Abstract
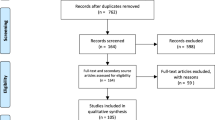
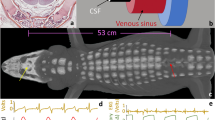
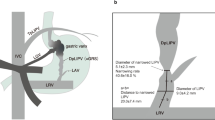
EXAMINATION of dissections and casts of the venous system of twenty-five specimens of the common seal has confirmed, in the main, the findings of previous workers1. In addition, the casts revealed the existence of a large vein lying in the spinal canal external to the dura mater. In the lumbar and thoracic regions this extradural vein is single and lies dorsal to the cord; it receives three major tributaries from each renal plexus, and also communicates with almost every segmental vein of the trunk and with the vena azygos. In the cervical region it divides into two smaller veins which lie one on each side of the cord, with numerous anastomosing channels passing between them. These two veins unite deep to the posterior arch of the atlas, and the sinus thus formed communicates with the intracranial sinuses by two veins, each of which passes through the corresponding condylar canal.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burow, A., Müller's Arch. Anat., Physiol., wiss. Med., 230 (1838). Murie, J., Trans. Zool. Soc. Lond., 8, 501 (1874). Burne, R. H., Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond., 1, 385 (1910).
Finer, B., Anaesthesia (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HARRISON, R., TOMLINSON, J. & BERNSTEIN, L. The Caval Sphincter in Phoca vitulina L.. Nature 173, 86–87 (1954). https://doi.org/10.1038/173086b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/173086b0
This article is cited by
-
Glomera im Supracardialraum des Seehundes (Phoca vitulina L.)
Zeitschrift f�r Zellforschung und Mikroskopische Anatomie (1969)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.