Abstract
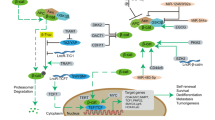
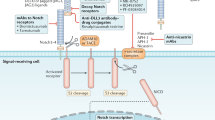
Data from certain leukemias as well as brain and breast cancer indicate that there is a small population of tumor cells with ‘stem cell’ characteristics and the capacity for self-renewal. The self-renewing cells have many of the properties of normal stem cells and have been termed ‘cancer stem cells’. These cancer stem cells make up as few as 1% of the cells in a tumor, making them difficult to detect and study. Like normal stem cells, cancer stem cells have a number of properties permitting them to survive traditional cancer chemotherapy and radiation therapy. These cells express high levels of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) drug transporters, providing for a level of resistance; are relatively quiescent; have higher levels of DNA repair and a lowered ability to enter apoptosis. Combined cancer therapy approaches targeting the cancer stem cells and the non-stem cells may be developed with increased efficacy. Efforts to target the Hedgehog/Patched pathway, critical to embryonic growth and differentiation, and the ABCG2 drug efflux transporter will be presented.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Hajj M, Clarke MF . (2004). Self-renewal and solid tumor stem cells. Oncogene 23: 7274–7282.
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF . (2003). Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 3983–3988.
Athar M, Li C, Tang X, Chi S, Zhang X, Kim AL et al. (2004). Inhibition of smoothened signaling prevents ultraviolet B-induced basal cell carcinomas through regulation of Fas expression and apoptosis. Cancer Res 64: 7545–7552.
Bale AE, Yu KP . (2001). The hedgehog pathway and basal cell carcinomas. Hum Mol Genet 10: 757–762.
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Maitra A, Montes De Oca R, Gerstenblith MR, Briggs K et al. (2003). Widespread requirement for Hedgehog ligand stimulation in growth of digestive tract tumours. Nature 425: 846–851.
Bijlsma MF, Spek CA, Zivkovic D, van de Water S, Rezaee F, Peppelenbosch MP . (2006). Repression of smoothened by patched-dependent (pro-)vitamin D3 secretion. PLoS Biol 4: 1397–1410.
Brinster RL . (1976). Participation of teratocarcinoma cells in mouse embryo development. Cancer Res 36: 3412–3414.
Chen JK, Taipale J, Cooper MK, Beachy PA . (2002). Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of cyclopamine to Smoothened. Genes Dev 16: 2743–2748.
Chidambaram A, Goldstein AM, Gailani MR, Gerrard B, Bale SJ, DiGiovanna JJ et al. (1996). Mutations in the human homolog of the Drosophila patched gene in Caucasian and African American nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome patients. Cancer Res 56: 4599–4601.
Dean M . (1997). Towards a unified model of tumor suppression: lessons learned from the human patched gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1332: M43–M52.
Dean M . (2006). Cancer stem cells: redefining the paradigm of cancer treatment strategies. Mol Interv 6: 140–148.
Dean M, Fojo T, Bates S . (2005). Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 275–284.
Folkman J . (2002). Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol 29: 15–18.
Gailani MR, Stahle-Backdahl M, Leffell DJ, Glynn M, Zaphiropoulos PG, Pressman C et al. (1996). The role of the human homologue of Drosophila patched in sporadic basal cell carcinomas. Nature Genetics 14: 78–81.
Goodell MA, Brose K, Paradis G, Conner AS, Mulligan RC . (1996). Isolation and functional properties of murine hematopoietic stem cells that are replicating in vivo. J Exp Med 183: 1797–1806.
Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE . (2002). Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nature Rev Cancer 2: 48–58.
Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulous PG, Gailani MR, Shanley S, Chidambaram A et al. (1996). Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell 85: 841–851.
Hamburger AW, Salmon SE . (1977). Primary bioassay of human tumor stem cells. Science 197: 461–463.
Hemmati HD, Nakano I, Lazareff JA, Masterman-Smith M, Geschwind DH, Bronner-Fraser M et al. (2003). Cancerous stem cells can arise from pediatric brain tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 15178–15183.
Henrich CJ, Bokesch HR, Dean M, Bates SE, Robey RW, Goncharova EI et al. (2006). A high-throughput cell-based assay for inhibitors of ABCG2 activity. J Biomol Screen 11: 176–183.
