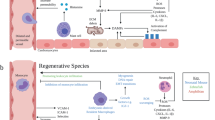
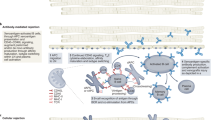
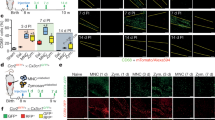
Abstract
RECENT observation of the occurrence in human beings of auto-antibodies specific to heart tissue has given support to the hypothesis of an auto-immune ætiology in rheumatic fever, following myocardial infarction and postcardiotomy state1,2. In the rabbit, heart-specific antibodies have been produced readily against heterologous heart tissue and much less readily against homologous heart tissue3–5. While there is good evidence from clinical and experimental sources of the existence of antiheart antibodies whether from autologous, homologous or heterologous stimuli, there is considerable confusion as to the part they play in cytotoxic action on the heart. If antiheart antibodies are cytotoxic then they could readily influence developing embryonic heart tissue to produce either arrested growth with persistent anomalies or death. The possibility that such an immune (auto-immune) mechanism may play a part in the development of congenital heart disease seemed worthy of investigation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaplan, M. H., Ann. New York Acad. Sci., 86, 974 (1960).
Gery, I., Davies, A. M., and Ehrenfield, E. N., Lancet, i, 471 (1960).
Gery, I., and Davies, A. M., J. Immunol., 87, 351 (1961).
Gery, I., and Davies, A. M., J. Immunol., 87, 357 (1961).
Kaplan, M. H., and Meyeserian, M., J. Immunol., 88, 450 (1961).
Ouchterlony, O., Acta Path. et microbiol. scand., 26, 507 (1949).
Gluecksohn-Waelsch, S., Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol., 19, 41 (1954).
Gluecksohn-Waelsch, S., J. Embryol. Exp. Morph., 5, 83 (1957).
Ebert, J. D., J. Exp. Zool., 115, 351 (1950).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CAWLEY, L., RINER, A. & HOUSER, C. Development of the Fœtus in Female Rats injected with Homologous Heart Tissue. Nature 197, 1307–1309 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/1971307b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1971307b0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.