Abstract
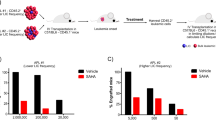
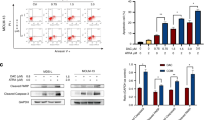
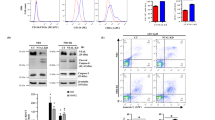
Recent clinical studies in China and USA showed that arsenic trioxide (As2O3) is an effective treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) patients refractory to all-trans retinoic acid (RA). We here investigate the effects of As2O3on RA-resistant APL in vivo and in vitro using our RA-resistant APL model system. As2O3 can induce inhibition of cellular growth of both RA-sensitive NB4 and RA-resistant UF-1 APL cells via induction of apoptosis in vitro. The expression of BCL-2 protein decreased in a dose- and time-dependent manner in NB4 cells. Interestingly, the levels of BCL-2 protein were not modulated by As2O3, but it did upregulate BAX protein in UF-1 cells. UF-1 cells (1 × 107) were transplanted into hGM-CSF-producing transgenic SCID mice and successfully formed subcutaneous tumors. After 40 days of implantation, mice were treated with As2O3, all-trans RA and PBS for 21 days. In all-trans RA- and PBS-treated mice, tumors grew rapidly, with a 4.5-fold increase in volume at day 21 compared to the initial size. In marked contrast, tumor size was decreased to half of the initial size by the treatment of As2O3, which resulted in cells with the typical appearance of apoptosis. Interestingly, one of the As2O3-treated mice showed mature granulocytes in the diminished tumor, suggesting that As2O3 had dual effects on RA-resistant APL cells in vivo: both inducing apoptosis and differentiation of the leukemic cells. We conclude that our RA-resistant APL model will be useful for evaluating novel therapeutic approaches to patients with RA-resistant APL, and for further investigation of the metabolism of As2O3 in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Thé H, Chomienne C, Lanotte M, Degos L, Dejean A . The t(15;17) translocation of acute promyelocytic leukemia fuses the retinoic acid receptor α gene to a novel transcribed locus Nature 1991 347: 558–561
Kakizuka A, Miller WH Jr, Umesono K, Warrell RP Jr, Frankel SR, Murty VVVS, Dmitrovsky E, Evans RM . Chromosomal translocation t(15;17) in human acute promyelocytic leukemia fuses RARα with a novel putative transcription factor, PML Cell 1991 66: 663–674
Grignani F, Ferrucci PF, Testa U, Talamo G, Fagioli M, Alcalay M, Mencarelli A, Grignani F, Peschle C, Nicoletti I, Pelicci PG . The acute promyelocytic leukemia specific PML/RARα protein inhibits differentiation and promotes survival of myeloid precursor cells Cell 1993 74: 423–431
Warrell RP Jr, de Thé H, Wang ZY, Degos L . Acute promyelocytic leukemia New Engl J Med 1993 329: 177–189
Huang ME, Ye YC, Chen SR, Chai JR, Lu JX, Zhoa L, Gu HT, Wang ZY . Use of all-trans retinoic acid in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1988 72: 567–572
Castaigne S, Chomienne C, Daniel MT, Ballarini P, Berger R, Fenaux P, Degos L . All-trans retinoic acid as a differentiation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia. I. Clinical results Blood 1990 76: 1704–1709
Warrell RP Jr, Frankel SR, Miller WH Jr, Sheinberg DA, Itri LM, Hittelman WN, Vyas R, Andreeff M, Tafuri A, Jakubowski A, Gabrilove J, Gordon MS, Dmitrovski E . Differentiation therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia with tretinoin (all-trans-retinoic acid) New Engl J Med 1991 324: 1385–1393
Kanamaru A, Takemoto Y, Tanimoto M, Murakami H, Asou N, Kobayashi T, Kuriyama K, Ohmoto E, Sakamaki H, Tsubaki K, Hiraoka H, Yamada O, Oh H, Saito K, Matsuda S, Minato K, Ueda T, Ohno R . All-trans retinoic acid for the treatment of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1995 85: 1202–1206
