Abstract
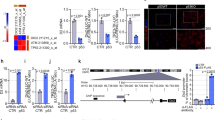
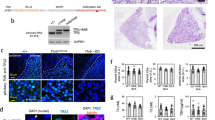
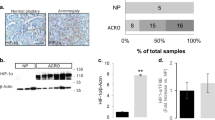
Thyroid hormone receptor-β1 (TRβ1) belongs to the ligand-inducible transcription factor superfamily. We have previously described that stable TRβ1 expression impairs fibroblast proliferation diminishing levels and activity of the main regulators of the G1/S transition. To unmask the underlying molecular mechanism of this action, we have investigated the expression of cyclin D1, E and A2 upon serum stimulation in TRβ1 expressing cells, finding a strong downregulation of their mRNAs, concomitant with low protein levels. The inhibition of the transcriptional activation in response to serum of these cyclins is differently exerted. For cyclin D1, we demonstrate that TRβ1 represses its promoter as a consequence of the downregulation of c-jun levels, diminished AP-1 activation and loss of c-jun recruitment to its binding sites on cyclin D1 promoter. For cyclin E and A2, it is the impairment of the cyclinD/Rb/E2F pathway by TRβ1 that prevents the activation of these two E2F target genes. Indeed, recruitment of E2F-1 to cyclin A2 promoter could not be detected. In summary, we propose that apo-TRβ1 exerts its antiproliferative action through a mechanism that could constitute a model by which other nuclear receptors may control cell division.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrera-Hernandez G, Zhan Q, Wong R, Cheng SY . (1998). Thyroid hormone receptor is a negative regulator in p53-mediated signaling pathways. DNA Cell Biol 17: 743–750.
Benkoussa M, Brand C, Delmotte MH, Formstecher P, Lefebvre P . (2002). Retinoic acid receptors inhibit AP1 activation by regulating extracellular signal-regulated kinase and CBP recruitment to an AP1-responsive promoter. Mol Cell Biol 22: 4522–4534.
Bhat MK, Yu C, Yap N, Zhan Q, Hayashi Y, Seth P et al. (1997). Tumor suppressor p53 is a negative regulator in thyroid hormone receptor signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 272: 28989–28993.
Botz J, Zerfass-Thome K, Spitkovsky D, Delius H, Vogt B, Eilers M et al. (1996). Cell cycle regulation of the murine cyclin E gene depends on an E2F binding site in the promoter. Mol Cell Biol 16: 3401–3409.
Campanero MR, Armstrong MI, Flemington EK . (2000). CpG methylation as a mechanism for the regulation of E2F activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 6481–6486.
Chan IH, Privalsky ML . (2006). Thyroid hormone receptors mutated in liver cancer function as distorted antimorphs. Oncogene 25: 3576–3588.
Chassande O, Fraichard A, Gauthier K, Flamant F, Legrand C, Savatier P et al. (1997). Identification of transcripts initiated from an internal promoter in the c-erbA alpha locus that encode inhibitors of retinoic acid receptor-alpha and triiodothyronine receptor activities. Mol Endocrinol 11: 1278–1290.
Deogracias R, Espliguero G, Iglesias T, Rodriguez-Pena A . (2004). Expression of the neurotrophin receptor trkB is regulated by the cAMP/CREB pathway in neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 26: 470–480.
Furumoto H, Ying H, Chandramouli GV, Zhao L, Walker RL, Meltzer PS et al. (2005). An unliganded thyroid hormone beta receptor activates the cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent kinase/retinoblastoma/E2F pathway and induces pituitary tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Biol 25: 124–135.
Garcia-Silva S, Aranda A . (2004). The thyroid hormone receptor is a suppressor of ras-mediated transcription, proliferation, and transformation. Mol Cell Biol 24: 7514–7523.
Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG . (2000). The coregulator exchange in transcriptional functions of nuclear receptors. Genes Dev 14: 121–141.
Gonzalez-Sancho JM, Garcia V, Bonilla F, Munoz A . (2003). Thyroid hormone receptors/THR genes in human cancer. Cancer Lett 192: 121–132.
Gottlicher M, Heck S, Herrlich P . (1998). Transcriptional cross-talk, the second mode of steroid hormone receptor action. J Mol Med 76: 480–489.
Hashimoto K, Curty FH, Borges PP, Lee CE, Abel ED, Elmquist JK et al. (2001). An unliganded thyroid hormone receptor causes severe neurological dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 3998–4003.
