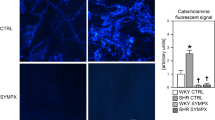
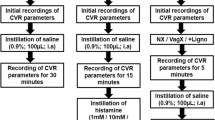
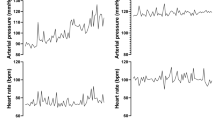
Abstract
HAEMORRHAGE causes an increase of the concentration of renin1–4 and of angiotensin5–8 in blood; when the blood volume of anaesthetized dogs is reduced this rise in concentration of renin4 and of angiotensin7 can be prevented by local anaesthesia of the renal nerves, which suggests that it is brought about by reflex activation of the nerves. The changes of angiotensin concentration correlate not with changes of arterial pressure but with changes of central venous pressure7. Changes of central venous pressure are usually accompanied by changes of pressure in the atria and the pulmonary circulation; these areas are plentifully supplied by vagal afferent fibres and so it seemed possible that the vagus nerve might form the afferent limb of the reflex. We have therefore studied the effect on the generation of angiotensin of interrupting conduction in the vagus nerve.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamilton, A. S., and Collins, D. A., Amer. J. Physiol., 136, 275 (1942).
Dexter, L., Frank, H. A., Haynes, F. W., and Altschule, M. D., J. Clin. Invest., 22, 847 (1943).
Brown, J. J., Davies, D. L., Lever, A. F., Robertson, J. I. S., and Verniory, A., J. Physiol., 182, 649 (1966).
Bunag, R. D., Page, I. H., and McCubbin, J. W., Circulation Res., 19, 851 (1966).
Scornik, O. A., and Paladini, A. C., Amer. J. Physiol., 206, 553 (1964).
Regoli, D., and Vane, J. R., J. Physiol., 183, 513 (1966).
Hodge, R. L., Lowe, R. D., and Vane, J. R., J. Physiol., 185, 613 (1966).
Brown, J. J., Hodge, R. L., Lever, A. F., Lowe, R. D., Robertson, J. I. S., and Vane, J. R., Nature, 215, 853 (1967).
Vane, J. R., Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother., 23, 360 (1964).
Vane, J. R., Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother., 12, 344 (1957).
Regoli, D., and Vane, J. R., Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother., 23, 351 (1964).
Gaddum, J. H., Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother., 8, 321 (1953).
Paton, W. D. M., J. Physiol., 137, 35P (1953).
Armitage, A. K., and Vane, J. R., Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother., 22. 204 (1964).
Ng, K. K. F., and Vane, J. R., Nature, 216, 762 (1967).
Ng, K. K. F., and Vane, J. R., Nature, 218, 144 (1968).
Paintal, A. S., and Rosenberg, M. E., J. Physiol., 189, 6P (1966).
Ferreira, S. H., and Vane, J. R., Nature, 215, 1237 (1967).
Gupta, P. D., Henry, J. P., Sinclair, R., and Von Baumgarten, R., Amer. J. Physiol., 211, 1429 (1966).
Gauer, O. H., and Henry, J. P., Physiol. Rev., 43, 423 (1963).
Baisset, A., and Montastruc, P., J. Physiol. (Paris), 49, 33 (1957).
Share, L., and Levy, M. N., Amer. J. Physiol., 210, 157 (1966).
Share, L., and Levy, M. N., Amer. J. Physiol., 203, 425 (1962).
Bartter, F. C., and Gann, D. S., Circulation, 21, 1016 (1960).
Cort, J. H., and Liechardus, B., Physiol. Bohemoslov., 12, 300 (1963).
Atkins, E. L., and Pearce, J. W., Canad. J. Biochem. Physiol., 37, 91 (1959).
Gilmore, J. P., and Weisfeldt, M. L., Circulation Res., 17, 144 (1965).
Hodge, R. L., Lowe, R. D., and Vane, J. R., Nature, 211, 491 (1966).
Share, L., Amer. J. Med., 42, 701 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HODGE, R., LOWE, R., NG, K. et al. Role of the Vagus Nerve in the Control of the Concentration of Angiotensin II in the Circulation. Nature 221, 177–179 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1038/221177a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/221177a0
This article is cited by
-
Action of parasympathetic agents on renin secretionin vitro
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (1984)
-
Renin release after furosemide and ethacrynic acid in man
Klinische Wochenschrift (1981)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.