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, Li XS, Xiong SM, Qiu QY, Zhu J, Tang W, Sun GL, Yang KQ, Chen Y, Zhou L, Fang ZW, Wang YT, Ma J, Zhang P, Zhang TD, Chen SJ, Chen Z, Wang ZY . Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). II. Clinical efficiency and pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients Blood 1997 89: 3354–3360
Soignet SL, Maslak P, Wang Z-G, Thanwar S, Calleja E, Dardashti LJ, Corso D, DeBlasio A, Gabrilove J, Scheinberg DA, Pandorfi PP, Warrell RP Jr . Complete remission after treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide New Engl J Med 1998 339: 1341–1348
Chen GQ, Zhu J, Shi XG, Ni JH, Zhong HJ, Si GY, Jin XL, Tang W, Li XS, Xong SM, Shen ZX, Sun GL, Ma J, Zhang P, Zhang TD, Gazin C, Naoe T, Chen SJ, Wang ZY, Chen Z . In vitro studies on cellular and molecular mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia: As2O3 induces NB4 cells apoptosis with downregulation of bcl-2 expression and modulation of PML-RARα/PML proteins Blood 1996 88: 1052–1061
Chen GQ, Shi XG, Tang W, Xiong SM, Zhu J, Cai X, Han ZG, Ni JH, Shi GY, Jia PM, Liu MM, He KL, Niu C, Ma J, Zhang P, Zhang TD, Paul P, Naoe T, Kitamura K, Miller WH, Waxman S, Wang ZY, de The H, Chen SJ, Chen Z . Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): I. As2O3 exerts dose-dependent dual effects on APL cells Blood 1997 89: 3345–3354
Kizaki M, Matsushita H, Takayama N, Muto A, Ueno H, Awaya N, Kawai Y, Asou H, Kamada N, Ikeda Y . Establishment and characterization of a novel acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line (UF-1) with retinoic acid-resistant features Blood 1996 88: 1824–1833
Fukuchi Y, Kizaki M, Kinjo K, Awaya N, Ito M, Kawai Y, Umezawa A, Hata J, Ueyama Y, Ikeda Y . Establishment of a retinoic acid resistant human acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) model in hGM-CSF transgenic SCID mice Br J Cancer 1998 78: 878–884
Lanotte M, Martin-Thouvenin V, Najman S, Balerini P, Valensi F, Berger R . NB4, a maturation inducible cell line with t(15;17) marker isolated from a human acute promyelocytic leukemia (M3) Blood 1991 77: 1080–1086
Miyakawa Y, Fukuchi Y, Ito M, Kobayashi K, Kumamochi T, Ikeda Y, Takeda Y, Yanaka T, Miyasaka M, Nakahata T, Tamaoki N, Nomura T, Ueyama Y, Shimamura K . Establishment of humangranulocyte–macrophage colony stimulating factor producingtransgenic SCID mice Br J Haematol 1996 95: 437–442
Workman P, Balmain A, Hickman JA, MoNally NJ, Mitchison NA, Pirepoint CG, Raymond R, Rowlatt C, Stephens TC, Wallace J . UKCCCR guidelines for the welfare of animals in experimental neoplasia Br J Cancer 1988 58: 109–113
Lo Coco F, Nervi C, Avvisati G, Mandelli F . Acute promyelocytic leukemia: a curable disease Leukemia 1998 12: 1866–1880
Kizaki M, Ueno H, Matsushita H, Takayama N, Muto A, Awaya N, Ikeda Y . Retinoid resistance in leukemic cells Leuk Lymphoma 1997 25: 425–434
Fenaux P, Chomienne C, Degos L . Acute promyelocytic leukemia: biology and treatment Semin Oncol 1997 24: 92–102
Mandelli F, Diverio D, Avvisati G, Luciano A, Barbui T, Bernasconi C, Broccia G, Cerri R, Falda M, Fioritoni G, Leoni F, Liso V, Petti MC, Rodeghiero F, Saglio G, Vegna ML, Visani G, Jehn U, Willemze R, Muus P, Pelicci PG, Biondi A, Lo Coco F . Molecular remission in PML/RARα-positive acute promyelocytic leukemia by combined all-trans retinoic acid and idarubicin (AIDA) therapy Blood 1997 90: 1014–1021
Tallman MS, Andersen JW, Schiffer CA, Appelbaum FR, Feusner JH, Ogden A, Shepherd L, Willman C, Bloomfield CD, Rowe JM, Wiernik PH . All-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia New Engl J Med 1997 337: 1201–1208
Altabef M, Garcia M, Lavau C, Bae S-C, Dejean A, Samarut J . A retrovirus carrying the promyelocyte-retinoic acid receptor PML-RARα fusion genes transforms hematopioetic progenitors in vitro and induces acute leukamia EMBO J 1996 15: 2707–2716
