Abstract
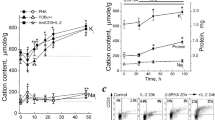
RECENT publications1,2 reporting the induction of leukæmia in mice by cell-free extracts have reawakened general interest in the role of viruses as oncogenic agents and, as a corollary, in the metabolic alterations induced by these agents. It has been shown in this laboratory that alterations in host cell metabolism induced by virus can be detected very soon after infection3. The current investigation was undertaken to see if analogous effects could be observed in vivo using one of the viruses inducing tumours. The agent investigated here was that described by Friend2 as producing a Leukæmia in mice, characterized by splenomegaly and an accumulation in the spleen of stem cells. The basic experiments were performed as follows: 150 mice were infected i.v. with 0.2 ml. of a cell-free filtrate from spleens of mice carrying the infection. 150 control mice received the same amount of cell-free filtrate prepared from normal spleen. Beginning the day after inoculation of the virus, and at the intervals thereafter indicated in Fig. 1, six infected and six control mice were selected at random and given intraperitoneal injection of 5 µc. of phosphorus-32. 3 hr. later the spleens of these animals were removed, weighed, dried in pre-weighed planchets, reweighed, the radioactivity determined, and expressed as c.p.m./mgm. dry tissue. The averaged wet-weights of the spleens from a typical experiment as well as the averaged c.p.m./mgm. dry spleen are given in Fig. 1. As part of the same experiment, on the fifth day some of the control and the infected mice received 300 r. of total body X-irradiation. The results for weight and radioactivity of the spleens of these mice examined on subsequent days are also included in Fig. 1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gross, L., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 76, 27 (1951).
Friend, C., J. Exp. Med., 105, 307 (1957).
Levy, H. B., and Snellbaker, L. F., J. Inf. Dis., 98, 270 (1956). Levy, H. B., and Baron, S., ibid., 100, 109 (1957). Levy, H. B., Rowe, W. P., Snellbaker, L. F., and Hartley, J. W., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 96, 732 (1957).
Reinhard, E. H., Moore, C. V., Bierbaum, O. S., and Moore, S., J. Lab. Clin. Med., 31, 107 (1946).
McCain Lampkin, J., and Potter, M., J. Nat. Canc. Inst., 20, 1091 (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LEVY, H., BRODSKY, I. Metabolic Alteration in Leukæmia induced by a Virus. Nature 182, 1379–1380 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1038/1821379a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1821379a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.