Abstract
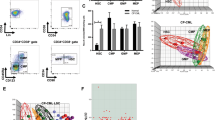
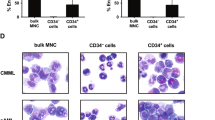
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is characterized by the expression of the P210 BCR/ABL fusion protein. The molecular mechanisms behind this oncogene-mediated hematological disease are, however, not fully understood. Here, we describe the establishment and phenotypic characterization of U937 cells in which P210 BCR/ABL can be conditionally expressed using tetracycline. The induction of BCR/ABL in the obtained clones resulted in a rapid phosphorylation of the STAT1, STAT3 and STAT5 molecules, consistent with the findings in other model systems. Phenotypic characterization of the clones revealed that BCR/ABL induces a slight decrease in the proliferation and viability, without a marked effect on cell cycle distribution, the rate of apoptosis or on cellular differentiation, as judged by several cell surface markers and capacity to reduce nitro blue tetrazolium. Interestingly, BCR/ABL was found to upregulate the expression of carcinoembryonic-related antigen (CEA)CAM1 (CD66a), which is a plasma membrane-linked glycoprotein belonging to the CEAs and involved in signal transduction and cellular adhesion. The expression of CEACAM1 was reversible upon imatinib treatment in BCR/ABL-expressing U937 cells as well as in BCR/ABL-positive K562 cells. The established cell lines may prove useful in further modeling and dissection of BCR/ABL-induced leukemogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Faderl S, Talpaz M, Estrov Z, O'Brien S, Kurzrock R, Kantarjian HM . The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 164–172.
Deininger MW, Goldman JM, Melo JV . The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2000; 96: 3343–3356.
Sawyers CL . Chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 1999; 340: 1330–1340.
Kabarowski JH, Witte ON . Consequences of BCR-ABL expression within the hematopoietic stem cell in chronic myeloid leukemia. Stem Cells 2000; 18: 399–408.
Cambier N, Zhang Y, Vairo G, Kosmopoulos K, Metcalf D, Nicola NA et al. Expression of BCR-ABL in M1 myeloid leukemia cells induces differentiation without arresting proliferation. Oncogene 1999; 18: 343–352.
Chalandon Y, Jiang X, Hazlewood G, Loutet S, Conneally E, Eaves A et al. Modulation of p210(BCR-ABL) activity in transduced primary human hematopoietic cells controls lineage programming. Blood 2002; 99: 3197–3204.
Sattler M, Salgia R . Activation of hematopoietic growth factor signal transduction pathways by the human oncogene BCR/ABL. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 1997; 8: 63–79.
Kisseleva T, Bhattacharya S, Braunstein J, Schindler CW . Signaling through the JAK/STAT pathway, recent advances and future challenges. Gene 2002; 285: 1–24.
Shuai K, Halpern J, ten Hoeve J, Rao X, Sawyers CL . Constitutive activation of STAT5 by the BCR-ABL oncogene in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Oncogene 1996; 13: 247–254.
Ilaria Jr RL, Van Etten RA . P210 and P190(BCR/ABL) induce the tyrosine phosphorylation and DNA binding activity of multiple specific STAT family members. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 31704–31710.
Carlesso N, Frank DA, Griffin JD . Tyrosyl phosphorylation and DNA binding activity of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins in hematopoietic cell lines transformed by Bcr/Abl. J Exp Med 1996; 183: 811–820.
Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J, Jove R . STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene 2000; 19: 2474–2488.
Sundstrom C, Nilsson K . Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer 1976; 17: 565–577.
Lozzio CB, Lozzio BB . Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood 1975; 45: 321–334.
Botling J, Oberg F, Nilsson K . CD49f (alpha 6 integrin) and CD66a (BGP) are specifically induced by retinoids during human monocytic differentiation. Leukemia 1995; 9: 2034–2041.
Olsson IL, Breitman TR . Induction of differentiation of the human histiocytic lymphoma cell line U-937 by retinoic acid and cyclic adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate-inducing agents. Cancer Res 1982; 42: 3924–3927.