Early E, Moore MAS, Kakizuka A, Nason-Burchenal K, Martin P, Evans RM . Transgenic expression of PML-RARα impairs myelopoiesis Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996 93: 7900–7904
He L-Z, Tribioli C, Rivi R, Peruzzi D, Pelicci PG, Soares V, Cattoretti C, Pandolfi PP . Acute leukemia with promyelocytic features in PML/RARα transgenic mice Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 5302–5307
Grisolano JL, Wesselschmidt RL, Pelicci PG, Ley TJ . Altered myeloid development and acute leukemia in transgenic mice expressing PML-RARα under control of cathepsin G regulatory sequences Blood 1997 89: 376–387
Brown D, Kogan S, Lagasse E, Weissman I, Alcalay M, Pelicci PG, Atwater S, Bishop JM . A PMLRARα transgene initiate murine promyelocytic leukemia Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 2551–2556
Sawyer CL, Gishizky ML, Quan S, Golde DW, Witte ON . Propagation of human blastic myeloid leukemias in SCID mouse Blood 1992 79: 2089–2098
Namikawa R, Ueda R, Kyoizumi S . Growth of human myeloid leukemias in the human marrow environment of SCID-hu mice Blood 1993 82: 2526–2536
Fukuchi Y, Miyakawa Y, Kobayashi K, Kuramochi T, Shimamura K, Tamaoki N, Nomura T, Ueyama Y, Ito M . Cytokine dependent growth of human TF-1 leukemic cell line in human GM-CSF and IL-3 producing transgenic SCID mice Leukemia Res 1998 22: 837–843
Reed JC . Double identity for proteins of the Bcl-2 family Nature 1997 387: 773–776
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ . Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, BAX, that accelerates programmed cell death Cell 1993 74: 609–619
Giannì M, Koken MHM, Chelbi-Alix MK, Benoit G, Lanotte M, Chen Z, de Thé H . Combined arsenic and retinoic acid treatment enhances differentiation and apoptosis in arsenic-resistant NB4 cells Blood 1998 91: 4300–4310
Lallemand-Breitenbach V, Guillemin M-C, Janin A, Daniel M-T, Degos L, Kogan SC, Bishop JM, de Thé H . Retinoic acid and arsenic synergize to eradicate leukemic cells in a mouse model of acute promyelocytic leukemia J Exp Med 1999 189: 1043–1052
Kizaki M, Muto A, Kinjo K, Ueno H, Ikeda Y . Application of heavy metal and cytokine for differentiation-inducing therapy in acute promyelocytic leukemia J Natl Cancer Inst 1998 90: 1906–1907
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture in Japan, the Special Cordination Funds for promoting Science and Technology of the Science and Technology Agency of the Japanese Government and the National Grant-in-Aid for the Establishment of a High Tech Research Center in a Private University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kinjo, K., Kizaki, M., Muto, A. et al. Arsenic trioxide (As2O3)-induced apoptosis and differentiation in retinoic acid-resistant acute promyelocytic leukemia model in hGM-CSF-producing transgenic SCID mice. Leukemia 14, 431–438 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401646
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401646
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pyroptosis and pyroptosis-inducing cancer drugs
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2022)
-
Downregulation of Mcl-1 through GSK-3β activation contributes to arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells
Leukemia (2013)
-
The NRF2-mediated oxidative stress response pathway is associated with tumor cell resistance to arsenic trioxide across the NCI-60 panel
BMC Medical Genomics (2010)
-
Differentiation of SWO-38 glioma cells induced by CDA-2 is mediated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2009)
-
Inhibitory effect of arsenic trioxide on growth and telomerase activity of SMMC-7721 and BEL-7402 hepatocarcinoma cells and determination of their GSH content
Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology (2006)