Abstract
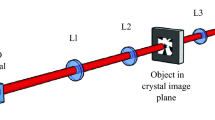
A TECHNIQUE has been developed for observing monochromatic Cathodoluminescence from semiconductors in the scanning electron microscope, enabling optical micro-analysis of materials to be carried out in a manner analogous to the electron probe X-ray microanalyser. The experimental arrangement is shown in Fig. 1. A three lens system gives a beam of electrons of 30 keV energy focused to a spot of 500 Å diameter at the specimen with a current density between 1 and 100 A cm−2. The specimen, in the form of a thin platelet, is mounted on a small movable liquid nitrogen cold finger, and is cooled to 100° K during observation. The Cathodoluminescence is recorded on one of two channels—a sample of the total emitted light is collected by a quartz light pipe, the signal being fed through a photomultiplier and amplifier to the display system of the microscope, to build up a scanning micrograph. Simultaneously an image of the specimen is focused on to the entrance slit of a prism spectrometer by means of a quartz lens in the vacuum wall of the system. The output signal from the spectrometer may then be fed by means of a second photomultiplier and a preamplifier into the detecting system of the microscope, in place of the signal from the total emitted luminescence, thus enabling a scanning micrograph to be built up from radiation of any desired wavelength. (Alternatively the complete emission spectrum may be observed by feeding the amplifier output on to a chart recorder and driving the spectrometer as in conventional optical spectroscopy.)
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams, P. M., and Yoffe, A. D., Phil. Mag., 18, 555 (1968).
Williams, P. M., and Yoffe, A. D., Radiat. Effects, 1, No. 1, 61 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WILLIAMS, P., YOFFE, A. Monochromatic Cathodoluminescence Image in the Scanning Electron Microscope. Nature 221, 952–953 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1038/221952a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/221952a0
This article is cited by
-
Cathodoluminescence applied to immunofluorescence: Present state and improved technical prospects by prism spectrometer light selection
Histochemistry (1978)
-
Scanning electron microscope studies of local variations in cathodoluminescence in striated ZnS platelets
Journal of Materials Science (1977)
-
Review: Image contrast in the scanning electron microscope
Journal of Materials Science (1970)
-
Scanning electron microscope studies of striations in ZnS
Journal of Materials Science (1970)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.