Abstract
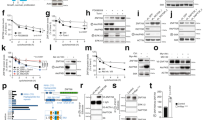
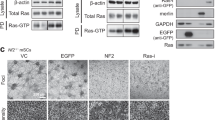
Mutational activation of Ras promotes oncogenesis by controlling cell cycle regulation and cell survival. Ras-mediated activation of both, the PI3K/AKT pathway and the MEK/ERK pathway, can trigger downregulation of the function of tuberin to block the activities of mTOR and p70S6K. Here we demonstrate that Ras-induced cell survival is accompanied by upregulation of p70S6K activity. Ras harbors the potential to negatively affect tuberin-induced apoptosis and p70S6K inactivation. These effects of Ras were found to depend on its potential to regulate the MEK/ERK pathway. Experiments using tuberin-negative fibroblasts revealed that the potential of Ras to counteract apoptosis depends on functional tuberin. Taken together, we provide evidence that the function of Ras to trigger inactivation of tuberin plays a major role in the regulation of cell survival upon mutational activation of the oncogene Ras. This is the first description of a functional interaction between the tumor suppressor tuberin and the oncogene Ras in regulating apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi H, Igawa M, Shina H, Urakami S, Shigeno K, Hino O . (2003). Human bladder tumors with 2-hit mutations of tumor suppressor gene TSC1 and decreased expression of p27. J Urol 170: 601–604.
Arrebola F, Canizares J, Cubero MA, Crespo PV, Warley A, Fernandez-Segura E . (2005). Biphasic behavior of changes in elemental composition during staurosporine-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis 10: 1317–1331.
Astrinidis A, Henske EP . (2005). Tuberous sclerosis complex: linking growth and energy signaling pathways with human disease. Oncogene 24: 7475–7481.
Ballif BA, Roux PP, Gerber SA, MacKeigan JP, Blenis J, Gygi SP . (2005). Quantitative phosphorylation profiling of the ERK/p90 ribosomal S6 kinase-signaling cassette and its targets, the tuberous sclerosis tumor suppressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 667–672.
Cox AD, Der CJ . (2003). The dark side of Ras: regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene 22: 8999–9006.
Dan HC, Sun M, Yang L, Feldman RI, Sui X-M, Ou CC et al. (2002). Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway regulates tuberous sclerosis tumor suppressor complex by phosphorylation of tuberin. J Biol Chem 277: 35364–35370.
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ . (2004). Cell death: critical control points. Cell 116: 205–219.
Downward J . (2004). PI 3-kinase, Akt and cell survival. Sem Cell Dev Biol 15: 177–182.
Dufner A, Thomas G . (1999). Ribosomal S6 kinase signaling and the control of translation. Exp Cell Res 253: 100–109.
Franke TF, Hornik CP, Segev L, Shostak GA, Sugimoto C . (2003). PI3K/Akt and apoptosis: size matters. Oncogene 22: 8983–8998.
Freilinger A, Rosner M, Krupitza G, Nishino M, Lubec G, Korsmeyer SJ et al. (2006). Tuberin activates the proapoptotic molecule BAD. Oncogene 25: 6467–6479.
Goncharova EA, Goncharov DA, Eszterhas AW, Hunter DS, Glassberg MK, Yeung RS et al. (2002). Tuberin regulates p70 S6 kinase activation and ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation. A role for the TSC2 tumor suppressor gene in pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM). J Biol Chem 277: 30958–30967.
Harada H, Andersen JS, Mann M, Terada N, Korsmeyer SJ . (2001). p70S6 kinase signals cell survival as well as growth, inactivating the pro-apoptotic molecule BAD. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 9666–9670.
Henry KW, Yuan X, Koszewski NJ, Onda H, Kwiatkowski DJ, Noonan DJ . (1998). Tuberous sclerosis gene 2 product modulates transcription mediated by steroid hormone receptor family members. J Biol Chem 273: 20535–20539.
Hornigold N, Devlin J, Davies AM, Aveyard JS, Habuchi T, Knowles MA . (1999). Mutation of the 9q34 gene TSC1 in sporadic bladder cancer. Oncogene 18: 2657–2661.
Inoki K, Li Y, Zhu T, Wu J, Guan K-L . (2002). TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR signalling. Nat Cell Biol 4: 648–657.
Inoki K, Zhu T, Guan K-L . (2003). TSC2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell 115: 577–590.
Jiang WG, Sampson J, Martin TA, Lee-Jones L, Watkins G, Douglas-Jones A et al. (2005). Tuberin and hamartin are aberrantly expressed and linked to clinical outcome in human breast cancer: the role of promoter methylation of TSC genes. Eur J Cancer 41: 1628–1636.
Kalejta RF, Shenk T, Beavis AJ . (1997). Use of a membrane-localized green fluorescent protein allows simultaneous identification of transfected cells and cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry. Cytometry 29: 286–291.
