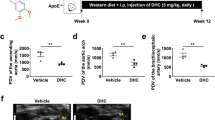
Abstract
Deregulated crosstalk within nuclear receptor/transcription factor family, comprising of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and liver X receptor-α (LXR-α), can give rise to cooperativity between lipid peroxidation and inflammation leading to atherogenic process. The present study addressed to explore the effect of statins and vitamin ‘C’ on transcriptional expression of genes coding for this nuclear receptor/transcription factor family within mononuclear cells revealed for the first time that both mevastatin and vitamin ‘C’ have common action in that they significantly downregulate the expression of PPARs (α, γ) genes and upregulate LXR-α gene expression as compared to the control. The similar phenomenon was observed in mononuclear cells obtained from coronary heart disease (CHD) patients who were receiving atorvastatin treatment (20 mg HS). Further, the observed upregulatory effect of LXR-α gene expression was in conformity with the downregulatory effect of LXR-α on its effector gene matrix metalloproteinase-9. Based on these results, we propose that LXR-α-dependent signaling pathway may be a crucial target for the therapeutic intervention in human CHD, and in addition to statins, vitamin ‘C’ deserves a close scrutiny for the treatment of CHD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyum A (1968): Ficoll–Hypaque method for separating mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 77 (Suppl), 57–62.
Carcamo JM, Pedraza A, Borquez-Ojeda O & Golde DW (2002): Vitamin C suppresses TNF-α induced NF-κB activation by inhibiting I kappa B alpha phosphorylation. Biochemistry 41, 12995–13002.
Centrillo A, Joseph SB, Marathon C, Mangelsdorf DJ & Tontonoz P (2003): Liver X receptor-dependent repression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 10443–10449.
Chomczynski P & Sacchi N (1987): Single step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidium thiocyanate phenol–chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162, 156–159.
Girando L, Inoue M & Hanahan D (2004): An amino-phosphate targets MMP-9-expressing macrophages and angiogenesis to impair cervical carcinogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 114, 623–633.
Hillstrom RJ, Yacapin-Ammons AK & Lynch SM (2003): Vitamin C inhibits lipid oxidation in human HDL. J. Nutr. 133, 3047–3051.
Kaul D (2003): Cholesterol-receptor mediated genomics in health and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 9, 442–449.
Kaul D, Sikand K & Shukla A R (2004): Effects of green tea polyphenols on the genes with atherosclerotic potential. Phytother. Res. 18, 177–179.
Kutuk O & Basaga H (2003): Inflammation meets oxidation: NF-κB as a mediator of initial lesion development in atherosclerosis. Trends Mol. Med. 9, 546–557.
Lechleitner M (2002): Non lipid related effects of statins. J. Clin. Basic Cardiol. 5, 205–208.
Levine GN, Frei B, Koulouris SN, Gerhard MD, Keaney Jr JF & Vita JA (1996): Ascorbic acid reverses endothelial vasomotor dysfunction in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 93, 1107–1113.
Loshak D (2002): Effect of vitamin C on aggregation of human platelets in smokers and nonsmokers. Med. Klin. 97, 263–269.
Marx N, Schonbeck U, Lazar MA, Libby P & Plutzky J (1998): Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activators inhibit gene expression and migration in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Circulation 83, 1097–1103.
Salonen RM, Nyyssonen K, Porkala-Sarataho E, Voutilainen S, Rissanen TH, Tuomainen TP, Valkonen VP, Ristonmaa U, Lakka HM, Vanharanta M, Salonen JT & Poulsen HE (2003): Six-year effect of combined vitamin C and E supplementation on atherosclerotic progression: the Antioxidant Supplementation in Atherosclerosis Prevention (ASAP) Study. Circulation 107, 947–953.
Tontonoz P & Mangelsdorf DJ (2003): Liver X receptor signaling pathways in cardiovascular disease. Mol. Endocrinol. 17, 985–993.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guarantor: D Kaul.
Contributors: D Kaul and MI Baba.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaul, D., Baba, M. Genomic effect of vitamin ‘C’ and statins within human mononuclear cells involved in atherogenic process. Eur J Clin Nutr 59, 978–981 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602203
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602203
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Modulation of LXR-α and the effector genes by Ascorbic acid and Statins in psoriatic keratinocytes
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2014)
-
Human coronary heart disease: importance of blood cellular miR-2909 RNomics
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2014)