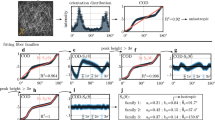
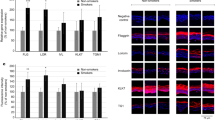
Abstract
ELASTIN, a fibrous protein invariably associated with collagen1,2, has been quantitatively measured in a variety of mammalian tissues3,4. The amino-acid composition of elastin prepared from various animal sources including aorta5, lung6 and ligamentum nuchæ7 has been reported and the elastin content of human dermis has been determined8,9. The purpose of this work was to determine tho amino-acid composition of human dermal elastin and compare it with that of the elastin-like proteins found in increased amounts in chronically sun-damaged skin (actinic elastosis) and pseudoxanthoma elasticum8.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
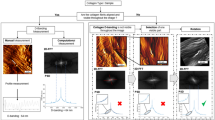
References
Hall, D. A., Keech, M. K., Reid, R., Tunbridge, R. E., and Wood, H. J., J. Gerontol., 10, 388 (1955).
Lansing, A. I., in The Arterial Watt, edit. by Lansing, A. I., 186 (Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, 1959).
Lowry, O. H., Gilligan, D. R., and Katersky, E. H., J. Biol. Chem., 139, 795 (1941).
Neuman, R. E., and Logan, M. A., J. Biol. Chem., 186, 549 (1950).
Lansing, A. I., Roberts, E., Ramasarma, G. B., Rosenthal, T. B., and Alex, M., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 76, 714 (1951).
Hospelhorn, V. D., and Fitzpatrick, M. J., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm., 6, 191 (1961).
Partridge, S. M., and Davis, H. F., Biochem. J., 61, 21 (1955).
Smith, jun., J. G., Davidson, E. A., and Clark, R. D., Nature, 195, 716 (1962).
Weinstein, G. D., and Boucek, R. J., J. Invest. Derm., 35, 227 (1960).
Loewi, G., Glynn, L. E., and Dorling, J. L., J. Path. Bact., 80, 1 (1960).
Smith, jun., J. G., Davidson, E. A., Sams, jun., W. M., and Clark, R. D., J. Invest. Derm., 39, 347 (1962).
Smith, jun., J. G., Sams, jun., W. M., Davidson, E. A., and Clark, R. D., Arch. Derm., 86, 741 (1962).
Neuman, R. E., and Logan, M. A., J. Biol. Chem., 184, 299 (1950).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SMITH, J., DAVIDSON, E. & HILL, R. Composition of Normal and Pathological Cutaneous Elastin. Nature 197, 1108–1109 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/1971108b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1971108b0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.