Abstract
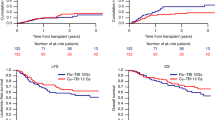
A cohort of 76 patients with previous chemotherapy for Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin lymphomas received high-dose carmustine, etoposide, cytosine-arabinoside and melphalan (BEAM) followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and was followed for relapse and development of leukemic complications. Six patients, four with Hodgkin’s disease and two with non-Hodgkin lymphomas, developed leukemic complications, myelodysplasia (MDS) in four cases and overt acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in two. All six showed an abnormal karyotype, in four of them highly characteristic of therapy-related MDS (t-MDS) and therapy-related AML (t-AML). The cumulative risk of t-MDS and t-AML increased from 16 months after start of the primary chemotherapy for lymphoma and reached 17.3% (s.e. 8.5%) after 74 months. If calculated from start of BEAM and ASCT, the cumulative risk increased as early as 4 months and reached 24.3% (s.e. 12.9%) after 43 months. For the whole course of the disease, the relative risk (RR) of AML was 357 (95% CI: 43–1290), as two overt leukemias were observed vs 0.0056 expected cases of de novo AML. In the present cohort the risk of t-MDS and t-AML although high, did not differ from our previous experience in patients treated conventionally for Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin lymphomas, and did not differ for patients receiving stem cells isolated from the bone marrow as compared to patients receiving stem cells isolated from peripheral blood. Antecedent chemotherapy seems to be the critical factor for the development of t-MDS and t-AML rather than the BEAM and ASCT regimen, which however may accelerate the evolution of the disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedersen-Bjergaard, J., Pedersen, M., Myhre, J. et al. High risk of therapy-related leukemia after BEAM chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation for previously treated lymphomas is mainly related to primary chemotherapy and not to the BEAM–transplantation procedure. Leukemia 11, 1654–1660 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2400809
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2400809
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Second Malignancies after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2018)
-
Therapy-related myelodysplasia and leukemia occur infrequently following VP-16 priming and autotransplantation without total body irradiation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2004)
-
Secondary myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myelogenous leukemia are significant complications following autologous stem cell transplantation for lymphoma
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2003)
-
Therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome after autologous stem cell transplantation for breast cancer
Leukemia (2002)
-
Front-line high-dose therapy with autologous stem cell transplantation for high risk Hodgkin's disease: comparison with combined-modality therapy
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2002)