Abstract
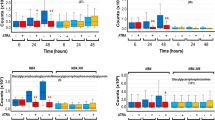
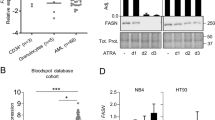
The cellular prion protein (PrPc) is a sialoglycoprotein involved in the pathogenesis of prion diseases. It has been identified at the plasma membrane of several cell types. All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) is known to induce differentiation of human leukemia cell lines in vitro. PrPc messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) and protein are down-regulated upon ATRA-induced differentiation of HL60 cells. In this report, we have investigated the regulation of PrPc mRNA and protein expression during ATRA-treatment of maturation-sensitive (NB4) and -resistant (NB4-R1 and NB4-R2) cell lines. In ATRA-induced maturation of NB4 cells, down-regulation of PrPc mRNA and protein were observed. We also show that down-regulation of PrPc mRNA is dependent on protein synthesis. Moreover, the same down-regulation of prion protein by ATRA was observed at the surface of maturation-resistant, ATRA-responsive NB4-R1 cells. In contrast, the maturation-resistant and ATRA-unresponsive NB4-R2 subline showed no variation in membrane prion protein expression. These results demonstrate a dissociation between the regulation of prion protein expression by ATRA and the process of granulocyte maturation. We propose that retinoids should be investigated further as a preventive strategy to slow down prion disease progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basler K, Oesch B, Scott M, Westaway D, Wälchli M, Groth DF, McKinley MP, Prusiner SB, Weissmann C . Scrapie and cellular PrP isoforms are encoded by the same chromosomal gene Cell 1986 46: 417–428
Caughey B, Raymond GJ . The scrapie-associated form of PrP is made from a cell surface precursor that is both protease- and phospholipase-sensitive J Biol Chem 1991 266: 18217–18223
Oesch B, Westaway D, Wälchli M, McKinley MP, Kent SBH, Aebersold R, Barry RA, Tempst P, Teplow DB, Hood LE, Prusiner SB, Weissmann C . A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27–30 protein Cell 1985 40: 735–746
Prusiner SB . Molecular biology of prion diseases Science 1991 252: 1515–1522
Büeler H, Fischer M, Lang Y, Bluethmann H, Lipp HP, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB, Aguet M, Weissmann C . Normal development and behaviour of mice lacking the neuronal cell-surface PrP protein Nature 1992 356: 577–582
Büeler H, Aguzzi A, Sailer A, Greiner RA, Autenried P, Aguet M, Weissmann C . Mice devoid of PrP are resistant to scrapie Cell 1993 73: 1339–1347
Sailer A, Büeler H, Fischer M, Aguzzi A, Weissmann C . No propagation of prions in mice devoid of PrP Cell 1994 77: 967–968
Weissmann C, Büeler H, Fischer M, Sailer A, Aguzzi A, Aguet M . PrP-deficient mice are resistant to scrapie Ann NY Acad Sci 1994 724: 235–240
Bendheim PE, Brown HR, Rudelli RD, Scala LJ, Goller NL, Wen GY, Kascsak RJ, Cashman NR, Bolton DC . Nearly ubiquitous tissue distribution of the scrapie agent precursor protein Neurology 1992 42: 149–156
Fournier JG, Escaig-Haye F, Billette de Villemeur T, Robain O, Lasmézas CI, Deslys JP, Dormont D, Brown P . Distribution and submicroscopic immunogold localization of cellular prion protein (PrPc) in extracerebral tissues Cell Tiss Res 1998 292: 77–84
MacGregor I, Hope J, Barnard G, Kirby L, Drummond O, Pepper D, Hornsey V, Barclay R, Bessos H, Turner M, Prowse C . Application of a time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay for the analysis of normal prion protein in human blood and its components Vox Sang 1999 77: 88–96
Holada K, Mondoro TH, Muller J, Vostal JG . Increased expression of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C resistant prion proteins on the surface of activated platelets Br J Haematol 1998 103: 276–282
Starke R, Cramer E, Harrison P . Expression of cell-associated prion protein on normal human platelets Br J Haematol 2000 110: 748–750
Antoine N, Cesbron JY, Coumans B, Jolois O, Zorzi W, Heinen E . Differential expression of cellular prion protein on human blood and tonsil lymphocytes Haematologica 2000 85: 475–480
Li R, Liu D, Zanusso G, Liu T, Fayen JD, Huang JH, Petersen RB, Gambetti P, Sy MS . The expression and potential function of cellular prion protein in human lymphocytes Cell Immunol 2001 207: 49–58
