Abstract
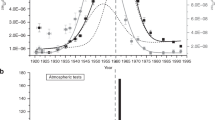
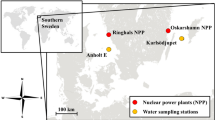
THE significance of radionuclides in organisms of marine and fresh water environments has been discussed by Seymour1, Krumholz2, and many others3. Samples of marine animals from the western central Pacific Ocean have been found to accumulate fission products, such as cerium-144 and zirconium-95. Lowman et al.4 have pointed out that induced isotopes of the essential trace elements, such as manganese-54, iron-55, cobalt-60 and zinc-65, form a large part of the total radioactivity present in Pacific plankton and fishes. The passage of radionuclides from the primary producers, various attached plants and phyto-plankton, through grazing animals to larger predators, presents many important problems5. Laboratory experiments have recently shown that algae accumulate appreciable levels of radionuclides from radiation-contaminated waters6,7. Long-lived nuclides impounded in stationary bodies of water are probably available for the rest of their physical half-lives for incorporation into aquatic flora and fauna. The long-range effects on life in natural water can only be surmised.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seymour, A., in Radioactive Fallout from Nuclear Weapons Tests, A.E.C., 1961 Conf. Germantown, Md., TID 7632 (Office Tech. Services, 1962).
Krumholz, L. A., in Radioactive Fallout from Nuclear Weapons Tests, A. E.C., 1961 Conf. Germantown, Md., TID 7632 (Office Tech. Services, 1962).
Klement, A. W., and Wallen, I. E., A Selected List of References on Marine and Aquatic Radiobiology (U.S. Atomic Energy Comm., Washington, D.C., 1960).
Lowman, F. G., Polumbo, R. F., and South, D. J., U.S. Atomic Energy Comm. Rep. UWFL-51 (Office Tech. Services, U.S. Dept. Commerce, 1957).
Nat. Acad. Sci. Rep. Committee on Effects of Atomic Radiation on Oceanography and Fisheries, Pub. 551 (Washington, D.C., 1957).
Thomas, W. H., Lear, D. W., and Haxo, F. T., Limnol. and Oceanogr. Supp., 7, 66 (1962).
Rice, T. R., and Willis, V. M., Limnol. and Oceanogr., 4, 277 (1959).
U.S. Atomic Energy Comm., Health and Safety Lab. Fallout Program, Quart. Summary Rep. (New York, October 1, 1962).
Gustafson, P. F., Brar, S. S., and Mishra, V. C., Nature, 195, 557 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BURKHOLDER, P. Radioactivity in Some Aquatic Plants. Nature 198, 601–603 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/198601a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/198601a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.