70 and sustained tyrosine phosphorylation of LAT and SLP-76 in c-Cbl deficient thymocytes. J Immunol 1999; 162: 7133–7139.
Yasuda T, Maeda A, Kurosaki M, Tezuka T, Hironaka K, Yamamoto T et al. Cbl suppresses B cell receptor-mediated phospholipase C (PLC) gamma2 activation by regulating B cell linker protein-PLC-gamma2 binding. J Exp Med 2000; 191: 641–650.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Institute of Health Training Grant 5-T32-HL67742 (BTP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nolz, J., Tschumper, R., Pittner, B. et al. ZAP-70 is expressed by a subset of normal human B-lymphocytes displaying an activated phenotype. Leukemia 19, 1018–1024 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403726
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403726
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Profiling of human lymphocytes reveals a specific network of protein kinases modulated by endurance training status
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Targeting B cell receptor signalling in cancer: preclinical and clinical advances
Nature Reviews Cancer (2018)
-
Gefitinib targets ZAP-70-expressing chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and inhibits B-cell receptor signaling
Cell Death & Disease (2014)
-
Detection methods of ZAP-70 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2012)
-
The role of prognostic factors in assessing ‘high-risk’ subgroups of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Leukemia (2007)