Abstract
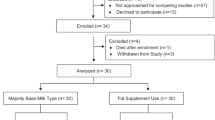
Objective: To investigate the effects of a milk formula supplemented with a α-linolenic acid (ALA) (18:2 n-6/18:3 n-3 ratio near 6/1) on plasma and red blood cell (RBC) fatty acids (FAs) in premature infants and compare with a non supplemented formula (18:2 n-6/18:3 n-3=22/1). Design and subjects: Infants of mothers who elected not to breast-feed were randomly assigned to either a high α linolenic formula (HLF: n=31) group or a low α-linolenic formula (LLF: n=32) control group. Infants fed human milk (HM: n=25) were enrolled concurrently as a reference group. Anthropometric and biological measurements were made after two days (D2) and 15 d (D15) of enteral feeding and at the 37th week (W37) of postconceptual age. In HLF, the 18:3 n-3 content was 1.95% of total FAs (0.77% of total energy) and the 18:2 n-6/18:3 n-3 ratio was near 6/1. In LLF, the 18:3 n-3 content was 0.55% of total FAs (0.22% of total energy) and the 18:2 n-6/18:3 n-3 ratio was 22/1. Results: ALA supplementation had minimal effect on the n-6 series, did not alter the anthropometric data and confirmed the conversion of ALA into docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Throughout the study, it maintained, the RBC membrane DHA values within the confidence interval of those obtained in the HM group. Such was not the case with LLF Conclusion: α-linolenic acid supplementation (from Rapeseed oil and in a 18:2 n-6/18:3 n-3 ratio=6) in premature infant formula can contribute efficiently to the maintenance of the n-3 status in the premature newborns
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Billeaud, C., Bouglé, D., Sarda, P. et al. Effects of preterm infant formula supplementation with α-linolenic acid with a linoleate/α-linolenate ratio of 6: a multicentric study. Eur J Clin Nutr 51, 520–526 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600436
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600436
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effects of dietary PUFA patterns and FADS genotype on breast milk PUFAs in Chinese lactating mothers
Genes & Nutrition (2023)
-
Selenium Deficiency a Factor in Endemic Goiter Persistence in Sub‐Saharan Africa
World Journal of Surgery (2011)
-
The effect of α‐linolenic acid and linoleic acid on the growth and development of formula‐fed infants: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials
Lipids (2005)
-
Preterm infant formula supplementation with α linolenic acid and docosahexaenoic acid
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2003)