Cashman NR, Loertscher R, Nalbantoglu J, Shaw I, Kascsak RJ, Bolton DC, Bendheim PE . Cellular isoform of the scrapie agent protein participates in lymphocyte activation Cell 1990 61: 185–192
Dodelet VC, Cashman NR . Prion protein expression in human leukocyte differentiation Blood 1998 91: 1556–1561
Dürig J, Giese A, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Rosenthal C, Schmücker U, Bieschke J, Dührsen U, Kretzschmar HA . Differential constitutive and activation-dependent expression of prion protein in human peripheral blood leucocytes Br J Haematol 2000 108: 488–496
Barclay GR, Hope J, Birkett CR, Turner ML . Distribution of cell-associated prion protein in normal adult blood determined by flow cytometry Br J Haematol 1999 107: 804–814
Mabbott NA, Brown KL, Bruce ME . T lymphocyte activation and the cellular form of the prion protein, PrPc Biochem Soc Trans 1997 25: 307S
Mabbott NA, Brown KL, Manson J, Bruce ME . T-lymphocyte activation and the cellular form of the prion protein Immunology 1997 92: 161–165
Holada K, Vostal JG . Different levels of prion protein (PrPc) expression on hamster, mouse and human blood cells Br J Haematol 2000 110: 472–480
Eisenhauer EA, Lippman SM, Kavanagh JJ, Parades-Espinoza M, Arnold A, Hong WK, Massimini G, Schleuniger U, Bollag W, Holdener EE, Krakoff I . Combination 13-cis-retinoic acid and interferon alpha-2a in the therapy of solid tumors Leukemia 1994 8: 1622–1625
Castaigne S, Chomienne C, Daniel MT, Ballerini P, Berger R, Fenaux P, Degos L . All-trans retinoic acid as a differentiation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia. I. Clinical results Blood 1990 76: 1704–1709
Chomienne C, Ballerini P, Balitrand N, Daniel MT, Fenaux P, Castaigne S, Degos L . All-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemias. II. In vitro studies: structure–function relationship Blood 1990 76: 1710–1717
Huang ME, Ye YC, Chen SR, Chai JR, Lu JX, Zhoa L, Gu LJ, Wang ZY . Use of all-trans retinoic acid in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1988 72: 567–572
Kogan SC, Bishop JM . Acute promyelocytic leukemia: from treatment to genetics and back Oncogene 1999 18: 5261–5267
Breitman TR, Selonick SE, Collins SJ . Induction of differentiation of the human promyelocytic leukemia cell line (HL-60) by retinoic acid Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1980 77: 2936–2940
Lanotte M, Martin-Thouvenin V, Najman S, Balerini P, Valensi F, Berger R . NB4, a maturation inducible cell line with t(15;17) marker isolated from a human acute promyelocytic leukemia (M3) Blood 1991 77: 1080–1086
Duprez E, Ruchaud S, Houge G, Martin-Thouvenin V, Valensi F, Kastner P, Berger R, Lanotte M . A retinoid acid ‘resistant’ t(15;17) acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line: isolation, morphological, immunological, and molecular features Leukemia 1992 6: 1281–1287
Ruchaud S, Duprez E, Gendron MC, Houge G, Genieser HG, Jastorff B, Doskeland SO, Lanotte M . Two distinctly regulated events, priming and triggering, during retinoid-induced maturation and resistance of NB4 promyelocytic leukemia cell line Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994 91: 8428–8432
Duprez E, Benoit G, Flexor M, Lillehaug JR, Lanotte M . A mutated PML/RARA found in the retinoid maturation resistant NB4 subclone, NB4-R2, blocks RARA and wild-type PML/RARA transcriptional activities Leukemia 2000 14: 255–261
de Thé H, Chomienne C, Lanotte M, Degos L, Dejean A . The t(15;17) translocation of acute promyelocytic leukaemia fuses the retinoic acid receptor alpha gene to a novel transcribed locus Nature 1990 347: 558–561
Kakizuka A, Miller WH Jr, Umesono K, Warrell RP Jr, Frankel SR, Murty VVVS, Dmitrovsky E, Evans RM . Chromosomal translocation t(15;17) in human acute promyelocytic leukemia fuses RAR alpha with a novel putative transcription factor, PML Cell 1991 66: 663–674
Benedetti L, Grignani F, Scicchitano BM, Jetten AM, Diverio D, Lo Coco F, Avvisati G, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Adamo S, Levin AA, Pelicci PG, Nervi C . Retinoid-induced differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia involves PML-RARalpha-mediated increase of type II transglutaminase Blood 1996 87: 1939–1950
Gianni M, Zanotta S, Terao M, Rambaldi A, Garattini E . Interferons induce normal and aberrant retinoic-acid receptors type alpha in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells: potentiation of the induction of retinoid-dependent differentiation markers Int J Cancer 1996 68: 75–83
