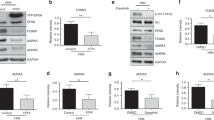
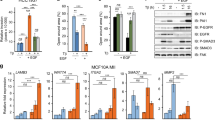
Abstract
Gα12, the α-subunit of G12, which has been referred to as the gep oncogene, stimulates mitogenic pathways in different cell types and readily induces neoplastic transformation of fibroblast cell lines. Recently, we have shown that the oncogenic pathway activated by Gα12 involves the receptor tyrosine kinase platelet derived growth factor receptor-α (PDGFRα) and JAK3. In the present study, we demonstrate that the GTPase-deficient activated mutant of Gα12 activates signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) via PDGFRα as well as JAK3. Here we show that Gα12 stimulates the phosphorylation of STAT3 at both Tyrosine-705 and Serine-727 residues. Studies to delineate the mechanism by which Gα12 stimulates STAT3 have indicated that the Tyrosine-705-phosphorylation of STAT3 involves the tyrosine kinases, Janus Kinase-3 as well as Src kinase, whereas the Serine-727 phosphorylation of STAT3 occurs via the receptor tyrosine kinase, PDGFRα and phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase pathway. Our results also indicate that the coexpression of the dominant negative, DNA binding mutant of STAT3 (STAT3DB) inhibits the foci formation as well as anchorage-independent growth of Gα12QL-transfectants, thereby establishing the critical role of STAT3 in Gα12QL-mediated neoplastic cell growth. The results presented here demonstrate, for the first time, the ability of Gα12 to recruit multiple receptor-, nonreceptor-, and Ser/Thr kinases to stimulate STAT3-signaling to promote neoplastic transformation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RTKs:
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases
- GPCR:
-
G protein coupled receptors
- G protein:
-
guanine nucleotide-binding protein
- PDGFR:
-
platelet derived growth factor receptor
- PI3K:
-
phosphatidylinositol-3-OH-kinase
- JAK:
-
Janus kinase
- STAT:
-
signal transducer and activator of transcription
References
Berclaz G, Altermatt HJ, Rohrbach V, Siragusa A, Dreher E, Smith PD . (2001). Int J Oncol 19: 1155–1160.
Boulton TG, Zhong Z, Wen Z, Darnell Jr JE, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD . (1995). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 6915–6919.
Bowman T, Broome MA, Sinibaldi D, Wharton W, Pledger WJ, Sedivy JM et al. (2001). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 7319–7324.
Bromberg J, Darnell Jr JE . (2000). Oncogene 19: 2468–2473.
Bromberg JF, Horvath CM, Besser D, Lathem WW, Darnell Jr JE . (1998). Mol Cell Biol 18: 2553–2558.
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C et al. (1999). Cell 98: 295–303.
Burke WM, Jin X, Lin HJ, Huang M, Liu R, Reynolds RK et al. (2001). Oncogene 20: 7925–7934.
Chakraborty A, Dyer KF, Cascio M, Mietzner TA, Tweardy DJ . (1999). Blood 93: 15–24.
Chan AM, Fleming TP, McGovern ES, Chedid M, Miki T, Aaronson SA . (1993). Mol Cell Biol 13: 762–768.
Cirri P, Chiarugi P, Marra F, Raugei G, Camici G, Manao G et al. (1997). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 239: 493–497.
Dhanasekaran N, Dermott JM . (1996). Cell Signal 8: 235–245.
Fung MM, Rohwer F, McGuire KL . (2003). Cell Signal 15: 625–636.
Garcia R, Bowman TL, Niu G, Yu H, Minton S, Muro-Cacho CA et al. (2001). Oncogene 20: 2499–2513.
Gutkind JS, Coso OA, Xu N . (1998) In: G Proteins, Receptors and Diseases, Spiegel S (ed). Humana Press: Clifton, UK, pp 101–117.
Huang M, Page C, Reynolds RK, Lin J . (2000). Gynecol Oncol 79: 67–73.
Jain N, Zhang T, Kee WH, Li W, Cao X . (1999). J Biol Chem 274: 24392–24400.
Jiang H, Wu D, Simon MI . (1993). FEBS Lett 330: 319–322.
