Summary:
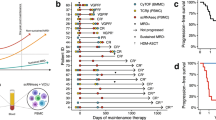
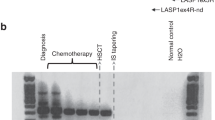
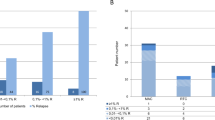
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) is an effective and potentially curative treatment for some cases of multiple myeloma (MM). The curative efficacy of allo-SCT may be largely attributed to its immunological activity, the graft-versus-myeloma (GVM) effect. To evaluate the kinetics of residual myeloma cells, we analyzed the follow-up bone marrow samples of three MM patients by means of a real-time molecular assay. We identified a consistent correlation between onset of graft-versus-host disease and disease response. These data suggest that real-time molecular follow-up can be used to monitor the GVM effect and that it can be employed in the clinical setting to tailor post transplant immunomodulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gahrton G, Svensson H, Cavo M et al. Progress in allogenic bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma: a comparison between transplants performed 1983–93 and 1994–98 at European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation centres. Br J Haematol 2001; 113: 209–216.
Corradini P, Voena C, Tarella C et al. Molecular and clinical remissions in multiple myeloma: role of autologous and allogeneic transplantation of hematopoietic cells. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 208–215.
van Rhee F, Lin F, Cullis JO et al. Relapse of chronic myelogenous leukemia after allogeneic bone marrow transplant: the case for giving donor leukocyte transfusions before the onset of hematologic relapse. Blood 1994; 83: 3377–3383.
Voena C, Locatelli G, Castellino C et al. Qualitative and quantitative PCR detection of the residual myeloma cell contamination after positive selection of CD34+ cells with small and large scale Miltenyi cell sorting system. Br J Haematol 2002; 117: 642–645.
Bladé J, Samson D, Reece D et al. Criteria for evaluating disease response and progression in patients with multiple myeloma treated by high-dose therapy and haemopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol 1998; 102: 1115–1123.
Voena C, Ladetto M, Astolfi M et al. A novel nested-PCR strategy for the detection of rearranged immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes in B cell tumors. Leukemia 1997; 11: 1793–1798.
Corradini P, Voena C, Astolfi M et al. High-dose sequential chemoradiotherapy in multiple myeloma: residual tumor cells are detectable in bone marrow and peripheral blood cell harvests and after autografting. Blood 1995; 85: 1596–1602.
Martinelli G, Terragna C, Zamagni E et al. Polymerase chain reaction-based detection of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma patients receiving allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 2000; 85: 930–934.
Metha J, Singhal S . Graft-versus-myeloma. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 22: 835–843.
Appelbaum F . Haematopoietic cell transplantation as immunotherapy. Nature 2001; 411: 385–389.
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported in part by grants from AIRC, Fondazione Michelangelo and Compagnia di San Paolo.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Claudia Voena and Mauro Malnati equally contributed to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voena, C., Malnati, M., Majolino, I. et al. Detection of minimal residual disease by real-time PCR can be used as a surrogate marker to evaluate the graft-versus-myeloma effect after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 32, 791–793 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704207
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704207