Koenig RJ, Lazar MA, Hodin RA, Brent GA, Larsen PR, Chin WW et al. (1989). Inhibition of thyroid hormone action by a non-hormone binding c-erbA protein generated by alternative mRNA splicing. Nature 337: 659–661.
Krude T, Jackman M, Pines J, Laskey RA . (1997). Cyclin/Cdk-dependent initiation of DNA replication in a human cell-free system. Cell 88: 109–119.
Le Cam L, Polanowska J, Fabbrizio E, Olivier M, Philips A, Ng Eaton E et al. (1999). Timing of cyclin E gene expression depends on the regulated association of a bipartite repressor element with a novel E2F complex. EMBO J 18: 1878–1890.
Lin HM, Zhao L, Cheng SY . (2002). Cyclin D1 Is a ligand-independent co-repressor for thyroid hormone receptors. J Biol Chem 277: 28733–28741.
Nygard M, Wahlstrom GM, Gustafsson MV, Tokumoto YM, Bondesson M . (2003). Hormone-dependent repression of the E2F-1 gene by thyroid hormone receptors. Mol Endocrinol 17: 79–92.
O'Shea PJ, Williams GR . (2002). Insight into the physiological actions of thyroid hormone receptors from genetically modified mice. J Endocrinol 175: 553–570.
Pfaffl MW . (2001). A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29: 45.
Pfahl M . (1993). Nuclear receptor/AP-1 interaction. Endocr Rev 14: 651–658.
Porlan E, Vega S, Iglesias T, Rodriguez-Pena A . (2004). Unliganded thyroid hormone receptor beta1 inhibits proliferation of murine fibroblasts by delaying the onset of the G1 cell-cycle signals. Oncogene 23: 8756–8765.
Rayman JB, Takahashi Y, Indjeian VB, Dannenberg JH, Catchpole S, Watson RJ et al. (2002). E2F mediates cell cycle-dependent transcriptional repression in vivo by recruitment of an HDAC1/mSin3B corepressor complex. Genes Dev 16: 933–947.
Sanz-Gonzalez SM, Castro C, Perez P, Andres V . (2004). Role of E2F and ERK1/2 in STI571-mediated smooth muscle cell growth arrest and cyclin A transcriptional repression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 317: 972–979.
Shaulian E, Karin M . (2001). AP-1 in cell proliferation and survival. Oncogene 20: 2390–2400.
Sherr CJ . (1995). Mammalian G1 cyclins and cell cycle progression. Proc Assoc Am Physicians 107: 181–186.
Wisdom R . (1999). AP-1: one switch for many signals. Exp Cell Res 253: 180–185.
Yamaguchi K, Lantowski A, Dannenberg AJ, Subbaramaiah K . (2005). Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress the induction of c-Jun and its target genes including COX-2. J Biol Chem 280: 32569–32577.
Yap N, Yu CL, Cheng SY . (1996). Modulation of the transcriptional activity of thyroid hormone receptors by the tumor suppressor p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 4273–4277.
Zhang J, Lazar MA . (2000). The mechanism of action of thyroid hormones. Annu Rev Physiol 62: 439–466.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr MR Campanero and Dr M Diaz-Guerra for critically reading the manuscript and Dr T Iglesias for helpful discussions and valuable comments. We are also indebted to Dr MR Campanero, Dr R Pestell and Dr V Andrés for E2F and cyclin D1 and A2 reporter plasmids and Dr P Maruvada for TRβ mutants. This work was supported by grants to AR-P from Dirección General de Investigación Científica y Técnica (MEC-BFU2004-01498). EP is supported by a grant-associated contract, and OGV is recipient of a pre-doctoral fellowship from Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia associated to the MEC grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Porlan, E., Vidaurre, O. & Rodríguez-Peña, A. Thyroid hormone receptor-β (TRβ1) impairs cell proliferation by the transcriptional inhibition of cyclins D1, E and A2. Oncogene 27, 2795–2800 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210936
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210936
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Thyroid receptor β might be responsible for breast cancer associated with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: a new insight into pathogenesis
Immunologic Research (2022)
-
Ezh2 promotes TRβ lysine methylation-mediated degradation in hepatocellular carcinoma
Genes & Genomics (2022)
-
Targeting the DIO3 enzyme using first-in-class inhibitors effectively suppresses tumor growth: a new paradigm in ovarian cancer treatment
Oncogene (2021)
-
Involvement of cyclins in mammalian spermatogenesis
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2008)