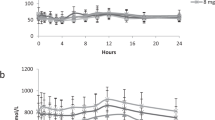
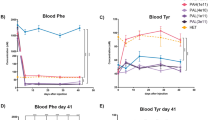
Abstract
THE essential role of vitamin B6 (used as a group name to include pyridoxine, pyridoxal and pyridoxamine) in maintaining the proper function of the central nervous system has been established1. Mental retardation, hyperirritability, and convulsive seizures are manifestations of deficient vitamin B6 metabolism. The similarity of the clinical syndrome of phenylketonuria suggests some malfunction of vitamin B6. Results of our studies on experimental phenylketonuria in rats indicate that inhibition of B6 function contributes to the pathogenesis of phenylketonuria.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coursin, D. B., Vitam. Horm., 22, 755 (1964).
Loo, Y. H., and Ritman, P., Nature, 203, 1237 (1964).
Yuwiler, A., and Louttit, R. T., Science, 134, 831 (1961).
Loo, Y. H., Diller, E., and Owen, jun, J. E., Nature, 194, 1286 (1962).
Polidora, V. J., Boggs, D. E., and Waisman, H. A., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 113, 817(1963).
Umbreit, W. W., and Waddell, J. G., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 70, 293 (1949).
Fisher, R. A., and Yates, F., Statistical Tables for Biological, Agricultural, and Medical Research, sixth ed. (Hafner Publishing Co., New York, 1963).
György, P., Biochem. J., 29, 741 (1935).
Birch, T. W., György, P., and Harris, L. J., Biochem. J., 29, 2830 (1935).
Lovenberg, W., Weissbach, H., and Udenfriend, S., J. Biol. Chem., 237, 89 (1962).
Rabinowitz, J. C., Snell, E. E., J. Biol. Chem., 176, 1157 (1948).
Jepson, J. B., Lovenberg, W., Zaltzman, P., Oates, J. A., Sjoerdsma, A., and Udenfriend, S., Biochem. J., 74, 5P (1960).
Diller, E. R., Kory, M., and Harvey, O. A., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 108, 637 (1961).
Pilgrim, F. J., Zabarenke, L. M., and Patton, R. A., J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol., 44, 26 (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HOONG LOO, Y., RITMAN, P. Phenylketonuria and Vitamin B6 Function. Nature 213, 914–916 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/213914a0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/213914a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.