Olsson I, Gullberg U, Ivhed I, Nilsson K . Induction of differentiation of the human histiocytic lymphoma cell line U-937 by 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. Cancer Res 1983; 43: 5862–5867.
Ghaffari S, Daley GQ, Lodish HF . Growth factor independence and BCR/ABL transformation: promise and pitfalls of murine model systems and assays. Leukemia 1999; 13: 1200–1206.
Van Etten RA . Models of chronic myeloid leukemia. Curr Oncol Rep 2001; 3: 228–237.
Wong S, Witte ON . Modeling Philadelphia chromosome positive leukemias. Oncogene 2001; 20: 5644–5659.
Drexler HG, MacLeod RA, Uphoff CC . Leukemia cell lines: in vitro models for the study of Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia. Leukemia Res 1999; 23: 207–215.
Kabarowski JH, Allen PB, Wiedemann LM . A temperature sensitive p210 BCR-ABL mutant defines the primary consequences of BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase expression in growth factor dependent cells. EMBO J 1994; 13: 5887–5895.
Cortez D, Reuther G, Pendergast AM . The Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase activates mitogenic signaling pathways and stimulates G1-to-S phase transition in hematopoietic cells. Oncogene 1997; 15: 2333–2342.
Klucher KM, Lopez DV, Daley GQ . Secondary mutation maintains the transformed state in BaF3 cells with inducible BCR/ABL expression. Blood 1998; 91: 3927–3934.
Pierce A, Owen-Lynch PJ, Spooncer E, Dexter TM, Whetton AD . p210 Bcr-Abl expression in a primitive multipotent haematopoietic cell line models the development of chronic myeloid leukaemia. Oncogene 1998; 17: 667–672.
Carlesso N, Griffin JD, Druker BJ . Use of a temperature-sensitive mutant to define the biological effects of the p210BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase on proliferation of a factor-dependent murine myeloid cell line. Oncogene 1994; 9: 149–156.
Chai SK, Nichols GL, Rothman P . Constitutive activation of JAKs and STATs in BCR-Abl-expressing cell lines and peripheral blood cells derived from leukemic patients. J Immunol 1997; 159: 4720–4728.
Mui AL . The role of STATs in proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 1999; 55: 1547–1558.
Hirano T, Ishihara K, Hibi M . Roles of STAT3 in mediating the cell growth, differentiation and survival signals relayed through the IL-6 family of cytokine receptors. Oncogene 2000; 19: 2548–2556.
Coffer PJ, Koenderman L, de Groot RP . The role of STATs in myeloid differentiation and leukemia. Oncogene 2000; 19: 2511–2522.
Danial NN, Rothman P . JAK-STAT signaling activated by Abl oncogenes. Oncogene 2000; 19: 2523–2531.
Nieborowska-Skorska M, Wasik MA, Slupianek A, Salomoni P, Kitamura T, Calabretta B et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)5 activation by BCR/ABL is dependent on intact Src homology (SH)3 and SH2 domains of BCR/ABL and is required for leukemogenesis. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 1229–1242.
Stryckmans PA, Debusscher L, Collard E . Cell kinetics in chronic granulocytic leukaemia (CGL). Clin Haematol 1977; 6: 21–40.
Thiele J, Zirbes TK, Lorenzen J, Kvasnicka HM, Dresbach S, Manich B et al. Apoptosis and proliferation (PCNA labelling) in CML – a comparative immunohistological study on bone marrow biopsies following interferon and busulfan therapy. J Pathol 1997; 181: 316–322.
Bedi A, Zehnbauer BA, Barber JP, Sharkis SJ, Jones RJ . Inhibition of apoptosis by BCR-ABL in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 1994; 83: 2038–2044.
McGahon A, Bissonnette R, Schmitt M, Cotter KM, Green DR, Cotter TG . BCR-ABL maintains resistance of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells to apoptotic cell death. Blood 1994; 83: 1179–1187.
