Abstract
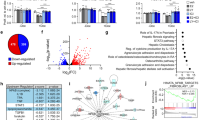
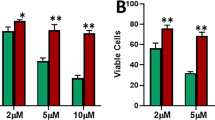
The zinc-finger protein A20/TNFAIP3, an inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation, has been shown to protect MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells from TNFα-induced apoptosis. As estrogen receptor (ER) status is an important parameter in the development and progression of breast cancer, we analysed the effect of 17β-estradiol (E2) treatment on the expression of A20. We found that A20 is a new E2-regulated gene, whose expression correlates with ER expression in both cell lines and tumor samples. With the aim of investigating the impact of A20 expression on MCF-7 cells in response to ER ligands, we established stably transfected-MCF-7 cells overexpressing A20 (MCF-7-A20). These cells exhibited a phenotype of resistance to the 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen cytostatic and pro-apoptotic actions and of hyper-response to E2. Dysregulations in bax, bcl2, bak, phospho-bad, cyclin D1, cyclin E2, cyclin D2 and cyclin A2 proteins expression were shown to be related to the resistant phenotype developed by the MCF-7-A20 cells. Interestingly, we found that A20 was also overexpressed in MVLN and VP tamoxifen-resistant cell lines. Furthermore, high A20 expression levels were observed in more aggressive breast tumors (ER-negative, progesterone receptor-negative and high histological grade). These overall findings strongly suggest that A20 is a key protein involved in tamoxifen resistance, and thus represents both a new breast cancer marker and a promising target for developing new strategies to prevent the emergence of acquired mechanisms of drug resistance in breast cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainbinder E, Revach M, Wolstein O, Moshonov S, Diamant N, Dikstein R . (2002). Mechanism of rapid transcriptional induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha-responsive genes by NF-kappaB. Mol Cell Biol 22: 6354–6362.
Badia E, Duchesne MJ, Semlali A, Fuentes M, Giamarchi C, Richard-Foy H et al. (2000). Long-term hydroxytamoxifen treatment of an MCF-7-derived breast cancer cell line irreversibly inhibits the expression of estrogenic genes through chromatin remodeling. Cancer Res 60: 4130–4138.
Berstein LM, Wang JP, Zheng H, Yue W, Conaway M, Santen RJ . (2004). Long-term exposure to tamoxifen induces hypersensitivity to estradiol. Clin Cancer Res 10: 1530–1534.
Bloom HJG, Richardson WW . (1957). Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 11: 359–377.
Bredel M, Bredel C, Juric D, Duran GE, Yu RX, Harsh GR et al. (2006). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced protein 3 as a putative regulator of nuclear factor-kappaB-mediated resistance to O6-alkylating agents in human glioblastomas. J Clin Oncol 24: 274–287.
Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H . (2001). Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem 276: 9817–9824.
Codd JD, Salisbury JR, Packham G, Nicholson LJ . (1999). A20 RNA expression is associated with undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma and poorly differentiated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Pathol 187: 549–555.
De Goeij AF, Scheres HM, Rousch MJ, Hondius GG, Bosman FT . (1988). Progesterone receptor quantification with radiolabeled promegestone (R 5020) in frozen sections of endometrium and breast cancer tissue. J Steroid Biochem 29: 465–474.
Demirpence E, Duchesne MJ, Badia E, Gagne D, Pons M . (1993). MVLN cells: a bioluminescent MCF-7-derived cell line to study the modulation of estrogenic activity. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 46: 355–364.
Dixit VM, Green S, Sarma V, Holzman LB, Wolf FW, O’Rourke K et al. (1990). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induction of novel gene products in human endothelial cells including a macrophage-specific chemotaxin. J Biol Chem 265: 2973–2978.
EBCTC Group (1998). Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Lancet 351: 1451–1467.
Faridi J, Wang L, Endemann G, Roth RA . (2003). Expression of constitutively active Akt-3 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells reverses the estrogen and tamoxifen responsivity of these cells in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 9: 2933–2939.
