Abstract
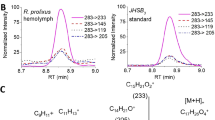
SINCE Karlson1 isolated α-ecdysone from silkworm pupae, other workers have isolated and identified three more ecdysones—β-ecdysone (crustecdysone)2, 26-hydroxy-β-ecdysone3 and 2-deoxy-β-ecdysone4—in extracts of insects and crustaceans. Additional types of ecdysones will probably be described when other species of arthropods are closely examined, as indicated by the work of Burdette and Bullock5 on silkworm pupae. The presence in one organism of several different ecdysones, differing only slightly in structure and in biological activity, has proved enigmatic. It has been suggested that these compounds are all intermediates in a single ecdysone synthesis degradation scheme6, and Horn et al.7 have suggested that α-ecdysone is the precursor of β-ecdysone (crustecdysone). We now present evidence that this contention is indeed correct; specifically, that both crustaceans and insects are able to convert α-ecdysone to β-ecdysone.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karlson, P., in Vitamins and Hormones (edit. by Harris, R. S., Marrian, G. F., and Thimann, K. V.), 14, 227 (Academic Press, 1956).
Hampshire, F., and Horn, D. H. S., Chem. Commun., 37 (1966).
Thompson, M. J., Kaplanis, J. N., Robbins, W. E., and Yamamoto, R. T., Chem. Commun., 650 (1967).
Galbraith, M. N., Horn, D. H. S., Middleton, E. J., and Hackney, R. J., Chem. Commun., 83 (1968).
Burdette, W. J., and Bullock, M. W., Science, 140, 1311 (1963).
Kaplanis, J. N., Thompson, M. J., Yamamoto, R. T., Robbins, W. E., and Louloudes, S. J., Steroids, 8, 605 (1966).
Horn, D. H. S., Middleton, E. J., Wunderlich, J. A., and Hampshire, F., Chem. Commun., 339 (1966).
Hüppi, G., and Siddall, J. B., Tetrahedron Lett., 1113 (1968).
Ohtaki, T., Milkman, R. D., and Williams, C. M., Biol. Bull., 135, 322 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KING, D., SIDDALL, J. Conversion of α-Ecdysone to β-Ecdysone by Crustaceans and Insects. Nature 221, 955–956 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1038/221955a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/221955a0
This article is cited by
-
Haemolymph ecdysteroids level following the injection of ecdysone or ecdysterone; its relation with tegument and midgut response inAeshna cyanea (Insecta, Odonata)
Experientia (1980)
-
The morphological response of Kc-H cells to ecdysteroids: Hormonal specificity
Wilhelm Roux's Archives of Developmental Biology (1980)
-
Ecdysteroids inLimulus larvae
Experientia (1979)
-
In vitro secretion of ecdysteroids by Y-organs and lack of secretion by mandibular organs of the crayfish following molt induction
Journal of Comparative Physiology ? B (1979)
-
Biosynthesis ofα- andβ-ecdysone by the CrayfishOrconectes limosus in vivo and by its Y-Organs in vitro
Experientia (1976)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.