Abstract
Aim:
This study was performed to determine the effects of glutamine enriched total parenteral nutrition (TPN) on the patients with acute pancreatitis (AP).
Method:
Forty patients with AP, who had Ranson's score between 2 and 4 received either standard TPN (control group) or TPN with glutamine (treatment group). The patients in the treatment group received TPN containing 0.3 g/kg/days glutamine. At the end of the study, patients were evaluated for nutritional and inflammatory parameters, length of TPN and length of hospital stay.
Results:
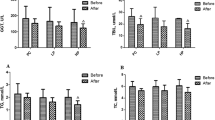
The length of TPN applications were 10.5±3.6 days and 11.6±2.5 days, and the length of hospital stays were 14.2±4.4 and 16.4±3.9 days for the treatment and control groups (NS), and the complication rates in the treatment and control groups were 10 and 40%, respectively (P<0.05). The transferrin level increased by 11.7% in the group that received glutamine-enriched TPN (P<0.05), whereas the transferrin level decreased by 12.1% in the control group (NS). At the end of the study, slight but not significant changes were determined in both groups in fasting blood sugar, albumin, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, total cholesterol concentrations, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activities, leukocytes, CD4, CD8, serum Zn, Ca and P levels compare to the baseline levels (NS). Significant decreases were determined in serum lipase, amylase activities and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in both groups (P<0.05).
Conclusions:
The results of this study have shown that glutamine supplementation to TPN have beneficial effects on the prevention of complications in patients with AP.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Assi S, O'Keefe SJ (2002). Nutrition support during acute pancreatitis. Nutrition 18, 938–943.
Fish J, Sporay G, Beyer K, Jones J, Kihara T, Kennedy A et al. (1997). A prospective randomized study of glutamine-enriched parenteral compared with enteral feeding in postoperative patients. Am J Clin Nutr 65, 977–983.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972). Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18, 499–552.
Fürst P, Pogan K, Stehle P (1997). Glutamine dipeptides in clinical nutrition. Nutrition 13, 731–737.
Griffiths RD, Jones C, Palmer TE (1997). Sixth month outcome of critically ill patients given glutamine-supplemented parenteral nutrition. Nutrition 13, 295–302.
Guillou PJ (1999). Enteral versus parenteral nutrition in acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 13, 345–355.
Hall JC, Heel K, McMauley R (1996). Glutamine. Br J Surg 83, 305–312.
Hardy G, Bovan SJ, Mc Elroy B (1993). Stability of glutamine in parenteral feeding solution. Lancet 342, 186.
Havala T, Shronts E, Cerra F (1989). Nutritional support in pancreatitis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 18, 525–542.
Kalfarentzos FE, Karavias DD, Karatzas TM, Alevizatos BA, Androulakis JA (1991). TPN in severe acute pancreatitis. J Am Coll Nutr 10, 156–162.
Karner J, Roth E, Fürst P (1989). Glutamine containing dipeptides as infusion substrates in the septic state. Surgery 106, 893–900.
Karwowska KA, Dworacki G, Szulc R, Trybus M, Zeromski J (2001). Influence of glutamine enriched parenteral nutrition on nitrogen balance and immunological status in patients undergoing elective aortic anevrysms repair. Nutrition 17, 475–478.
Konstantinides FN, Boehm KA, Cerra FB, Rdamer WJ, Strom MC, Adderly JT et al. (1988). Real time cost-effective method for determining total urinary nitrogen in clinical nitrogen-balance studies. Clin Chem 34, 2518–2520.
Latifi R, McIntoch JK, Dudrick SJ (1991). Nutritional management of acute and chronic pancreatitis. Surg Clin North Am 71, 579–595.
Maroulis J, Kalfarentzos F (2000). Complications of parenteral nutrition at the end of the century. Clin Nutr 19, 295–304.
Marik PE, Zaloga GP (2004). Meta-analysis of parenteral nutrition versus enteral nutrition in patients with acute pancreatitis. BMJ 328, 1407–1413.
McBurney M, Young LS, TR Ziegler, Wilmore DW (1994). A cost-evaluation of glutamine supplemented parenteral nutrition in adult bone marrow transplant patients. J Am Diet Assoc 94, 1263–1266.