Ferran C, Stroka DM, Badrichani AZ, Cooper JT, Wrighton CJ, Soares M et al. (1998). A20 inhibits NF-kappaB activation in endothelial cells without sensitizing to tumor necrosis factor-mediated apoptosis. Blood 91: 2249–2258.
Gottardis MM, Jordan VC . (1988). Development of tamoxifen-stimulated growth of MCF-7 tumors in athymic mice after long-term antiestrogen administration. Cancer Res 48: 5183–5187.
Grey ST, Arvelo MB, Hasenkamp W, Bach FH, Ferran C . (1999). A20 inhibits cytokine-induced apoptosis and nuclear factor kappaB-dependent gene activation in islets. J Exp Med 190: 1135–1146.
Harnish DC, Scicchitano MS, Adelman SJ, Lyttle CR, Karathanasis SK . (2000). The role of CBP in estrogen receptor cross-talk with nuclear factor-kappaB in HepG2 cells. Endocrinology 141: 3403–3411.
Heyninck K, Denecker G, De Valck D, Fiers W, Beyaert R . (1999). Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-induced necrotic cell death by the zinc finger protein A20. Anticancer Res 19: 2863–2868.
Honig SF . (1996). Treatment of metastatic disease. In: Harris JR, Lippman ME, Morrow M, Hellman S (eds). Disease of the Breast. Lippincott-Raven: Philadelphia, pp 669–734.
Jaattela M, Mouritzen H, Elling F, Bastholm L . (1996). A20 zinc finger protein inhibits TNF and IL-1 signaling. J Immunol 156: 1166–1173.
Janicke RU, Lee FH, Porter AG . (1994). Nuclear c-Myc plays an important role in the cytotoxicity of tumor necrosis factor alpha in tumor cells. Mol Cell Biol 14: 5661–5670.
Johnston SR . (1997). Acquired tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer--potential mechanisms and clinical implications. Anticancer Drugs 8: 911–930.
Kim R, Tanabe K, Emi M, Uchida Y, Toge T . (2005). Modulation of tamoxifen sensitivity by antisense Bcl-2 and trastuzumab in breast carcinoma cells. Cancer 103: 2199–2207.
Krikos A, Laherty CD, Dixit VM . (1992). Transcriptional activation of the tumor necrosis factor alpha-inducible zinc finger protein, A20, is mediated by kappa B elements. J Biol Chem 267: 17971–17976.
Kurokawa H, Lenferink AE, Simpson JF, Pisacane PI, Sliwkowski MX, Forbes JT et al. (2000). Inhibition of HER2/neu (erbB-2) and mitogen-activated protein kinases enhances tamoxifen action against HER2-overexpressing, tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 60: 5887–5894.
Laherty CD, Hu HM, Opipari AW, Wang F, Dixit VM . (1992). The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene product induces A20 zinc finger protein expression by activating nuclear factor kappa B. J Biol Chem 267: 24157–24160.
Lee EG, Boone DL, Chai S, Libby SL, Chien M, Lodolce JP et al. (2000). Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-kappaB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice. Science 289: 2350–2354.
Li HL, Wang AB, Zhang R, Wei YS, Chen HZ, She ZG et al. (2006). A20 inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis through negative Fas/Fas ligand-dependent activation of caspase-8 and mitochondrial pathways in murine RAW264.7 macrophages. J Cell Physiol 208: 307–318.
Longo CR, Patel VI, Shrikhande GV, Scali ST, Csizmadia E, Daniel S et al. (2005). A20 protects mice from lethal radical hepatectomy by promoting hepatocyte proliferation via a p21waf1-dependent mechanism. Hepatology 42: 156–164.
Louie MC, Zou JX, Rabinovich A, Chen HW . (2004). ACTR/AIB1 functions as an E2F1 coactivator to promote breast cancer cell proliferation and antiestrogen resistance. Mol Cell Biol 24: 5157–5171.
Lu M, Miller KD, Gokmen-Polar Y, Jeng MH, Kinch MS . (2003). EphA2 overexpression decreases estrogen dependence and tamoxifen sensitivity. Cancer Res 63: 3425–3429.
