Abstract
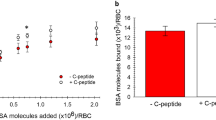
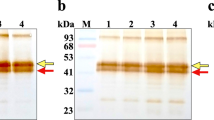
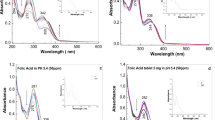
COHN1 has shown that carotene and vitamin A are concentrated in fraction III-O of plasma, which is a lipoprotein. It has been known for some time2 that vitamin A can occur in water-soluble form in the urine of human beings in certain pathological conditions. In such cases protein is invariably present in the urine. It does not follow, however, that urine which contains protein can take up vitamin A when added to it. Adequate explanation of this phenomenon has not been forthcoming. The function of vitamin A in the visual cycle has been very elegantly demonstrated by Wald3. Recently, Morton4 has shown that retinene, which is an important factor in the visual cycle, is vitamin A aldehyde, and he has also shown5 how it can be prepared in the laboratory. It was therefore considered that attempts should be made to prepare a water-soluble compound of vitamin A with plasma protein and study its properties. The present preliminary communication summarizes the results obtained in this Institute.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohn, E. J., Ann. Int. Med., 26, 341 (1947).
Lawrie, N. R., Moore, T., and Rajagopal, K. R., Biochem. J., 35, 825 (1941).
Wald, G., J. Gen. Physiol., 19, 351 (1935).
Morton, R. A., Nature, 153, 69 (1944).
Morton, R. A., et al., Biochem. J., 42, 516 (1948).
Cohn et al., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 68, 459 (1946).
Edsall, J. T., in “Advances in Protein Chemistry”, 3, 443 (Academic Press, Inc., New York, 1947).
Argenson, M. G., Bull. Soc. Chim., 27, 1000 (1902).
Morton, R. A., “Vitamins”, 184 (Adam Hilger, London, 1942). Oncley, J. L., Gurd, F. R. N., and Melin, M., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 72, 461 (1950).
Moore, T., and Sharman, I. M., Brit. J. Nut., 5, 126 (1951). Lindqvist, T., “Studien Über das Vitamin A beim Menschen”, 151 (Uppsala, 1938).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
RAJAGOPAL, K., DATTA, P. Reaction of Vitamin A Aldehyde with Plasma Albumin. Nature 170, 370–371 (1952). https://doi.org/10.1038/170370a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/170370a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.