Knowles MA, Habuchi T, Kennedy W, Cuthbert-Heavens D . (2003a). Mutation spectrum of the 9q34 tuberous sclerosis gene TSC1 in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Res 63: 7652–7656.
Knowles MA, Hornigold N, Pitt E . (2003b). Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) gene involvement in sporadic tumours. Biochem Soc Transact 31: 597–602.
Kolb TM, Duan L, Davis MA . (2005). Tsc2 expression increases the susceptibility of renal tumor cells to apoptosis. Toxicol Sci 88: 331–339.
Kwiatkowski DJ . (2003). Tuberous sclerosis: from tubers to mTOR. Annals Hum Genet 67: 87–96.
Li Y, Corradetti MN, Inoki K, Guan K-L . (2003). TSC2: filling the GAP in the mTOR signaling pathway. Trends Biochem Sci 29: 32–38.
Ma L, Zhenbang C, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Pandolfi PP . (2005). Phosphorylation and functional inactivation of TSC2 by Erk implications for tuberous sclerosis and cancer pathogenesis. Cell 121: 179–193.
Manning BD, Tee AR, Logsdon MN, Blenis J, Cantley LC . (2002). Identification of the tuberous sclerosis complex-2 tumor suppressor gene product tuberin as a target of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/akt pathway. Mol Cell 10: 151–162.
Miloloza A, Rosner M, Nellist M, Halley D, Bernaschek G, Hengstschläger M . (2000). The TSC1 gene product, hamartin, negatively regulates cell proliferation. Hum Mol Genet 9: 1721–1727.
Pan D, Dong J, Zhang Y, Gao X . (2004). Tuberous sclerosis complex: from Drosophila to human disease. Trends Cell Biol 14: 78–85.
Potter CJ, Pedraza LG, Xu T . (2002). Akt regulates growth by directly phosphorylating Tsc2. Nat Cell Biol 4: 658–665.
Rosner M, Hengstschläger M . (2004). Tuberin binds p27 and negatively regulates its interaction with the SCF component Skp2. J Biol Chem 279: 48707–48715.
Rosner M, Hofer K, Kubista K, Hengstschläger M . (2003). Cell size regulation by the human TSC tumor suppressor proteins depends on PI3K and FKBP38. Oncogene 22: 4786–4798.
Roux PP, Ballif BA, Anjum R, Gygi SP, Blenis J . (2004). Tumor-promoting phorbol esters and activated Ras inactivate the tuberous sclerosis tumor suppressor complex via p90 ribosomal S6 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 13489–13494.
Shah OJ, Wang Z, Hunter T . (2004). Inappropriate activation of the TSC/Rheb/mTOR/S6 K cassette induces IRS1/2 depletion, insulin resistance, and cell survival deficiencies. Curr Biol 14: 1650–1656.
Shaw RJ, Cantley LC . (2006). Ras, PI(3)K and mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature 441: 424–430.
Soucek T, Hölzl G, Bernaschek G, Hengstschläger M . (1998a). A role of the tuberous sclerosis gene-2 product during neuronal differentiation. Oncogene 16: 2197–2204.
Soucek T, Pusch O, Wienecke R, DeClue JE, Hengstschläger M . (1997). Role of the tuberous sclerosis gene-2 product in cell cycle control. Loss of the tuberous sclerosis gene-2 induces quiescent cells to enter S phase. J Biol Chem 272: 29301–29308.
Soucek T, Yeung RS, Hengstschläger M . (1998b). Inactivation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 upon loss of the tuberous sclerosis complex gene-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 15653–15658.
Tee AR, Fingar DC, Manning BD, Kwiatkowski DJ, Cantley LC, Blenis J . (2002). Tuberous sclerosis complex-1 and -2 gene products function together to inhibit mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-mediated downstream signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 13571–13576.
Wohlfart S, Sebinger D, Gruber P, Buch J, Polgar D, Krupitza G et al. (2004). FAS (CD95) mutations are rare in gastric MALT lymphoma but occur more frequently in primary gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am J Pathol 164: 1081–1089.
Xiao G-H, Shoarinejad F, Jin F, Golemis EA, Yeung RS . (1997). The tuberous sclerosis 2 gene product, tuberin, functions as a Rab5 GTPase activating protein (GAP) in modulating endocytosis. J Biol Chem 272: 6097–6100.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Drs AJ Beavis, J Blenis, B Manning, T Ströbel, R Yeung for reagents. This research has been supported by the Herzfelder'sche Familienstiftung (Vienna, Austria) by the RedBull company (Salzburg, Austria) and by the FWF Austrian Science Fund (P18894-B12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freilinger, A., Rosner, M., Hanneder, M. et al. Ras mediates cell survival by regulating tuberin. Oncogene 27, 2072–2083 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210844
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210844
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Renal involvement in tuberous sclerosis complex and von Hippel–Lindau disease: shared disease mechanisms?
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2009)
-
Tuberin, p27 and mTOR in different cells
Amino Acids (2009)
-
Skp2 inversely correlates with p27 and tuberin in transformed cells
Amino Acids (2009)