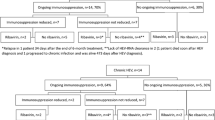
Summary:
We recently reported an increased incidence of cirrhosis in hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected stem cell transplant (SCT) recipients. Here, we describe our experience in the treatment of these patients, which has been, to date, poorly reported in the literature. Among 99 HCV-infected HCT recipients, 36 had HCV-related liver lesions on biopsy requiring therapy. Owing to HCV treatment contraindications, only 61% of patients (22/36) could be treated. In all, 12 patients received more than one course of anti-HCV treatment if they had HCV RNA still detectable after the first course of treatment and no treatment contraindications. Combined therapy (pegylated interferon (IFN): n=9, or standard IFN: n=9, in combination with ribavirin) led to sustained virological response in 4/18 (20%) patients as compared to 2/20 (10%) in patients who received IFN alone. Hematological toxicity was more frequent with combined therapy. While anemia responded to erythropoietin and/or dose modification, thrombocytopenia usually led to treatment interruption (n=3). This study thus highlights the efficacy of combined therapy and emphasizes the fact that the undue safety concerns are not a problem when treating this particular population.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strasser SI, Myerson D, Spurgeon CL et al. Hepatitis C virus infection and bone marrow transplantation: a cohort study with 10-year follow-up. Hepatology 1999; 29: 1893–1899.
Locasciulli A, Testa M, Valsecchi MG et al. The role of hepatitis C and B virus infections as risk factors for severe liver complications following allogeneic BMT: a prospective study by the Infectious Disease Working Party of the European Blood and Marrow Transplantation Group. Transplantation 1999; 68: 1486–1491.
Peffault de Latour R, Levy V, Asselah T et al. Long-term outcome of hepatitis C infection after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 2004; 103: 1618–1624.
Poynard T, Marcellin P, Lee SS et al. Randomised trial of interferon alpha2b plus ribavirin for 48 weeks or for 24 weeks versus interferon alpha2b plus placebo for 48 weeks for treatment of chronic infection with hepatitis C virus. International Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group (IHIT). Lancet 1998; 352: 1426–1432.
Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC et al. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet 2001; 358: 958–965.
Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 975–982.
Hadziyannis SJ, Sette Jr H, Morgan TR et al. Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med 2004; 140: 346–355.
Giardini C, Galimberti M, Lucarelli G et al. Alpha-interferon treatment of chronic hepatitis C after bone marrow transplantation for homozygous beta-thalassemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 20: 767–772.
Maury S, Mary JY, Rabian C et al. Prolonged immune deficiency following allogeneic stem cell transplantation: risk factors and complications in adult patients. Br J Haematol 2001; 115: 630–641.
Bittencourt H, Rocha V, Chevret S et al. Association of CD34 cell dose with hematopoietic recovery, infections, and other outcomes after HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplantation. Blood 2002; 99: 2726–2733.
Perez-Olmeda M, Soriano V, Asensi V et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis C in HIV-infected patients with interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 2003; 19: 1083–1089.
Dumortier J, Scoazec JY, Chevallier P, Boillot O . Treatment of recurrent hepatitis C after liver transplantation: a pilot study of peginterferon alfa-2b and ribavirin combination. J Hepatol 2004; 40: 669–674.
Schirren CA, Zachoval R, Gerlach JT et al. Antiviral treatment of recurrent hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection after liver transplantation: association of a strong, multispecific, and long-lasting CD4+ T cell response with HCV-elimination. J Hepatol 2003; 39: 397–404.
Ljungman P, Andersson J, Aschan J et al. Oral ribavirin for prevention of severe liver disease caused by hepatitis C virus during allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Clin Infect Dis 1996; 23: 167–169.
Ljungman P, Gomez-Garcia V, Ferrant A et al. Long-term follow-up of hepatitis C virus-infected patients after stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33 (Suppl.): S30 (abstract).
Ivantes CA, Amarante H, Ioshii SO, Pasquini R . Hepatitis C virus in long-term bone marrow transplant survivors. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 1181–1185.
Marcellin P, Levy S, Erlinger S . Therapy of hepatitis C: patients with normal aminotransferase levels. Hepatology 1997; 26 (3 Suppl. 1): 133S–136S.
Torriani FJ, Rodriguez-Torres M, Rockstroh JK et al. Peginterferon Alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection in HIV-infected patients. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 438–450.
Chung RT, Andersen J, Volberding P et al. Peginterferon Alfa-2a plus ribavirin versus interferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C in HIV-coinfected persons. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 451–459.
Carrat F, Bani-Sadr F, Pol S et al. Pegylated interferon alfa-2b vs standard interferon alfa-2b, plus ribavirin, for chronic hepatitis C in HIV-infected patients: a randomized controlled trial. Jama 2004; 292: 2839–2848.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peffault de Latour, R., Asselah, T., Lévy, V. et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus in allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant 36, 709–713 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705120
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705120
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Treatment of hepatitis C in a pediatric patient using simeprevir and sofosbuvir immediately after an umbilical cord blood transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2016)
-
Long-term follow-up of HCV-infected hematopoietic SCT patients and effects of antiviral therapy
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2012)
-
HCV and Chemotherapy: Does Infection Change Management?
Current Hepatitis Reports (2012)
-
References
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2009)