Martin LA, Farmer I, Johnston SR, Ali S, Marshall C, Dowsett M . (2003). Enhanced estrogen receptor (ER) alpha, ERBB2, and MAPK signal transduction pathways operate during the adaptation of MCF-7 cells to long term estrogen deprivation. J Biol Chem 278: 30458–30468.
Mauro C, Pacifico F, Lavorgna A, Mellone S, Iannetti A, Acquaviva R et al. (2006). ABIN-1 binds to NEMO/IKKgamma and co-operates with A20 in inhibiting NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem 281: 18482–18488.
McCallum HM, Lowther GW . (1996). Long-term culture of primary breast cancer in defined medium. Breast Cancer Res Treat 39: 247–259.
Murphy LC, Peng B, Lewis A, Davie JR, Leygue E, Kemp A et al. (2005). Inducible upregulation of oestrogen receptor-beta1 affects oestrogen and tamoxifen responsiveness in MCF7 human breast cancer cells. J Mol Endocrinol 34: 553–566.
Nabha SM, Glaros S, Hong M, Lykkesfeldt AE, Schiff R, Osborne K et al. (2005). Upregulation of PKC-delta contributes to antiestrogen resistance in mammary tumor cells. Oncogene 24: 3166–3176.
Nguyen H, Sankaran S, Dandekar S . (2006). Hepatitis C virus core protein induces expression of genes regulating immune evasion and anti-apoptosis in hepatocytes. Virology 354: 58–68.
Onose A, Hashimoto S, Hayashi S, Maruoka S, Kumasawa F, Mizumura K et al. (2006). An inhibitory effect of A20 on NF-kappaB activation in airway epithelium upon influenza virus infection. Eur J Pharmacol 541: 198–204.
Opipari Jr AW, Hu HM, Yabkowitz R, Dixit VM . (1992). The A20 zinc finger protein protects cells from tumor necrosis factor cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem 267: 12424–12427.
Patel VI, Daniel S, Longo CR, Shrikhande GV, Scali ST, Czismadia E et al. (2006). A20, a modulator of smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis, prevents and induces regression of neointimal hyperplasia. FASEB J 20: 1418–1430.
Pichon MF, Broet P, Magdelenat H, Delarue JC, Spyratos F, Basuyau JP et al. (1996). Prognostic value of steroid receptors after long-term follow-up of 2257 operable breast cancers. Br J Cancer 73: 1545–1551.
Pike MC, Spicer DV, Dahmoush L, Press MF . (1993). Estrogens, progestogens, normal breast cell proliferation, and breast cancer risk. Epidemiol Rev 15: 17–35.
Ring A, Dowsett M . (2004). Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance. Endocr Relat Cancer 11: 643–658.
Safe S . (2001). Transcriptional activation of genes by 17 beta-estradiol through estrogen receptor-Sp1 interactions. Vitam Horm 62: 231–252.
Santen RJ, Song RX, Zhang Z, Yue W, Kumar R . (2004). Adaptive hypersensitivity to estrogen: mechanism for sequential responses to hormonal therapy in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10: 337S–345S.
Sarma V, Lin Z, Clark L, Rust BM, Tewari M, Noelle RJ et al. (1995). Activation of the B-cell surface receptor CD40 induces A20, a novel zinc finger protein that inhibits apoptosis. J Biol Chem 270: 12343–12346.
Stein B, Yang MX . (1995). Repression of the interleukin-6 promoter by estrogen receptor is mediated by NF-kappa B and C/EBP beta. Mol Cell Biol 15: 4971–4979.
Storz P, Doppler H, Ferran C, Grey ST, Toker A . (2005). Functional dichotomy of A20 in apoptotic and necrotic cell death. Biochem J 387: 47–55.
Tewari M, Wolf FW, Seldin MF, O’Shea KS, Dixit VM, Turka LA . (1995). Lymphoid expression and regulation of A20, an inhibitor of programmed cell death. J Immunol 154: 1699–1706.
