Abstract
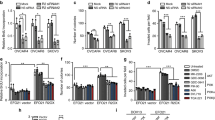
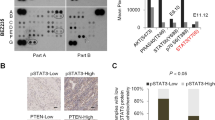
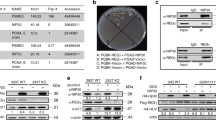
The tumor suppressor gene phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) regulates the phosphatidylinositol-3′-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway and has been shown to correlate with poor prognosis in high-grade astrocytomas when mutational inactivation or loss of the PTEN gene occurs. PTEN mutation leads to constitutive activation of protein kinase B (PKB)/Akt with phosphorylation at the PKB/Akt sites Thr-308 and Ser-473. Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) has been shown to regulate PKB/Akt activity with the loss of PTEN in prostate cancer. We now demonstrate that ILK activity regulates PKB/Akt activity in glioblastoma cells. The activity of ILK is constitutively elevated in a serum-independent manner in PTEN mutant cells, and transfection of wild-type PTEN under the control of an inducible promoter into mutant PTEN cells inhibits ILK activity. Transfection of ILK antisense (ILKAS) or exposure to a small-molecule ILK inhibitor suppresses the constitutive phosphorylation of PKB/Akt on Ser-473 in PTEN-mutant glioblastoma cell lines. In addition, the delivery of ILKAS to PTEN-negative glioblastoma cells resulted in apoptosis. Rag-2M mice bearing established (∼100 mg) human U87MG glioblastoma tumors, treated QD × 5 for 3 consecutive weeks with ILKAS (i.p. 5 mg/kg), exhibited stable disease with ⩽7% increase in tumor volume over the 3-week course of treatment. In contrast, animals treated with an oligonucleotide control or saline exhibited a >100% increase in tumor volume over the same time period. Our initial results indicate that therapeutic strategies targeting ILK may be beneficial in the treatment of glioblastomas.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ILK:
-
integrin-linked kinase
- PI3K:
-
phosphatidylinositol-3′-kinase
- PTEN:
-
phosphatase and tensin homologue
- MMAC1:
-
mutated in multiple advanced cancers
- PI(3, 4, 5) P3:
-
phosphatidylinositol-3, 4, 5-triphosphate
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- CI:
-
combination index
- GBM:
-
glioblastoma multiforme
- ODN:
-
oligonucleotides
References
Cheney W, Neuteboom STC, Vaillancourt M-T, Ramachandra M and Bookstein R . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 2318–2323.
Choe G, Horvath S, Cloughesy TF, Crosby K, Seligson D, Palotie A, Inge L, Smith BL, Sawyers CL and Mischel PS . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 2742–2746.
Chung DH, Lee JI, Kook MC, Kim JR, Kim SH, Choi EY, Park SH and Song HG . (1998). Virchows Arch., 433, 113–117.
Cruet-Hennequart S, Maubant S, Luis J, Gauduchon P, Staedel C and Dedhar S . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 1688–1702.
D'Amico M, Hulit J, Amanatullah DF, Zafonte BT, Albanese C, Bouzahzah B, Fu M, Augenlicht LH, Donehower LA, Takemaru K, Moon RT, Davis R, Lisanti MP, Shtutman M, Zhurinsky J, Ben-Ze'ev A, Troussard AA, Dedhar S and Pestell RG . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 32649–32657.
Daumas-Duport C, Scheithauer BW, O'Fallon J and Kelly P . (1988). Cancer, 62, 2152–2165.
Delcommenne M, Tan C, Gray V, Rue L, Woodgett J and Dedhar S . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 11211–11216.
Edwards L, Thiessen B, Yan H, Dedhar S and Bally M . (2003). Neuro-Oncology, 5, 300 (abstract).
Edwards LA, Shabbits J, Bally MB and Dedhar S . (2004). Integrin-linked Kinase (ILK) in Combination Molecular Targeting: Cancer Treatment and Research. Kluwer: New York.
Ermoian RP, Furniss CS, Lamborn KR, Basila D, Berger MS, Gottschalk AR, Nicholas MK, Stokoe D and Haas-Kogan DA . (2002). Clin. Cancer Res., 8, 1100–1106.
Graff JR, Deddens JA, Konicek BW, Colligan BM, Hurst BM, Carter HW and Carter JH . (2001). Clin. Cancer Res., 7, 1987–1991.
Haas-Koogan DA, Shaley N, Wong M, Mills G, Yount G and Stokoe D . (1998). Curr. Biol., 8, 1195–1198.
Hannigan GE, Leung-Hagesteijn C, Fitz-Gibbon L, Coppolino M, Radeva G, Filmus J, Bell JC and Dedhar S . (1996). Nature, 379, 91–96.
Hu Y, Cherton-Horvat G, Dragowska V, Baird S, Korneluk RG, Durkin JP, Mayer LD and LaCasse EC . (2003). Clin. Cancer Res., 9, 2826–2836.
Ishii T, Furuoka H, Muroi Y and Nishimura M . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 26970–26975.
Katso R, Okkenhaug K, Ahmadi K, White S, Timms J and Waterfield MD . (2001). Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 17, 615–675.
Knobbe CB, Merlo A and Reifenberger G . (2002). Neuro-Oncology, 4, 196–211.
Li DM and Sun H . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 2124–2129.
Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podyspaniana K, Bose S, Wang SI, Puc J, Miliaresis C, Rodgers L, McCombie R, Bigner SH, Giovanella BC, Ittmann M, Tycko B, Hibshoosh B, Wigler MH and Parsons R . (1997). Science, 275, 1943–1947.
Liaw D, Marsh DJ, Li J, Dahia PL, Wang SI, Zheng Z, Bose S, Call KM, Tsou HC, Peacocke M, Eng C and Parsons R . (1997). Nat. Genet., 16, 64–67.
Marsh DJ, Roth S, Lunetta KL, Hemminki A, Dahia PL, Sistonen P, Zheng Z, Caron S, van Orsouw NJ, Bodmer WF, Cottrell SE, Dunlop MG, Eccles D, Hodgson SV, Jarvinen H, Kellokumpu I, Markie D, Neale K, Phillips R, Rozen P, Syngal S, Vijg J, Tomlinson IP, Aaltonen LA and Eng C . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 5017–5021.
Nelen MR, van Staveren WC, Peeters EA, Hassel MB, Gorlin RJ, Hamm H, Lindboe CF, Fryns JP, Sijmons RH, Woods DG, Mariman EC, Padberg GW and Kremer H . (1997). Hum. Mol. Genet., 6, 1383–1387.
Novak A, Hsu SC, Leung-Hagesteijn C, Radeva G, Papkoff J, Montesano R, Roskelley C, Grosschedl R and Dedhar S . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 4374–4379.
Obara S, Nakata M, Takeshima H, Katagiri H, Asano T, Oka Y, Maryuma I and Kuratsu J . (2004). Can. Lett., 208, 115–122.
Park M-J, Kim M-S, Park I-C, Kang H-S, Yoo H, Park S-H, Rhee CH, Hong S-I and Lee S-H . (2002). Can. Res., 62, 6318–6322.
Persad S, Attwell S, Gray V, Delecommenne M, Troussard A, Sanghera J and Dedhar S . (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 1322–1324.
Persad S, Attwell S, Gray V, Mawji N, Deng JT, Leung D, Yan J, Sanghera J, Walsh MP and Dedhar S . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 27462–27469.
Pore N, Liu S, Haas-Kogan DA, O'Rourke DM and Maity A . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 236–241.
Stambolic V, Suzuki A, de la Pompa JL, Brothers GM, Mirtsos C, Sasaki T, Ruland J, Penniger JM, Siderovski DP and Mak TW . (1998). Cell, 95, 29–39.
Steck PA, Pershouse MA, Jasser SA, Yung WK, Lin H, Ligon AH, Langford LA, Baumgard ML, Hattier T, Thaylon D, Frye C, Hu R, Swedlund B, Teng DHR and Tavtigian SV . (1997). Nat. Genet., 15, 356–362.
Stolarov J, Chang K, Reiner A, Rodgers L, Hannon GJ, Wigler MH and Mittal V . (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 13043–13048.
Tan C, Cruet-Hennequart S, Troussard A, Fazli L, Costello P, Sutton K, Wheeler J, Gleave M, Sanghera J and Dedhar S . (2004). Cancer Cell., 5, 79–90.
Tan C, Mui A and Dedhar S . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 3109–3116.
Troussard AA, Costello P, Yoganathan TN, Kumagai S, Roskelley CD and Dedhar S . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 5444–5452.
Tsou HC, Teng DH, Ping XL, Brancolini V, Davis T, Hu R, Xie XX, Gruener AC, Schrager CA, Christiano AM, Eng C, Steck P, Ott J, Tavtigian SV and Peacocke M . (1997). Am. J. Hum. Genet., 61, 1036–1043.
Tu Y, Li F and Wu C . (1998). Mol. Biol. Cell, 9, 3367–3382.
Wang SI, Puc J, Li J, Bruce JN, Cairns P and Sidransky D . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 4183–4186.
Waterhouse DN, Dragowska WH, Gelmon KA, Mayer LD and Bally MB . (2004). Can. Biol. Ther., 3, 197–204.
White DE, Cardiff RD, Dedhar S and Muller WJ . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 7064–7072.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Mike Wigler and Linda Rogers at Cold Spring Harbour for their generous contribution of the U87 cells with the vector constructs. The Animal Technicians of Advanced Therapeutics for maintaining the mice, and QLT Inc./Kinetek Pharmaceuticals for the small-molecule ILK inhibitor. This research was funded by the NCIC Terry Fox New Frontiers Initiative.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edwards, L., Thiessen, B., Dragowska, W. et al. Inhibition of ILK in PTEN-mutant human glioblastomas inhibits PKB/Akt activation, induces apoptosis, and delays tumor growth. Oncogene 24, 3596–3605 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208427
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208427
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Chitinase-3 like-protein-1 function and its role in diseases
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2020)
-
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) regulates KRAS, IPP complex and Ras suppressor-1 (RSU1) promoting lung adenocarcinoma progression and poor survival
Journal of Molecular Histology (2020)
-
USP15 stabilizes MDM2 to mediate cancer-cell survival and inhibit antitumor T cell responses
Nature Immunology (2014)
-
Integrin-Linked Kinase (ILK) Expression Correlates with Tumor Severity in Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma
Pathology & Oncology Research (2013)
-
A novel role of ribonuclease inhibitor in regulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and ILK signaling pathway in bladder cancer cells
Cell and Tissue Research (2013)