Abstract
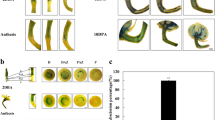
THE plant hormone abscisic acid has been shown to promote abscission and dormancy, to inhibit cell elongation and to be involved in several hormone mediated plant responses1,2. The action of this hormone may involve the inhibition of specific mRNA synthesis3 or more generally the inhibition of DNA synthesis4. The results reported here describe the striking effects of abscisic acid on the growth and morphogenesis of Lemna polyrhiza. The offshoot primordia of this species usually develop as vegetative fronds, but in some conditions the ontogenetic growth pattern is modified in such a way that specialized resting fronds, turions, are produced. These are morphologically and physiologically quite different from the normal vegetative fronds, and are important in enabling the plant to overwinter in a dormant state5. Turion formation has been suggested to occur in environmental conditions which maintain the photosynthetic rate above that necessary to sustain growth and respiration5,6.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohkuma, K., Lyon, J. L., Addicott, F. T., and Smith, O. E., Science, 142, 1592 (1963).
Aspinall, D., Paleg, E. G., and Addicott, F. T., Austral. J. Biol. Sci., 20, 869 (1967).
Villiers, T. A., Planta, 82, 342 (1968).
van Overbeek, J., Loeffler, J. E., and Mason, M. I. R., Science, 156, 1497 (1967).
Jacobs, D. L., Ecol. Monog., 17, 438 (1947).
Henssen, A., Flora, 141, 523 (1954).
Eagles, C. F., and Wareing, P. F., Nature, 199, 874 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
STEWART, G. Abscisic Acid and Morphogenesis in Lemna polyrhiza L.. Nature 221, 61–62 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1038/221061a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/221061a0
This article is cited by
-
Accumulation of starch in duckweeds (Lemnaceae), potential energy plants
Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants (2021)
-
Turion formation and behaviour inSpirodela polyrhiza at two levels of phosphate supply
Biologia Plantarum (1986)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.