Abstract
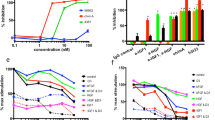
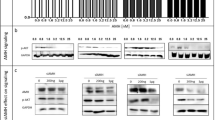
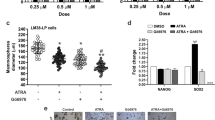
The present study addresses the effect of targeting type I insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-IR) with antisense strategies in in vivo growth of breast cancer cells. Our research was carried out on C4HD tumors from an experimental model of hormonal carcinogenesis in which the synthetic progestin medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) induced mammary adenocarcinomas in Balb/c mice. We employed two different experimental strategies. With the first one we demonstrated that direct intratumor injection of phosphorothioate antisense oligodeoxynucleotides (AS[S]ODNs) to IGF-IR mRNA resulted in a significant inhibition of C4HD tumor growth. In the second experimental strategy, we assessed the effect of intravenous (i.v.) injection of AS [S]ODN on C4HD tumor growth. This systemic treatment also resulted in significant reduction in tumor growth. The antitumor effect of IGF-IR AS[S]ODNs in both experimental protocols was due to a specific antisense mechanism, since growth inhibition was dose-dependent and no abrogation of tumor proliferation was observed in mice treated with phosphorothioate sense ODNs (S[S]ODNs). In addition, IGF-IR expression was inhibited in tumors from mice receiving AS[S]ODNs, as compared to tumors from control groups. We then investigated signal transduction pathways modulated in vivo by AS[S]ODNs treatment. Tumors from AS[S]ODN-treated mice of both intratumoral and intravenous protocols showed a significant decrease in the degree of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) tyrosine phosphorylation. Activation of two of the main IGF-IR signaling pathways, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI-3K)/Akt and p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) was abolished in tumors growing in AS[S]ODN-treated animals. Moreover, ErbB-2 tyrosine phosphorylation was blocked by in vivo administration of AS[S]ODNs. On the other hand, we found no regulation of either progesterone receptor expression or activity by in vivo AS[S]ODNs administration. Our results for the first time demonstrated that breast cancer growth can be inhibited by direct in vivo administration of IGF-IR AS[S]ODNs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeyinka A, Nui Y, Cherlet T, Snell L, Watson PH and Murphy LC . (2002). Clin. Cancer Res., 8, 1747–1753.
Arteaga CL and Osborne CK . (1989). Cancer Res., 49, 6237–6241.
Backer JM, Myers Jr MG, Sun XJ, Chin DJ, Shoelson SE, Miralpeix M and White MF . (1993). J. Biol. Chem., 268, 8204–8212.
Balana ME, Labriola L, Salatino M, Movsichoff F, Peters G, Charreau EH and Elizalde PV . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 34–47.
Balana ME, Lupu R, Labriola L, Charreau EH and Elizalde PV . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 6370–6379.
Baserga R . (1999). Exp. Cell Res., 253, 1–6.
Boonyaratanakornkit V, Scott MP, Ribon V, Sherman L, Anderson SM, Maller JL, Miller WT and Edwards DP . (2001). Mol. Cell, 8, 269–280.
Burfeind P, Chernicky CL, Rininsland F, Ilan J and Ilan J . (1996). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 7263–7268.
Chakravarti A, Loeffler JS and Dyson NJ . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 200–207.
Chernicky CL, Tan H, Yi L, Loret de Mola JR and Ilan J . (2002). Mol. Pathol., 55, 102–109.
Chernicky CL, Yi L, Tan H, Gan SU and Ilan J . (2000). Cancer Gene Ther., 7, 384–395.
Cho H, Aronica SM and Katzenellenbogen BS . (1994). Endocrinology, 134, 658–664.
Clemm DL, Sherman L, Boonyaratanakornkit V, Schrader WT, Weigel NL and Edwards DP . (2000). Mol. Endocrinol., 14, 52–65.
Coppola D, Ferber A, Miura M, Sell C, D'Ambrosio C, Rubin R and Baserga R . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 4588–4595.
Cui X, Zhang P, Deng W, Oesterreich S, Lu Y, Mills GB and Lee AV . (2003). Mol. Endocrinol., 17, 575–588.
Dunn SE, Ehrlich M, Sharp NJ, Reiss K, Solomon G, Hawkins R, Baserga R and Barrett JC . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 3353–3361.
Elizalde PV, Lanari C, Molinolo AA, Guerra FK, Balana ME, Simian M, Iribarren AM and Charreau EH . (1998). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 67, 305–317.
Ignar-Trowbridge DM, Nelson KG, Bidwell MC, Curtis SW, Washburn TF, McLachlan JA and Korach KS . (1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 89, 4658–4662.
Katzenellenbogen BS and Norman MJ . (1990). Endocrinology, 126, 891–898.
Labriola L, Salatino M, Proietti CJ, Pecci A, Coso OA, Kornblihtt AR, Charreau EH and Elizalde PV . (2003). Mol. Cell. Biol., 23, 1095–1111.
Lange CA, Richer JK, Shen T and Horwitz KB . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 31308–31316.
Lange CA, Shen T and Horwitz KB . (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 1032–1037.