Labbaye C, Zhang J, Casanova JL, Lanotte M, Teng J, Miller WH Jr, Cayre YE . Regulation of myeloblastin messenger RNA expression in myeloid leukemia cells treated with all-trans retinoic acid Blood 1993 81: 475–481
Kascsak RJ, Rubenstein R, Merz PA, Tonna-DeMasi M, Fersko R, Carp RI, Wisniewski HM, Diringer H . Mouse polyclonal and monoclonal antibody to scrapie-associated fibril proteins J Virol 1987 61: 3688–3693
Dürig J, Giese A, Schmücker U, Kretzschmar HA, Dührsen U . Decreased prion protein expression in human peripheral blood leucocytes from patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria Br J Haematol 2001 112: 658–662
Laemmli UK . Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4 Nature 1970 227: 680–685
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N . Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction Anal Biochem 1987 162: 156–159
Caughey B, Race RE, Ernst D, Buchmeier MJ, Chesebro B . Prion protein biosynthesis in scrapie-infected and uninfected neuroblastoma cells J Virol 1989 63: 175–181
Caughey B . In vitro expression and biosynthesis of prion protein Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 1991 172: 93–107
Aguzzi A . Prion diseases, blood and the immune system: concerns and reality Haematologica 2000 85: 3–10
Diomede L, Sozzani S, Luini W, Algeri M, De Gioia L, Chiesa R, Lievens PMJ, Bugiani O, Forloni G, Tagliavini F, Salmona M . Activation effects of a prion protein fragment (PrP-(106–126)) on human leucocytes Biochem J 1996 320: 563–570
Satoh JI, Kurohara K, Yukitake M, Kuroda Y . Constitutive and cytokine-inducible expression of prion protein gene in human neural cell lines J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1998 57: 131–139
Mouillet-Richard S, Laurendeau I, Vidaud M, Kellermann O, Laplanche JL . Prion protein and neuronal differentiation: quantitative analysis of prnp gene expression in a murine inducible neuroectodermal progenitor Microbes Infect 1999 1: 969–976
Puckett C, Concannon P, Casey C, Hood L . Genomic structure of the human prion protein gene Am J Hum Genet 1991 49: 320–329
Westaway D, Cooper C, Turner S, Da Costa M, Carlson GA, Prusiner SB . Structure and polymorphism of the mouse prion protein gene Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994 91: 6418–6422
Pendino F, Flexor M, Delhommeau F, Buet D, Lanotte M, Ségal-Bendirdjian E . Retinoids down-regulate telomerase and telomere length in a pathway distinct from leukemia cell differentiation Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001 98: 6662–6667
Goldmann W, O'Neill G, Cheung F, Charleson F, Ford P, Hunter N . PrP (prion) gene expression in sheep may be modulated by alternative polyadenylation of its messenger RNA J Gen Virol 1999 80: 2275–2283
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to Mrs C Doliger and Mr M Schmid from the Service Commun d'Imageries Cellulaires et Moléculaires of the Institut Universitaire d'Hématologie (Hôpital Saint-Louis) for confocal microscopy. This work was supported by grants from INSERM, the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer (ARC No. 9884, No. 5707), the Ministère de l'Enseignement Supérieur, de la Recherche Scientifique et Technique (MESRST No. 98C0275), the INTAS, the Coopération Franco-Algérienne (ALG4B207B). C Rybner is a recipient of a fellowship from the Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rybner, C., Hillion, J., Sahraoui, T. et al. All-trans retinoic acid down-regulates prion protein expression independently of granulocyte maturation. Leukemia 16, 940–948 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402443
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402443
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
RARB and STMN2 polymorphisms are not associated with sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD) in the Korean population
Molecular Biology Reports (2014)
-
Prion protein
AfCS-Nature Molecule Pages (2009)
-
Activation and repression of prion protein expression by key regions of intron 1
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2009)
-
Efficacy of gemtuzumab ozogamicin on ATRA- and arsenic-resistant acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) cells
Leukemia (2005)