Albrecht T, Schwab R, Henkes M, Peschel C, Huber C, Aulitzky WE . Primary proliferating immature myeloid cells from CML patients are not resistant to induction of apoptosis by DNA damage and growth factor withdrawal. Br J Haematol 1996; 95: 501–507.
Amos TA, Lewis JL, Grand FH, Gooding RP, Goldman JM, Gordon MY . Apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukaemia: normal responses by progenitor cells to growth factor deprivation, X-irradiation and glucocorticoids. Br J Haematol 1995; 91: 387–393.
Cortez D, Kadlec L, Pendergast AM . Structural and signaling requirements for BCR-ABL-mediated transformation and inhibition of apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 1995; 15: 5531–5541.
Daley GQ, Baltimore D . Transformation of an interleukin 3-dependent hematopoietic cell line by the chronic myelogenous leukemia-specific P210bcr/abl protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988; 85: 9312–9316.
Oberg F, Botling J, Nilsson K . Functional antagonism between vitamin D3 and retinoic acid in the regulation of CD14 and CD23 expression during monocytic differentiation of U-937 cells. J Immunol 1993; 150: 3487–3495.
Sirard C, Laneuville P, Dick JE . Expression of bcr-abl abrogates factor-dependent growth of human hematopoietic M07E cells by an autocrine mechanism. Blood 1994; 83: 1575–1585.
Druker BJ, Tamura S, Buchdunger E, Ohno S, Segal GM, Fanning S et al. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat Med 1996; 2: 561–566.
Druker BJ, Lydon NB . Lessons learned from the development of an Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor for chronic myelogenous leukemia. J Clin Invest 2000; 105: 3–7.
Hammarstrom S . The carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) family: structures, suggested functions and expression in normal and malignant tissues. Semin Cancer Biol 1999; 9: 67–81.
Beauchemin N, Draber P, Dveksler G, Gold P, Gray-Owen S, Grunert F et al. Redefined nomenclature for members of the carcinoembryonic antigen family. Exp Cell Res 1999; 252: 243–249.
Obrink B . CEA adhesion molecules: multifunctional proteins with signal-regulatory properties. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1997; 9: 616–626.
Thompson JA, Grunert F, Zimmermann W . Carcinoembryonic antigen gene family: molecular biology and clinical perspectives. J Clin Lab Anal 1991; 5: 344–366.
Hammarstrom S, Olsen A, Teglund S, Baranov V . The nature and expression of the human CEA family. In: Stanners CP (ed). Cell Adhesion and Communication Mediated by the CEA family. Basic and Clinical Perspectives. Amsterdam: Harwood Academic Publishers, 1998, pp 1–30.
Singer BB, Scheffrahn I, Heymann R, Sigmundsson K, Kammerer R, Obrink B . Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 expression and signaling in human, mouse, and rat leukocytes: evidence for replacement of the short cytoplasmic domain isoform by glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked proteins in human leukocytes. J Immunol 2002; 168: 5139–5146.
Skubitz KM, Campbell KD, Skubitz AP . CD66a, CD66b, CD66c, and CD66d each independently stimulate neutrophils. J Leukocyte Biol 1996; 60: 106–117.
Singer BB, Scheffrahn I, Obrink B . The tumor growth-inhibiting cell adhesion molecule CEACAM1 (C-CAM) is differently expressed in proliferating and quiescent epithelial cells and regulates cell proliferation. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 1236–1244.
Huang J, Hardy JD, Sun Y, Shively JE . Essential role of biliary glycoprotein (CD66a) in morphogenesis of the human mammary epithelial cell line MCF10F. J Cell Sci 1999; 112: 4193–4205.
Wagener C, Ergun S . Angiogenic properties of the carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1. Exp Cell Res 2000; 261: 19–24.
Skubitz KM, Campbell KD, Ahmed K, Skubitz AP . CD66 family members are associated with tyrosine kinase activity in human neutrophils. J Immunol 1995; 155: 5382–5390.