Thompson EW, Paik S, Brunner N, Sommers CL, Zugmaier G, Clarke R et al. (1992). Association of increased basement membrane invasiveness with absence of estrogen receptor and expression of vimentin in human breast cancer cell lines. J Cell Physiol 150: 534–544.
Tonetti DA, Chisamore MJ, Grdina W, Schurz H, Jordan VC . (2000). Stable transfection of protein kinase C alpha cDNA in hormone-dependent breast cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer 83: 782–791.
Tsai MS, Bogart DF, Castaneda JM, Li P, Lupu R . (2002). Cyr61 promotes breast tumorigenesis and cancer progression. Oncogene 21: 8178–8185.
Vendrell JA, Bieche I, Desmetz C, Badia E, Tozlu S, Nguyen C et al. (2005). Molecular changes associated with the agonist activity of hydroxy-tamoxifen and the hyper-response to estradiol in hydroxy-tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cell lines. Endocr Relat Cancer 12: 75–92.
Vendrell JA, Magnino F, Danis E, Duchesne MJ, Pinloche S, Pons M et al. (2004). Estrogen regulation in human breast cancer cells of new downstream gene targets involved in estrogen metabolism, cell proliferation and cell transformation. J Mol Endocrinol 32: 397–414.
Wertz IE, O’Rourke KM, Zhou H, Eby M, Aravind L, Seshagiri S et al. (2004). De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-kappaB signalling. Nature 430: 694–699.
Yamit-Hezi A, Nir S, Wolstein O, Dikstein R . (2000). Interaction of TAFII105 with selected p65/RelA dimers is associated with activation of subset of NF-kappa B genes. J Biol Chem 275: 18180–18187.
Yue W, Wang JP, Conaway M, Masamura S, Li Y, Santen RJ . (2002). Activation of the MAPK pathway enhances sensitivity of MCF-7 breast cancer cells to the mitogenic effect of estradiol. Endocrinology 143: 3221–3229.
Zetoune FS, Murthy AR, Shao Z, Hlaing T, Zeidler MG, Li Y et al. (2001). A20 inhibits NF-kappa B activation downstream of multiple Map3 kinases and interacts with the I kappa B signalosome. Characterization of a p75(NTR) apoptotic signaling pathway using a novel cellular model. Cytokine 15: 282–298.
Zhang GJ, Kimijima I, Onda M, Kanno M, Sato H, Watanabe T et al. (1999). Tamoxifen-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells relates to down-regulation of bcl-2, but not bax and bcl-X(L), without alteration of p53 protein levels. Clin Cancer Res 5: 2971–2977.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Val d’Aurelle Hospital (Montpellier, France) for providing tumor breast samples. We thank Dr P Roux for providing pTK-RL and pCIneo plasmids, Dr HD McCallum for sending the VP cells, Dr E Badia for providing the ERE-Luc plasmid, the MVLN, the CL6.8 and CL6.32 cells, and H Valles and V Denis for technical support. We thank Dr SL Salhi for presubmission editorial assistance. This work was supported by grants from the Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (Comité de l’Ardèche, Comité de la Saône et Loire), the Groupement des Entreprises Françaises dans la Lutte Contre le Cancer (Montpellier, France) and the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (ARC, France). JA Vendrell was supported by a fellowship from the Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (France).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vendrell, J., Ghayad, S., Ben-Larbi, S. et al. A20/TNFAIP3, a new estrogen-regulated gene that confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 26, 4656–4667 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210269
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210269
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
NF-κB/RelA controlled A20 limits TRAIL-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
TNFAIP3 promotes ALDH-positive breast cancer stem cells through FGFR1/MEK/ERK pathway
Medical Oncology (2022)
-
Identification of TNFAIP3 as relapse biomarker and potential therapeutic target for MOG antibody associated diseases
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
A20 promotes melanoma progression via the activation of Akt pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
TRAF6 maintains mammary stem cells and promotes pregnancy-induced mammary epithelial cell expansion
Communications Biology (2019)