Abstract
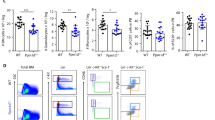
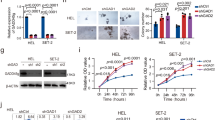
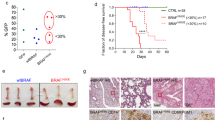
Tumors that acquire resistance against death stimuli constitute a severe problem in the context of cancer therapy. To determine genetic alterations that favor the development of stress-resistant tumors in vivo, we took advantage of polyclonal tumors generated after retroviral infection of newborn Eλ-MYC mice, in which the retroviral integration acts as a mutagen to enhance tumor progression. Tumor cells were cultivated ex vivo and exposed to γ-irradiation prior to their transplantation into syngenic recipients, thereby providing a strong selective pressure for pro-survival mutations. Secondary tumors developing from stress-resistant tumor stem cells were analysed for retroviral integration sites to reveal candidate genes whose dysregulation confer survival. In addition to the gene encoding the antiapoptotic Bcl-xL protein, we identified the gadd45b locus to be a novel common integration site in these tumors, leading to enhanced expression. In accord with a thus far undocumented role of Gadd45β in tumorigenesis, we showed that NIH3T3 cells overexpressing Gadd45β form tumors in NOD/SCID mice. Interestingly and differently to other known ‘classical’ antiapoptotic factors, high Gadd45β levels did not protect against MYC-, UV- or γ-irradiation-induced apoptosis, but conferred a strong and specific survival advantage to serum withdrawal.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 4OHT:
-
4-hydroxytamoxifen
- CIS:
-
common integration site
- eGFP:
-
enhanced green fluorescent protein
- FACS:
-
fluorescence-activated cell sorting
- Mo-MuLV:
-
Moloney-murine leukemia virus
- PI:
-
propidium iodide
- RT:
-
reverse transcriptase
References
Baxter E, Blyth K, Donehower L, Cameron E, Onions D, Neil J . (1996). Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced lymphomas in p53-deficient mice: overlapping pathways in tumor development? J Virol 70: 2095–2100.
Bernier J, Hall E, Giaccia A . (2004). Radiation oncology: a century of achievements. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 737–747.
Blyth K, Stewart M, Bell M, James C, Evan G, Neil J et al. (2000). Sensitivity to myc-induced apoptosis is retained in spontaneous and transplanted lymphomas of CD2-mycER mice. Oncogene 19: 773–782.
Chabner BA, Roberts T . (2005). Chemotherapy and the war on cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 65–71.
Das S, Cho J, Lambertz I, Kelliher MA, Eliopoulos AG, Du K et al. (2005). Tpl2/cot signals activate ERK, JNK, and NF-kappaB in a cell-type and stimulus-specific manner. J Biol Chem 280: 23748–23757.
De Smaele E, Zazzeroni F, Papa S, Nguyen DU, Jin R, Jones J et al. (2001). Induction of gadd45beta by NF-kappaB downregulates pro-apoptotic JNK signalling. Nature 414: 308–313.
Gupta M, Gupta S, Hoffman B, Liebermann DA . (2006). GADD45A and GADD45B protect hematopoietic cells from UV induced apoptosis via distinct signaling pathways including P38 activation and JNK inhibition. J Biol Chem 281: 17552–17558.
Gupta M, Gupta SK, Balliet AG, Hollander MC, Fornace AJ, Hoffman B et al. (2005). Hematopoietic cells from Gadd45a- and Gadd45b-deficient mice are sensitized to genotoxic-stress-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 24: 7170–7179.
Haupt Y, Alexander WS, Barri G, Klinken SP, Adams JM . (1991). Novel zinc finger gene implicated as myc collaborator by retrovirally accelerated lymphomagenesis in E mu-myc transgenic mice. Cell 65: 753–763.
Heinrichs S, Deppert W . (2003). Apoptosis or growth arrest: modulation of the cellular response to p53 by proliferative signals. Oncogene 22: 555–571.
Hwang HC, Martins CP, Bronkhorst Y, Randel E, Berns A, Fero M et al. (2002). Identification of oncogenes collaborating with p27Kip1 loss by insertional mutagenesis and high-throughput insertion site analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 11293–11298.
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA, Lowe SW . (2002). Apoptosis: a link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell 108: 153–164.
Kovalchuk AL, Qi CF, Torrey TA, Taddesse-Heath L, Feigenbaum L, Park SS et al. (2000). Burkitt lymphoma in the mouse. J Exp Med 192: 1183–1190.
Kroemer G, Jaattela M . (2005). Lysosomes and autophagy in cell death control. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 886–897.
Krug U, Ganser A, Koeffler H . (2002). Tumor suppressor genes in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Oncogene 21: 3475–3495.
Kues WA, Carnwath JW, Paul D, Niemann H . (2002). Cell cycle synchronization of porcine fetal fibroblasts by serum deprivation initiates a nonconventional form of apoptosis. Cloning Stem Cells 4: 231–243.
Leicht M, Marx G, Karbach D, Gekle M, Kohler T, Zimmer HG . (2003). Mechanism of cell death of rat cardiac fibroblasts induced by serum depletion. Mol Cell Biochem 251: 119–126.
Liebermann DA, Hoffman B . (2002). Myeloid differentiation (MyD) primary response genes in hematopoiesis. Oncogene 21: 3391–3402.
Lindsten T, Golden JA, Zong WX, Minarcik J, Harris MH, Thompson CB . (2003). The proapoptotic activities of Bax and Bak limit the size of the neural stem cell pool. J Neurosci 23: 11112–11119.