Johnson GL, Dhanasekaran N . (1989). Endocr Rev 10: 317–331.
Kumar RN, Radhika V, Audige VV, Rane SG, Dhanasekaran N . (2004). Cell Biochem Biophys 41: 63–74.
Kuroki M, O'Flaherty JT . (1999). Biochem J 341 (Part 3): 691–696.
Li L, Shaw PE . (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 17397–17405.
Lo RK, Cheung H, Wong YH . (2003). J Biol Chem 278: 52154–52165.
Lo RK, Wong YH . (2004). Mol Pharmacol 65: 1427–1439.
Nagao M, Kaziro Y, Itoh H . (1999). Oncogene 18: 4425–4434.
Pedranzini L, Leitch A, Bromberg J . (2004). J Clin Invest 114: 619–622.
Prasad MV, Dermott JM, Heasley LE, Johnson GL, Dhanasekaran N . (1995). J Biol Chem 270: 18655–18659.
Radhika V, Dhanasekaran N . (2001). Oncogene 20: 1607–1614.
Ram PT, Horvath CM, Iyengar R . (2000). Science 287: 142–144.
Ram PT, Iyengar R . (2001). Oncogene 20: 1601–1606.
Sambrook J, Russell DW . (2001). Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual, 3rd edn, pp 17.19–17.10.
Schuringa JJ, Dekker LV, Vellenga E, Kruijer W . (2001). J Biol Chem 276: 27709–27715.
Shore SK, Reddy EP . (1989). Oncogene 4: 1411–1413.
Turkson J, Bowman T, Adnane J, Zhang Y, Djeu JY, Sekharam M et al. (1999). Mol Cell Biol 19: 7519–7528.
Turkson J, Bowman T, Garcia R, Caldenhoven E, De Groot RP, Jove R . (1998). Mol Cell Biol 18: 2545–2552.
Valgeirsdottir S, Paukku K, Silvennoinen O, Heldin CH, Claesson-Welsh L . (1998). Oncogene 16: 505–515.
Vara Prasad MV, Shore SK, Dhanasekaran N . (1994). Oncogene 9: 2425–2429.
Vignais ML, Gilman M . (1999). Mol Cell Biol 19: 3727–3735.
Voyno-Yasenetskaya TA, Pace AM, Bourne HR . (1994). Oncogene 9: 2559–2565.
Wang YZ, Wharton W, Garcia R, Kraker A, Jove R, Pledger WJ . (2000). Oncogene 19: 2075–2085.
Wen Z, Zhong Z, Darnell Jr JE . (1995). Cell 82: 241–250.
Xu N, Bradley L, Ambdukar I, Gutkind JS . (1993). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 6741–6745.
Xu N, Voyno-Yasenetskaya T, Gutkind JS . (1994). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 201: 603–609.
Yamanaka Y, Nakajima K, Fukada T, Hibi M, Hirano T . (1996). EMBO J 15: 1557–1565.
Yokogami K, Wakisaka S, Avruch J, Reeves SA . (2000). Curr Biol 10: 47–50.
Yu CL, Meyer DJ, Campbell GS, Larner AC, Carter-Su C, Schwartz J et al. (1995). Science 269: 81–83.
Yu JC, Gutkind JS, Mahadevan D, Li W, Meyers KA, Pierce JH et al. (1994). J Cell Biol 127: 479–487.
Zhang Y, Cho YY, Petersen BL, Bode AM, Zhu F, Dong Z . (2003). J Biol Chem 278: 12650–12659.
Acknowledgements
The critical reading of the manuscript by Ms Kimia Kashef, Mr Zachariah Goldsmith, and Dr V Radhika is gratefully appreciated. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (GM49897).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Shore, S. & Dhanasekaran, N. Neoplastic transformation by the gep oncogene, Gα12, involves signaling by STAT3. Oncogene 25, 899–906 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209132
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209132
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The emerging roles of Gα12/13 proteins on the hallmarks of cancer in solid tumors
Oncogene (2022)
-
G protein alpha 12
AfCS-Nature Molecule Pages (2010)
-
The gep oncogenes, Gα12 and Gα13, upregulate the transforming growth factor-β1 gene
Oncogene (2009)