Abstract
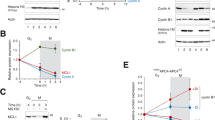
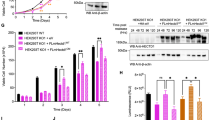
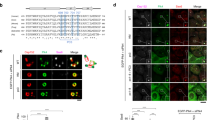
MEK1, a gene product that regulates cell growth and differentiation, also plays an important role in Golgi breakdown during the cell cycle. We have recently shown that polo-like kinase (Plk3) is Golgi localized and involved in Golgi dynamics during the cell cycle. To study the mode of action of Plk3 in the Golgi fragmentation cascade, we examined functional as well as physical interactions between Plk3 and MEK1/ERKs. In HeLa cells, although a significant amount of Plk3 signals dispersed in a manner similar to those of Golgi during mitosis concentrated Plk3 was detected at spindle poles, which colocalized with phospho-MEKs and phospho-ERKs. Pull-down assays showed that Plk3 physically interacted with MEK1 and ERK2. Nocodazole activated Plk3 and its activation was blocked by MEK-specific inhibitors (PD98059 or U0126). Moreover, transfection of activated MEK1 resulted in an enhanced kinase activity of Plk3; Plk3-induced fragmentation of Golgi stacks was significantly reduced after treatment with MEK inhibitors. Consistently, ectopic expression of activated MEK1, but not kinase-dead MEK1K97R, stimulated Plk3 to induce Golgi breakdown and the stimulation was not observed in cells expressing Plk3K52R. Furthermore, PLK3−/− murine embryonic fibroblast cells exhibited a significantly less fragmentation of the Golgi complex than that in wild-type cells after exposed to nocodazole. Thus, our studies strongly suggest that Plk3 may be a key protein kinase mediating MEK1 function in the Golgi fragmentation pathway during cell division.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya U, Mallabiabarrena A, Acharya JK and Malhotra V . (1998). Cell, 92, 183–192.
Beauvais F, Michel L and Dubertret L . (1995). J. Leukocyte Biol., 57, 851–855.
Cha H and Shapiro P . (2001). J. Cell Biol., 153, 1355–1367.
Colanzi A, Deerinck TJ, Ellisman MH and Malhotra V . (2000). J. Cell Biol., 149, 331–339.
Colanzi A, Sutterlin C and Malhotra V . (2003). J. Cell Biol., 161, 27–32.
Jesch SA, Lewis TS, Ahn NG and Linstedt AD . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 12, 1811–1817.
Kano F, Takenaka K, Yamamoto A, Nagayama K, Nishida E and Murata M . (2000). J. Cell Biol., 149, 357–368.
Kee HJ, Shin JH, Chang J, Chung KY, Shin DH, Kim YS, Kim SK and Kim SK . (2003). Yonsei Med. J., 44, 65–74.
Lin CY, Madsen ML, Yarm FR, Jang YJ, Liu X and Erikson RL . (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 12589–12594.
Lowe M, Gonatas NK and Warren G . (2000). J. Cell Biol., 149, 341–356.
Lowe M, Rabouille C, Nakamura N, Watson R, Jackman M, Jamsa E, Rahman D, Pappin DJ and Warren G . (1998). Cell, 94, 783–793.
Lucocq J, Warren G and Pryde J . (1991). J. Cell Sci., 100 (Part 4), 753–759.
Mansour SJ, Candia JM, Matsuura JE, Manning MC and Ahn NG . (1996). Biochemistry, 35, 15529–15536.
Ouyang B, Li W, Pan H, Meadows J, Hoffmann I and Dai W . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 6029–6036.
Ouyang B, Pan H, Lu L, Li J, Stambrook P, Li B and Dai W . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 28646–28651.
Ruan Q, Wang Q, Guan KL, Jhanwar-Uniyal M and Dai W Polo-like kinase 3 (Plk3) induces Golgi fragmentation and dispersal at the onset of mitosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2004. (in press).
Sutterlin C, Hsu P, Mallabiabarrena A and Malhotra V . (2002). Cell, 109, 359–369.
Sutterlin C, Lin CY, Feng Y, Ferris DK, Erikson RL and Malhotra V . (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 9128–9132.
Wang Q, Xie S, Chen J, Fukasawa K, Naik U, Traganos F, Darzynkiewicz Z, Jhanwar-Uniyal M and Dai W . (2002). Mol. Cell. Biol., 22, 3450–3459.
Yu SP, Yeh CH, Sensi SL, Gwag BJ, Canzoniero LM, Farhangrazi ZS, Ying HS, Tian M, Dugan LL and Choi DW . (1997). Science, 278, 114–117.
Zambrowicz BP, Friedrich GA, Buxton EC, Lilleberg SL, Person C and Sands AT . (1998). Nature, 392, 608–611.
Zheng CF and Guan KL . (1994). EMBO J., 13, 1123–1131.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Vivek Malhotra and Christine Sutterlin for helpful suggestions and discussions. We also thank Dr John Cogswell at GlaxoSmithKline for pCR259-Plk3 and pCR259-Plk3K52R expression constructs. The work is supported in part by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (RO1-CA74229) to WD and a fellowship award to SX from Philip Morris Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, S., Wang, Q., Ruan, Q. et al. MEK1-induced Golgi dynamics during cell cycle progression is partly mediated by Polo-like kinase-3. Oncogene 23, 3822–3829 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207479
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207479
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Polo-like kinases: structural variations lead to multiple functions
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2014)
-
Roles of Polo-like kinase 3 in suppressing tumor angiogenesis
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2012)
-
Inheritance and biogenesis of organelles in the secretory pathway
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2007)
-
The physiology of membrane transport and endomembrane-based signalling
The EMBO Journal (2006)
-
Regulation of cell cycle checkpoints by polo-like kinases
Oncogene (2005)