McClave SA, Ritchie CS (2000). Artificial nutrition in pancreatic disease: What lessons have we learned from the literature? Clin Nutr 19, 1–6.
McClave SA, Greene LM, Snider HL, Makk LJ, Cheadle WG, Owens NA et al. (1997). Comparison of the safety of early enteral and parenteral nutrition in mild acute pancreatitis. JPEN 21, 14–20.
Meier R, Beglinger C, Layer P, Gullo L, Keim V, Laugier R et al. (2002). ESPEN guidelines on nutrition in acute pancreatitis. Clin Nutr 21, 173–183.
Meier R, Ockenga J, Pertkiewicz M, Pap A, Milinic N, MacFie J (2006). ESPEN guidelines on enteral nutrition: pancreas. Clin Nutr 25, 275–284.
Morlion BJ, Stehle P, Wachtler P, Siedhoff HP, Köller M, König W et al. (1998). TPN with glutamine dipeptide after major abdominal surgery. Ann Surg 227, 303–308.
Neoptolemos JP, Raraty M, Sutton R (1998). Acute pancreatitis: the substantial human and financial costs. Gut 42, 886–891.
Neri A, Mariani F, Cosmo LD, Piccolomini JW, Testa G, Vuolo G (2001). Glutamine supplemented total parenteral nutrition in major abdominal surgery. Nutrition 17, 968–969.
O'Riordain MG, Fearon KC, De Beaux A (1996). Effects of glutamine on immune function in the surgical patient. Nutrition 12, 84–86.
Ockenga J, Borchert K, Rifai K, Manns MP, Bischoff SC (2002). Effect of glutamine enriched total parenteral nutrition in patients with acute pancreatitis. Clin Nutr 21, 409–416.
Oğuz M (1998). Glutamin ve beslenmedeki önemi. T Klin Cerrahi 3, 120–125. (Turkish).
Quamruddin AO, Chadwick RR (2000). Preventing pancreatic infection in acute pancreatitis. J Hospital Infect 44, 245–253.
Scolapio JS, Malhi-Chowla N, Ukleja A (1999). Nutrition supplementation in patients with acute and chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 28, 695–707.
Sitzman JV, Steinborn PA, Zinner MJ (1989). Total parenteral nutrition and alternate energy substartes in treatment of severe acute pancreatitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet 168, 311–317.
Van der Hulst RR, Van Kreel BK, Von Meyenfelt MF, Brummer RJ, Arends JW, Deutz NE (1993). Glutamine and the preservation of gut integrity. Lancet 44, 1363–1365.
Van der Hulst RR, Von Meyenfelt MF, Burman WA (1997). Glutamine and intestinal immune cells in humans. JPEN 21, 310–315.
Yoshida S, Kaibara A, Ishibashi N, Shirouzu K (2001). Glutamine supplementation in cancer patients. Nutrition 17, 766–768.
Ziegler TR, Bye R, Persinger RL (1998). Effects of glutamine supplementation on circulating lymphocytes after bone marrow transplantation: a pilot study. Am J Med Sci 315, 4–10.
Ziegler TR, Leader LM, Jonas CR, Griffiths DP (1997). Adjunctive therapies in nutritional support. Nutrition 13, 64–74.
Ziegler TR, Szeszycki EE, Estivariz CF, Puckett AB, Leader LM (1996). Glutamine: from basic science to clinical application. Nutrition 12, 68–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guarantor: H Şahin.
Contributor: HS was responsible for conception, design, analysis and interpretation of data, and the final approval of the version to be published. SMM helped to coordinate the study, do statistical analysis and write the report. NI helped to coordinate the study, do statistical analysis and write the report. EO helped in drafting the article and revising it critically for important intellectual content.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
şahin, H., Mercanlıgil, S., Inanç, N. et al. Effects of glutamine-enriched total parenteral nutrition on acute pancreatitis. Eur J Clin Nutr 61, 1429–1434 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602664
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602664
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prevalence of glutamine deficiency in ICU patients: a cross-sectional analytical study
Nutrition Journal (2015)
-
Parenteral glutamine supplementation in critical illness: a systematic review
Critical Care (2014)