Abstract
Objective:
To evaluate a simple method that uses only a heart rate monitor to predict total energy expenditure (TEE) and physical activity level (PAL) from 24 h heart rate (HR) measurements.
Design:
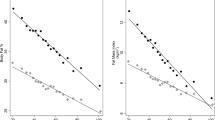
The simple method involved the determination of the physical activity ratio (PAR) from corresponding heart rate ratios (HRR) (ratio of observed to resting HR), from an individualized calibration curve relating activities with known PAR to the HRR. Several curve fits were evaluated for this curve. The PAL was calculated from minute to minute PAR. The TEE was computed as the product of the PAL and the predicted basal metabolic rate (BMR). The accuracy of the simple method was assessed by within-subject comparisons of the simple method versus the oxygen consumption – HR method and a time and motion study.
Setting:
Bangalore City, India.
Subjects:
In all, 17 healthy male subjects between 18 and 44 years were recruited for the study.
Interventions:
None.
Results:
The simple method correlated well with both the reference methods when using a calibration curve that involved the fitting of two straight lines at low and high PAR activities, respectively, to the PAR and HRR data. The mean error in TEE, as a product of BMR and PAL, was about 1%, but with limits of agreement between the methods that were about 20% of the TEE. However, the low mean error could have been due to a canceling of errors in the determination of BMR and PAL.
Conclusions:
The simple method is a relatively cheap, useful technique for evaluating TEE and PAL in resource-poor situations. It may particularly be of use in epidemiological investigations where population estimates of TEE and PAL are required.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Whitt MC, Irwin ML, Swartz AM, Strath SJ et al. (2000). Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32, S498–S516.
Bharathi AV, Sandhya N, Vaz M (2000). The development & characteristics of a physical activity questionnaire for epidemiological studies in urban middle class Indians. Indian J Med Res 111, 95–102.
Bhat DS, Yajnik CS, Sayyad MG, Raut KN, Lubree HG, Rege SS et al. (2005). Body fat measurement in Indian men: comparison of three methods based on a two-compartment model. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 29, 842–848.
Black A (2000). Critical evaluation of energy intake using the Goldberg cut-off for energy intake: basal metabolic rate. A practical guide to its calculation, use and limitations. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24, 1119–1130.
Bland JM, Altman DG (1995). Comparing methods of measurement: why plotting difference against standard is misleading. Lancet 346, 1085–1087.
Ceesay SM, Prentice AM, Day KC, Murgatroyd PR, Goldberg GR, Scott W et al. (1989). The use of heart rate monitoring in the estimation of energy expenditure: a validation study using indirect whole-body calorimetry. Br J Nutr 61, 175–186.
De Abajo S, Larriba R, Marquez S (2001). Validity and reliability of the Yale Physical activity survey in Spanish elderly. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 41, 479–485.
FAO/WHO/UNU (1985). Energy and protein requirements. Report of a joint FAO/WHO/UNU expert consultation. WHO Tech Rep Ser 724, 1–206.
FAO/WHO/UNU (2004). Human energy requirements. Report of a joint FAO/WHO/UNU expert consultation. FAO Food Nutr Tech Rep Ser 1, 92–96.
Ferro-Luzzi A, Petracchi C, Kuriyan R, Kurpad AV (1997). Basal metabolism of weight-stable chronically undernourished men and women: lack of metabolic adaptation and ethnic differences. Am J Clin Nutr 66, 1086–1093.
Haggarty P, Valenci M, McNeill G, Gonzalez NL, Moya SY, Pinelli A et al. (1997). Energy expenditure during work and its interaction with body weight. Br J Nutr 77, 359–373.
Kurpad AV, Kulkarni RN, Sheela ML, Shetty PS (1989a). Thermogenic responses to graded doses of noradrenaline in undernourished Indian male subjects. Br J Nutr 61, 201–208.
Kurpad AV, Kulkarni RN, Shetty PS (1989b). Reduced thermoregulatory thermogenesis in undernutrition. Eur J Clin Nutr 43, 27–33.
Lakka TA, Venalainen JM, Rauramaa R, Salonen R, Tuomilehto J, Salonen JT (1994). Relation of leisure-time physical activity and cardiorespiratory fitness to the risk of acute myocardial infarction in men. N Engl J Med 330, 1549–1554.
Lee IM, Hsieh CC, Paffenbarger Jr RS (1995). Exercise intensity and longevity in men. The Harvard Alumni Health Study. JAMA 273, 1179–1184.
Lof M, Hannestad U, Forsum E (2003). Comparison of commonly used procedures, including the doubly-labelled water technique, in the estimation of total energy expenditure of women with special reference to the significance of body fatness. Br J Nutr 90 (5), 961–968.
Paffenbarger Jr RS, Hyde RT, Wing AL, Lee IM, Jung DL, Kampert JB (1993). The association of changes in physical-activity level and other lifestyle characteristics with mortality among men. N Engl J Med 328, 538–545.
Racette SB, Schoeller DA, Kushner RF (1995). Comparison of heart rate and physical activity recall with doubly labeled water in obese women. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27, 126–133.
Ritz P, Coward WA (1995). Doubly labeled water measurement of total energy expenditure. Diabetes Metab 21, 241–251.
Schoeller DA, Van Santen E (1982). Measurements of energy expenditure in humans by doubly labeled water method. J Appl Physiol 53, 955–959.
Shetty PS, Sheela ML, Murgatroyd PR, Kurpad AV (1987). An open circuit indirect whole body calorimeter for the continuous measurement of energy expenditure of man in the tropics. Indian J Med Res 85, 453–460.
Spurr GB, Prentice AM, Murgatroyd PR, Goldberg GR, Reina JC, Christman NT (1988). Energy expenditure from minute-by-minute heart-rate recording: comparison with indirect calorimetry. Am J Clin Nutr 48, 552–559.
Weirs JBD (1949). New methods for calculating metabolic rate with specific reference to protein metabolism. J Physiol 109, 1–9.
WHO (1998). The World Health Report. Geneva: WHO.
WHO Expert Consultation (2004). Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 363, 157–163.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guarantor: AV Kurpad.
Contributors: AVK was involved in conception of idea, study design and analysis, and in writing the manuscript. RR was involved in study design, carrying out the study, data analysis and writing of manuscript. KNM was involved in carrying out the study and offered technical expertise for carrying out indirect calorimetry. MV was involved in study design, data analysis and writing of manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurpad, A., Raj, R., Maruthy, K. et al. A simple method of measuring total daily energy expenditure and physical activity level from the heart rate in adult men. Eur J Clin Nutr 60, 32–40 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602264
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602264
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Specific appetite, energetic and metabolomics responses to fat overfeeding in resistant-to-bodyweight-gain constitutional thinness
Nutrition & Diabetes (2014)
-
Activity logging using lightweight classification techniques in mobile devices
Personal and Ubiquitous Computing (2013)
-
A new method to estimate energy expenditure from abdominal and rib cage distances
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2011)