Lee AV, Jackson JG, Gooch JL, Hilsenbeck SG, Coronado-Heinsohn E, Osborne CK and Yee D . (1999). Mol. Endocrinol., 13, 787–796.
Lee CT, Park KH, Adachi Y, Seol JY, Yoo CG, Kim YW, Han SK, Shim YS, Coffee K, Dikov MM and Carbone DP . (2003). Cancer Gene Ther., 10, 57–63.
Lee CT, Wu S, Gabrilovich D, Chen H, Nadaf-Rahrov S, Ciernik IF and Carbone DP . (1996). Cancer Res., 56, 3038–3041.
Li W, Hyun T, Heller M, Yam A, Flechner L, Pierce JH and Rudikoff S . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 3909–3915.
Liu X, Turbyville T, Fritz A and Whitesell L . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 5432–5438.
Migliaccio A, Piccolo D, Castoria G, Di Domenico M, Bilancio A, Lombardi M, Gong W, Beato M and Auricchio F . (1998). EMBO J., 17, 2008–2018.
Nabel GJ, Nabel EG, Yang ZY, Fox BA, Plautz GE, Gao X, Huang L, Shu S, Gordon D and Chang AE . (1993). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 11307–11311.
Nakamura K, Hongo A, Kodama J, Miyagi Y, Yoshinouchi M and Kudo T . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 760–765.
Navarro M and Baserga R . (2001). Endocrinology, 142, 1073–1081.
Neuenschwander S, Roberts Jr CT and LeRoith D . (1995). Endocrinology, 136, 4298–4303.
Oesterreich S, Zhang P, Guler RL, Sun X, Curran EM, Welshons WV, Osborne CK and Lee AV . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 5771–5777.
Peruzzi F, Prisco M, Dews M, Salomoni P, Grassilli E, Romano G, Calabretta B and Baserga R . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 7203–7215.
Pietras RJ, Arboleda J, Reese DM, Wongvipat N, Pegram MD, Ramos L, Gorman CM, Parker MG, Sliwkowski MX and Slamon DJ . (1995). Oncogene, 10, 2435–2446.
Plautz GE, Yang ZY, Wu BY, Gao X, Huang L and Nabel GJ . (1993). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 4645–4649.
Prager D, Li HL, Asa S and Melmed S . (1994). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 2181–2185.
Qiu M, Olsen A, Faivre E, Horwitz KB and Lange CA . (2003). Mol. Endocrinol., 17, 628–642.
Ram TG, Dilts CA, Dziubinski ML, Pierce LJ and Ethier SP . (1996). Mol. Carcinog., 15, 227–238.
Resnicoff M, Abraham D, Yutanawiboonchai W, Rotman HL, Kajstura J, Rubin R, Zoltick P and Baserga R . (1995a). Cancer Res., 55, 2463–2469.
Resnicoff M, Burgaud JL, Rotman HL, Abraham D and Baserga R . (1995b). Cancer Res., 55, 3739–3741.
Resnicoff M, Coppola D, Sell C, Rubin R, Ferrone S and Baserga R . (1994a). Cancer Res., 54, 4848–4850.
Resnicoff M, Sell C, Rubini M, Coppola D, Ambrose D, Baserga R and Rubin R . (1994b). Cancer Res., 54, 2218–2222.
Rohlik QT, Adams D, Kull Jr FC and Jacobs S . (1987). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 149, 276–281.
Sasaoka T, Rose DW, Jhun BH, Saltiel AR, Draznin B and Olefsky JM . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 13689–13694.
Scrimgeour AG, Blakesley VA, Stannard BS and LeRoith D . (1997). Endocrinology, 138, 2552–2558.
Sell C, Dumenil G, Deveaud C, Miura M, Coppola D, DeAngelis T, Rubin R, Efstratiadis A and Baserga R . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 3604–3612.
Shen T, Horwitz KB and Lange CA . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 6122–6131.
Stewart AJ, Johnson MD, May FE and Westley BR . (1990). J. Biol. Chem., 265, 21172–21178.
Surmacz E, Guvakova MA, Nolan MK, Nicosia RF and Sciacca L . (1998). Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 47, 255–267.
Swantek JL and Baserga R . (1999). Endocrinology, 140, 3163–3169.
Tamm I, Dorken B and Hartmann G . (2001). Lancet, 358, 489–497.
Werner H and Le Roith D . (2000). Cell Mol. Life Sci., 57, 932–942.
Yu H and Rohan T . (2000). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 92, 1472–1489.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Lilly Centre for Women's Health, Eli Lilly and Company and from the Centro Argentino Brasilero de Biotecnología (CABBIO), both awarded to PV Elizalde, and by grant IDB 802/OC-AR PICT 0503402 from the National Agency of Scientific Promotion of Argentina. We thank N Lope for her expert assistance with animal care and C Lanari for providing the MPA-induced mammary tumor model.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salatino, M., Schillaci, R., Proietti, C. et al. Inhibition of in vivo breast cancer growth by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to type I insulin-like growth factor receptor mRNA involves inactivation of ErbBs, PI-3K/Akt and p42/p44 MAPK signaling pathways but not modulation of progesterone receptor activity. Oncogene 23, 5161–5174 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207659
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207659