Abstract
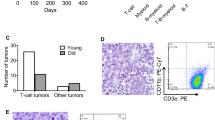
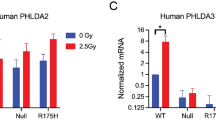
The Fas death receptor is a cell surface molecule involved in apoptosis as well as in proliferative or activating signals of many cells types, including T lymphocytes. Using quantitative real-time reverse transcription–PCR analysis, we confirm that expression of this gene is scarcely perceptible in thymic lymphomas induced by γ-irradiation in C57BL/6J mice. Notably, we also demonstrate for the first time that Fas expression is significantly upregulated in vivo both after single high dose of radiation and in thymic lymphoma-free mice. In addition, we determined its levels of expression in five mouse strains exhibiting different degrees of susceptibility (SPRET/Ei, SEG/Pas, BALB/cJ, C57BL/6J and RF/J). Interestingly, we found the highest levels of expression in SPRET/Ei and SEG/Pas strains (both derived from the Mus spretus species), which are known to have the most resistant phenotype, and the lowest levels in the most susceptible strains C57BL/6J and RF/J. DNA sequencing of the Fas promoter in all five strains showed many polymorphisms that can be classified into three functional haplotypes by using luciferase assays: (1) C57BL/6J and RF/J, (2) BALB/cJ and (3) SPRET/Ei and SEG/Pas. Promoter activities in response to single high doses of radiation correlated well with the levels of Fas expression and are consistent with the degree of strain susceptibility.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
Accessions
GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ
References
Adachi M, Suematsu S, Suda T, Watanabe D, Fukuyama H, Ogasawara J et al. (1996). Proc Natls Acad Sci USA 93: 2131–2136.
Booker JK, Reap EA, Cohen PL . (1998). J Immunol 161: 4536–4541.
Castro JE, Listman JA, Jacobson BA, Wang Y, López PA, Ju S et al. (1996). Immunity 5: 617–627.
Chan H, Bartos DP, Owen-Schaub LB . (1999). Mol Cell Biol 19: 2098–2108.
DeRyckere D, Mann DL, DeGregory J . (2003). J Immunol 171: 802–811.
Feuk L, Prince JA, Blennow K, Brookes AJ . (2003). Hum Mutat 21: 53–60.
Fleck M, Zhou T, Tatsuta T, Yang P, Wang P, Mountz JD . (1998). J Immunol 160: 3766–3775.
Hettmann T, DiDonato J, Karin M, Leiden JM . (1999). J Exp Med 189: 145–157.
Hettmann T, Leiden JM . (2000). J Immunol 165: 5004–5010.
Hoogendoorn B, Coleman SL, Guy CA, Smith K, Bowen T, Buckland PR et al. (2003). Hum Mol Genet 12: 2249–2254.
Kishimoto H, Surh CD, Sprent J . (1998). J Exp Med 187: 1427–1438.
Krammer PH . (2000). Nature 407: 789–795.
Kurasawa K, Hashimoto Y, Iwamoto I . (1999). Cell Immunol 194: 127–135.
Lai HC, Sytwu HK, Sun CA, Yu MH, Yu CP, Liu HS et al. (2003). Int J Cancer 103: 221–225.
Maas K, Westfall M, Pietenpol J, Olsen NJ, Aune T . (2005). Arthritis Rheumatism 52: 1047–1057.
Meléndez B, Santos J, Fernández-Piqueras J . (1999). Oncogene 18: 4166–4169.
Muschen M, Warskulat U, Beckann MW . (2000). J Mol Med 78: 312–325.
Nagata S, Suda T . (1995). Immunol Today 16: 39–43.
Nishimura Y, Ishii A, Kobayashi Y, Yamasaki Y, Yonehara S . (1995). J Immunol 154: 4395–4403.
Ogasawara J, Suda T, Nagata S . (1995). J Exp Med 181: 485–491.
Oukka M, Ho C, de la Brousse FC, Hoey T, Grusby MJ, Glimcher LH . (1998). Immunity 9: 295–304.
Pinkoski MJ, Green DR . (1999). Cell Death Differ 6: 1174–1181.
Rathmell JC, Thompson CB . (2002). Cell 109: S97–S107.
Reap EA, Roof K, Maynor K, Borrero M, Booker J, Cohen PL . (1997). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 5750–5755.
Santos J, Herranz M, Fernández M, Vaquero C, López P, Fernández-Piqueras J . (2001). Oncogene 20: 2186–2189.
Santos J, Montagutelli X, Acevedo A, López P, Vaquero C, Fernández M et al. (2002). Oncogene 21: 6680–6683.
Santos J, Pérez de Castro I, Herranz M, Pellicer A, Fernández-Piqueras J . (1996). Oncogene 12: 669–676.
Schmitz I, Clayton LK, Reinherz EL . (2003). Int Immunol 15: 1237–1248.
Sibley K, Rollinson S, Allan JM, Smith AG, Law GR, Roddam PL et al. (2003). Cancer Res 63: 4327–4330.
Siegel RM, Chan KM, Chun HJ, Lebardo MJ . (2000). Nat Immunol 1: 469–474.
Zheng Y, Ouaaz F, Bruzzo P, Singh V, Gerondakis S, Beg AA . (2001). J Immunol 166: 4949–4957.
Acknowledgements
We thank L González, M Matabuena, M Guerrero, MJ Bueno and R Peregil for aid with animals, P Fernández for helping with statistical analysis and E Pérez-Gómez for technical assistance. We are also grateful to Professor A Morales for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the European Commission (EURATOM Work Programme 2003, FI6R-CT-2003-508842 to JS), ‘Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia’ (SAF2003-05048) and ‘Ministerio de Salud y Consumo’ (Lymphoma Network, G03/179) to JF-P. MV-M is the recipient of a predoctoral fellowship from ‘Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia’ (FPU AP2002-0294).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villa-Morales, M., Santos, J. & Fernández-Piqueras, J. Functional Fas (Cd95/Apo-1) promoter polymorphisms in inbred mouse strains exhibiting different susceptibility to γ-radiation-induced thymic lymphoma. Oncogene 25, 2022–2029 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209234
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209234
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Deep genome sequencing and variation analysis of 13 inbred mouse strains defines candidate phenotypic alleles, private variation and homozygous truncating mutations
Genome Biology (2016)
-
FAS system deregulation in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma
Cell Death & Disease (2014)
-
Depletion of the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) sensitizes towards apoptosis via p53 and p73 posttranslational regulation
Oncogene (2013)
-
The stromal gene encoding the CD274 antigen as a genetic modifier controlling survival of mice with γ-radiation-induced T-cell lymphoblastic lymphomas
Oncogene (2010)
-
Identification of a novel cerebral malaria susceptibility locus (Berr5) on mouse chromosome 19
Genes & Immunity (2010)