Hirschmann-Jax C, Foster AE, Wulf GG, Nuchtern JG, Jax TW, Gobel U et al. (2004). A distinct ‘side population’ of cells with high drug efflux capacity in human tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 14228–14233.
James LF, Panter KE, Gaffield W, Molyneux RJ . (2004). Biomedical applications of poisonous plant research. J Agric Food Chem 52: 3211–3230.
Johnson RL, Rothman AL, Xie J, Goodrich LV, Bare JW, Bonifas JM et al. (1996). Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus syndrome. Science 272: 1668–1671.
Karhadkar SS, Bova GS, Abdallah N, Dhara S, Gardner D, Maitra A et al. (2004). Hedgehog signalling in prostate regeneration, neoplasia and metastasis. Nature 431: 707–712.
Kim M, Turnquist H, Jackson J, Sgagias M, Yan Y, Gong M et al. (2002). The multidrug resistance transporter ABCG2 (breast cancer resistance protein 1) effluxes Hoechst 33342 and is overexpressed in hematopoietic stem cells. Clin Cancer Res 8: 22–28.
Kondo T, Setoguchi T, Taga T . (2004). Persistence of a small subpopulation of cancer stem-like cells in the C6 glioma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 781–786.
Kruger JA, Kaplan CD, Luo Y, Zhou H, Markowitz D, Xiang R et al. (2006). Characterization of stem cell like cancer cells in immune competent mice. Blood 108: 3906–3912.
Lapidot T, Sirard C, Vormoor J, Murdoch B, Hoang T, Caceres-Cortes J et al. (1994). A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice. Nature 367: 645–648.
Mintz B, Illmensee K . (1975). Normal genetically mosaic mice produced from malignant teratocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72: 3585–3589.
Nakachi K, Hayashi T, Imai K, Kusunoki Y . (2004). Perspectives on cancer immuno-epidemiology. Cancer Sci 95: 921–929.
Nusslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E . (1980). Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in drosophila. Nature 287: 795–801.
Robey RW, Steadman K, Polgar O, Morisaki K, Blayney M, Mistry P et al. (2004). Pheophorbide a is a specific probe for ABCG2 function and inhibition. Cancer Res 64: 1242–1246.
Scharenberg CW, Harkey MA, Torok-Storb B . (2002). The ABCG2 transporter is an efficient Hoechst 33342 efflux pump and is preferentially expressed by immature human hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 99: 507–512.
Thayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW, Nielsen CM, Roberts DJ, Lauwers GY et al. (2003). Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature 425: 851–856.
Tostar U, Malm CJ, Meis-Kindblom JM, Kindblom LG, Toftgard R, Unden AB . (2006). Deregulation of the hedgehog signalling pathway: a possible role for the PTCH and SUFU genes in human rhabdomyoma and rhabdomyosarcoma development. J Pathol 208: 17–25.
Watkins DN, Berman DM, Burkholder SG, Wang B, Beachy PA, Baylin SB . (2003). Hedgehog signalling within airway epithelial progenitors and in small-cell lung cancer. Nature 422: 313–317.
Zhou S, Schuetz JD, Bunting KD, Colapietro AM, Sampath J, Morris JJ et al. (2001). The ABC transporter Bcrp1/ABCG2 is expressed in a wide variety of stem cells and is a molecular determinant of the side-population phenotype. Nat Med 7: 1028–1034.
Acknowledgements
Dedicated to George Vande Woude for teaching me (MD) to think big and take chances. This study was supported with Federal funds from the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Cancer Institute, Center for Cancer Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, H., Dean, M. Targeted therapy for cancer stem cells: the patched pathway and ABC transporters. Oncogene 26, 1357–1360 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210200
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210200
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
M2 macrophage microvesicle-inspired nanovehicles improve accessibility to cancer cells and cancer stem cells in tumors
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2021)
-
DOCK6 promotes chemo- and radioresistance of gastric cancer by modulating WNT/β-catenin signaling and cancer stem cell traits
Oncogene (2020)
-
MiR-514 attenuates proliferation and increases chemoresistance by targeting ATP binding cassette subfamily in ovarian cancer
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2018)
-
Metformin targets multiple signaling pathways in cancer
Chinese Journal of Cancer (2017)
-
The search for optimal cutoff points for apoptosis and proliferation rate in prognostification of early stage breast cancer patients treated with anthracyclines in adjuvant settings
Tumor Biology (2016)