Mikkers H, Allen J, Knipscheer P, Romeyn L, Hart A, Vink E et al. (2002). High-throughput retroviral tagging to identify components of specific signaling pathways in cancer. Nat Genet 32: 153–159.
Mikkers H, Berns A . (2003). Retroviral insertional mutagenesis: tagging cancer pathways. Adv Cancer Res 88: 53–99.
Okada H, Mak TW . (2004). Pathways of apoptotic and non-apoptotic death in tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 592–603.
Packham G, White EL, Eischen CM, Yang H, Parganas E, Ihle JN et al. (1998). Selective regulation of Bcl-XL by a Jak kinase-dependent pathway is bypassed in murine hematopoietic malignancies. Genes Dev 12: 2475–2487.
Paddenberg R, Loos S, Schoneberger HJ, Wulf S, Muller A, Iwig M et al. (2001). Serum withdrawal induces a redistribution of intracellular gelsolin towards F-actin in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts preceding apoptotic cell death. Eur J Cell Biol 80: 366–378.
Poirier Y, Kozak C, Jolicoeur P . (1988). Identification of a common helper provirus integration site in Abelson murine leukemia virus-induced lymphoma DNA. J Virol 62: 3985–3992.
Schmidt M, Hoffmann G, Wissler M, Lemke N, Mussig A, Glimm H et al. (2001). Detection and direct genomic sequencing of multiple rare unknown flanking DNA in highly complex samples. Hum Gene Ther 12: 743–749.
Schwieger M, Lohler J, Friel J, Scheller M, Horak I, Stocking C . (2002). AML1-ETO inhibits maturation of multiple lymphohematopoietic lineages and induces myeloblast transformation in synergy with ICSBP deficiency. J Exp Med 196: 1227–1240.
Selvakumaran M, Lin HK, Sjin RT, Reed JC, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B . (1994). The novel primary response gene MyD118 and the proto-oncogenes myb, myc, and bcl-2 modulate transforming growth factor beta 1-induced apoptosis of myeloid leukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol 14: 2352–2360.
Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB et al. (2004). Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol 6: 1221–1228.
Simm A, Bertsch G, Frank H, Zimmermann U, Hoppe J . (1997). Cell death of AKR-2B fibroblasts after serum removal: a process between apoptosis and necrosis. J Cell Sci 110(Part 7): 819–828.
Speidel D, Helmbold H, Deppert W . (2006). Dissection of transcriptional and non-transcriptional p53 activities in the response to genotoxic stress. Oncogene 25: 940–953.
Stewart M, MacKay N, Cameron ER, Neil JC . (2002). The common retroviral insertion locus Dsi1 maps 30 kilobases upstream of the P1 promoter of the murine Runx3/Cbfa3/Aml2 gene. J Virol 76: 4364–4369.
Tsujimoto Y . (2003). Cell death regulation by the Bcl-2 protein family in the mitochondria. J Cell Physiol 195: 158–167.
van der Lugt NM, Domen J, Verhoeven E, Linders K, van der Gulden H, Allen J et al. (1995). Proviral tagging in E mu-myc transgenic mice lacking the Pim-1 proto-oncogene leads to compensatory activation of Pim-2. EMBO J 14: 2536–2544.
van Lohuizen M, Verbeek S, Scheijen B, Wientjens E, van der Gulden H, Berns A . (1991). Identification of cooperating oncogenes in E mu-myc transgenic mice by provirus tagging. Cell 65: 737–752.
Yoo J, Ghiassi M, Jirmanova L, Balliet AG, Hoffman B, Fornace Jr AJ et al. (2003). Transforming growth factor-beta-induced apoptosis is mediated by Smad-dependent expression of GADD45b through p38 activation. J Biol Chem 278: 43001–43007.
Zazzeroni F, Papa S, Algeciras-Schimnich A, Alvarez K, Melis T, Bubici C et al. (2003). Gadd45 beta mediates the protective effects of CD40 costimulation against Fas-induced apoptosis. Blood 102: 3270–3279.
Zerbini LF, Wang Y, Czibere A, Correa RG, Cho JY, Ijiri K et al. (2004). NF-kappa B-mediated repression of growth arrest- and DNA-damage-inducible proteins 45alpha and gamma is essential for cancer cell survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 13618–13623.
Acknowledgements
We thank Karen Blyth and Ewan Cameron for conditional MYC overexpressing cell lines, Arne Düsedau for providing FACS sorter support and other members of the Stocking laboratory for helpful discussions. This work was part of the doctoral thesis of A Engelmann, Department of Biology, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany and was supported by a grant of the Deutsche Krebshilfe. The Heinrich-Pette-Institut is supported by the Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg and the German Ministry of Health and Social Safety.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engelmann, A., Speidel, D., Bornkamm, G. et al. Gadd45β is a pro-survival factor associated with stress-resistant tumors. Oncogene 27, 1429–1438 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210772
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210772
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification of Differentially Expressed Non-coding RNA in Porcine Alveolar Macrophages from Tongcheng and Large White Pigs Responded to PRRSV
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Methylation mediated Gadd45β enhanced the chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the stemness of liver cancer cells
Cell & Bioscience (2017)
-
Microarray profiling reveals suppressed interferon stimulated gene program in fibroblasts from scleroderma-associated interstitial lung disease
Respiratory Research (2013)
-
Using The Colon Cancer Multigene Recurrence Score to Determine Risk: Prognostic Milestone or a Step in the Right Direction?
Current Colorectal Cancer Reports (2010)