Abstract
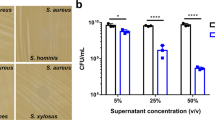
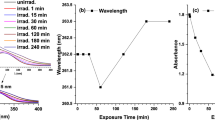
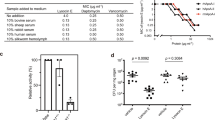
IT has been demonstrated previously1–3 that contact between resting sensitive staphylococci and penicillin results in a small firmly-bound uptake of the drug by the bacteria. When washed suspensions of Staphylococcus aureus with radioactive penicillin attached were ruptured by shaking with fine glass beads, subsequent radiometric assay of the deposit and supernatant after centrifuging suggested that the penicillin had been concentrated within the cytoplasm of the cell4. However, when unlabelled organisms were disrupted by the same method, it was found in a large number of experiments that while very little, if any, of the penicillin-binding capacity of the intact cell could be detected in the non-dialysable fraction of the cytoplasm, a larger percentage was frequently found in the cell-wall fraction than could be accounted for by the few intact bacteria present.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper, P. D., and Rowley, D., Nature, 163, 480 (1949).
Rowley, D., Cooper, P. D., Roberts, P. W., and Lester Smith, E., Biochem. J., 46, 157 (1950).
Maas, E. A., and Johnson, M. J., J. Bact., 57, 415 (1949).
Cooper, P. D., Rowley, D., and Dawson, I. M., Nature, 164, 842 (1949).
Few, A. V., Cooper, P. D., and Rowley, D., Biochem. J. (in the press).
Mitchell, P., and Moyle, J., Nature, 166, 218 (1950).
McQuillen, K., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 6, 534 (1950–51).
Gale, E. F., and Taylor, E. S., J. Gen. Microbiol., 1, 314 (1947).
Gale, E. F., and Rodwell, A. W., J. Gen. Microbiol., 3, 127 (1949).
Mitchell, P., and Moyle, J., J. Gen. Microbiol., 5, 421 (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
FEW, A., COOPER, P. & ROWLEY, D. Reaction of Penicillin with the Staphylococcal Cell Wall. Nature 169, 283–284 (1952). https://doi.org/10.1038/169283a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/169283a0
This article is cited by
-
Ver�nderungen des elektrokinetischen Potentials bei penicillinresistenten und penicillinempfindlichen Staphylokokken nach der Bearbeitung mit Fermenten
Archiv f�r Mikrobiologie (1957)
-
Ver�nderungen des elektrokinetischen Potentials bei der Adaptation der Staphylokokken an Penicillin
Archiv f�r Mikrobiologie (1956)
-
Die Wirkung von Antibiotika aufParamaecium caudatum
Protoplasma (1955)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.