Ebrahimnejad A, Flayeh R, Unteregger G, Wagener C, Brummer J . Cell adhesion molecule CEACAM1 associates with paxillin in granulocytes and epithelial and endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 2000; 260: 365–373.
McWhirter JR, Wang JY . Activation of tyrosinase kinase and microfilament-binding functions of c-abl by bcr sequences in bcr/abl fusion proteins. Mol Cell Biol 1991; 11: 1553–1565.
McWhirter JR, Wang JY . An actin-binding function contributes to transformation by the Bcr-Abl oncoprotein of Philadelphia chromosome-positive human leukemias. EMBO J 1993; 12: 1533–1546.
Sadekova S, Lamarche-Vane N, Li X, Beauchemin N . The CEACAM1-L glycoprotein associates with the actin cytoskeleton and localizes to cell–cell contact through activation of Rho-like GTPases. Mol Biol Cell 2000; 11: 65–77.
Salgia R, Uemura N, Okuda K, Li JL, Pisick E, Sattler M et al. CRKL links p210BCR/ABL with paxillin in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 29145–29150.
Watt SM, Sala-Newby G, Hoang T, Gilmore DJ, Grunert F, Nagel G et al. CD66 identifies a neutrophil-specific epitope within the hematopoietic system that is expressed by members of the carcinoembryonic antigen family of adhesion molecules. Blood 1991; 78: 63–74.
Grunert F, Kuroki M, Stocks SC . CEA family members expressed on hematopoietic cells and their possible role in cell adhesion and signaling. In: Stanners CP (ed). Cell Adhesion and Communication Mediated by the CEA family. Basic and Clinical Perspectives. Amsterdam: Harwood Academic Publishers, 1998, pp 99–119.
Carrasco M, Munoz L, Bellido M, Bernat S, Rubiol E, Ubeda J et al. CD66 expression in acute leukaemia. Ann Hematol 2000; 79: 299–303.
Sugita K, Mori T, Yokota S, Kuroki M, Koyama TO, Inukai T et al. The KOR-SA3544 antigen predominantly expressed on the surface of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells is nonspecific cross-reacting antigen-50/90 (CD66c) and invariably expressed in cytoplasm of human leukemia cells. Leukemia 1999; 13: 779–785.
Mori T, Sugita K, Suzuki T, Okazaki T, Manabe A, Hosoya R et al. A novel monoclonal antibody, KOR-SA3544 which reacts to Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells with high sensitivity. Leukemia 1995; 9: 1233–1239.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs J Groffen and N Heisterkamp (Childrens Hospital Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA) for providing AB1/pCDE, Dr GR Adolf (Ernst Boehringer Institut, Vienna, Austria) for supplying human TNFα and Dr E Buchdunger (Novartis, Basel, Switzerland) for providing imatinib mesylate. In addition, we thank H Svedberg (Department of Hematology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden) for help with the NBT reduction test and J Almkvist (Department of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Göteborg University, Göteborg, Sweden) for technical assistance with the antibodies against CEAs used for Western blot analysis. This study was supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer Society and the Swedish Children's Cancer Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Håkansson, P., Lassen, C., Olofsson, T. et al. Establishment and phenotypic characterization of human U937 cells with inducible P210 BCR/ABL expression reveals upregulation of CEACAM1 (CD66a). Leukemia 18, 538–547 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403255
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403255
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Antigens in chronic myeloid leukemia: implications for vaccine development
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2011)
-
High expression of CEACAM6 and CEACAM8 mRNA in acute lymphoblastic leukemias
Annals of Hematology (2008)
-
Expression of the p210BCR-ABL oncoprotein drives centrosomal hypertrophy and clonal evolution in human U937 cells
Leukemia (2007)
-
Deregulation of the Wilms' tumour gene 1 protein (WT1) by BCR/ABL1 mediates resistance to imatinib in human leukaemia cells
Leukemia (2007)