Abstract
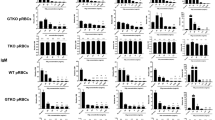
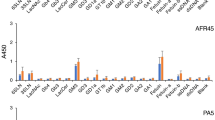
CELLULAR immunity is of primary importance in graft reactions. Sensitization seems to be based on surface interactions between small lymphocytes and cell-bound transplantation antigens; the effector mechanism involves contact interactions between sensitized lymphocytes and the grafted cells. Lymphocytes recognize cell membrane antigens and cause injury to the grafted cells essentially by cell surface processes, the nature of which is not clear. The application of surface-active substances, at both the sensitization and the effector phase, could be expected to make clear some aspects of cell contact interactions involved in graft reaction. We have studied, therefore, the effects of concanavalin A (conA) on a graft reaction system. ConA is a protein molecule with two sugar-binding sites1–6, which can interact with sugar moieties on cell surfaces7–9. The graft reaction system we used10,11 involved the sensitization of rat lymphocytes against mouse antigens by culturing the lymphocytes on monolayers of mouse fibroblasts for 5 days. This sensitization is characterized by a morphological transformation of small lymphocytes into medium or large cells12. The sensitized lymphocytes are capable of lysing mouse cells which are antigenically identical to the sensitizing cells. Antibodies are not produced, and the lytic reaction thus requires direct contact between the lymphocytes and the target cells13. The rate of lysis is measured by plating the sensitized lymphocytes on fibroblasts labelled with Na51CrO4 and measuring the amount of radioactivity released into the culture medium14,15.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Summer, J. B., Gralen, N., and Eriksson-Quensel, I. B., J. Biol. Chem., 125, 45 (1938).
Goldstein, I. J., Hollerman, C. E., and Merrick, J. M., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 97, 68 (1965).
So, L. L., and Goldstein, I. J., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 165, 398 (1968).
So, L. L., and Goldstein, I. J., Immunology, 99, 158 (1967).
Yariv, J., Kalb, A. J., and Levitzki, A., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 165, 303 (1968).
Poretz, R. D., and Goldstein, I. J., Biochemistry, 9, 2890 (1970).
Burger, M. M., Proc. US Nat. Acad. Sci., 62, 994 (1969).
Inbar, M., and Sachs, L., Nature, 223, 710 (1969).
Inbar, M., and Sachs, L., Proc. US Nat. Acad. Sci., 63, 1418 (1969).
Ginsburg, H., and Sachs, L., J. Cell. Comp. Physiol., 66, 199 (1965).
Ginsburg, H., Immunology, 14, 621 (1968).
Tyler, R. W., Ginsburg, H., and Everett, N. B., in Proc. Third Ann. Leucocyte Conf. (edit. by Rieke, W. O.), 451 (Appleton, New York, 1967).
Ginsburg, H., Ax, W., and Berke, G., in Excerpta Medica Foundation, Intern. Series Cong., No. 197 (1969).
Berke, G., Ax, W., Ginsburg, H., and Feldman, M., Immunology, 16, 643 (1969).
Berke, G., Yagil, G., Ginsburg, H., and Feldman, M., Immunology, 17, 723 (1969).
Cohen, I. R., Stavy, L., and Feldman, M. J., J. Exp. Med., 132, 1055 (1970).
Hirschhorn, K., Nat. Acad. Sci., Nat. Res. Council, 177 (1965).
Cohen, I. R., and Feldman, M., Cell. Immunol., 1, 521 (1971).
Clark, W. R., Berke, G., Feldman, M., and Sarid, S., Immunochemistry (in the press).
Perlmann, P., and Nilsson, H., Science, 168, 112 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
STAVY, L., TREVES, A. & FELDMAN, M. Effect of Concanavalin A on Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity. Nature 232, 56–58 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/232056a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/232056a0
This article is cited by
-
Lupin and Other Potentially Cross-Reactive Allergens in Peanut Allergy
Current Allergy and Asthma Reports (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.