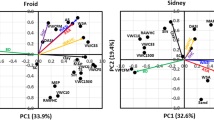
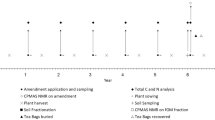
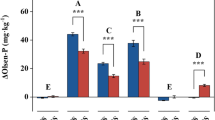
Abstract
NUMEROUS tests have been proposed for determining the “available” nitrogen in soils, but although they have proved successful under some conditions, they have not generally been reliable for predicting field crop response1–3. Most of these methods are based on the estimation of nitrogen which can be readily hydrolysed by dilute acids1 or mineralized by incubation over short periods of time3. It seems quite probable that nitrogen left in more resistant fractions of soil organic matter may also play a supporting part in supplying nitrogen that can be used by plants. Recent research at this Station indicates that more vigorous acid hydrolysis and extraction of soil releases considerable nitrogen from resistant organic complexes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Purvis, E. R., and Leo, M. W. M., Agric. Food Chem., 9, 15 (1961).
Richard, T. A., Attoe, O. J., Moskal, S., and Truog, E., Trans. Intern. Congr. Soil Sci. Seventh Congr., 2, 28 (1960).
Stanford, G., and Hanway, J., Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc., 19, 74 (1955).
Bremner, J. M., Methods of Analysis, Amer. Soc. Agron., 9, 1249 (1965).
Tinsley, J., Trans. Intern. Congr. Soil Sci., Fourth Congr., 1, 161 (1950).
Quinn, J. G., and Salomon, M., Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc., 28, 456 (1964).
Salomon, M., Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc., 26, 54 (1962).
Salomon, M., Nature, 200, 500 (1963).
Felbeck, jun., G. T., Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc., 29, 48 (1965).
Stevenson, F. J., Soil Sci., 83, 113 (1957).
Dubach, P., and Mehta, Soils and Fert., 26, 293 (1963).
Bremner, J. M., J. Agric. Sci., 39, 183 (1949).
Cheng, H. H., and Kurtz, L. T., Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc., 27, 312 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
QUINN, J., SALOMON, M. Hydrolysis of Soil Nitrogen by Strong Acids. Nature 211, 664–665 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1038/211664a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/211664a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.