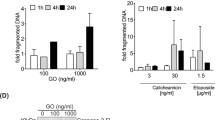
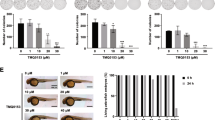
Abstract
The marine alkaloid ascididemin (ASC) was shown to exert cytotoxicity even against multidrug-resistant cancer cells. Here, we address the signaling pathways utilized by ASC to trigger apoptosis in Jurkat leukemia T cells. We show that ASC (0.5–20 μ M) induces a mitochondrial pathway that requires the activation of the initiator caspase-2 upstream of mitochondria. ASC-triggered apoptosis occurred independent of CD95, but required mitochondrial dysfunction. The activation of caspase-2 was shown to precede the processing of caspase-8, -9 and -3. The specific caspase-2 inhibitor zVDVADfmk abrogated ASC-induced DNA fragmentation almost completely. Overexpression of Bcl-xL blocked caspase-8 but not caspase-2 processing. Conversely, caspase-2 inhibition strongly reduced caspase-9 activation. As a possible link between caspase-2 and mitochondrial dysfunction, Bid was found to be cleaved by ASC. In addition, JNK was activated by ASC upstream of mitochondria via reactive oxygen species. The specific JNK inhibitor SP600125 partially inhibited caspase-2 and -9 processing as well as cytochrome c release and DNA fragmentation indicating that JNK contributes to, but is not necessary for ASC-mediated apoptosis. Thus, ASC triggers a pathway in which early activation of caspase-2 provides a possible link between its DNA-damaging activity and the induction of mitochondrial dysfunction. The activation of JNK contributes to this signaling upstream of mitochondria.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antlsperger DSM, Dirsch VM, Ferreira D, Su J-L, Kuo M-L and Vollmar AM . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 582–589.
Barr RK and Bogoyevitch MA . (2001). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 33, 1047–1063.
Beck WT, Mo YY and Bhat UG . (2001). Biochem. Soc. Trans., 29, 702–703.
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, O'Leary EC, Sakata ST, Xu W, Leisten JC, Motiwala A, Pierce S, Satoh Y, Bhagwat SS, Manning AM and Anderson DW . (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 13681–13686.
Bonnard I, Bontemps N, Lahmy S, Banaigs B, Combaut G, Francisco C, Colson P, Houssier C, Waring MJ and Bailly C . (1995). Anticancer Drug Des., 10, 333–346.
Bracher F . (1993). J. Heterocyclic Chem., 30, 157–159.
Bratton SB and Cohen GM . (2001). Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 22, 306–315.
Cai J and Jones DP . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 11401–11404.
Dassonneville L, Wattez N, Baldeyrou B, Mahieu C, Lansiaux A, Banaigs B, Bonnard I and Bailly C . (2000). Biochem. Pharmacol., 60, 527–537.
Dirsch VM, Gerbes AL and Vollmar AM . (1998). Mol. Pharmacol., 53, 402–407.
Dirsch VM, Stuppner H and Vollmar AM . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 5817–5823.
Droin N, Bichat F, Rebe C, Wotawa A, Sordet O, Hammann A, Bertrand R and Solary E . (2001). Blood, 97, 1835–1844.
Duan H and Dixit VM . (2002). Nature, 385, 86–89.
Ferri KF and Kroemer G . (2001). Nat. Cell Biol., 3, E255–E263.
Guo Y, Srinivasula SM, Druilhe A, Fernandes-Alnemri T and Alnemri ES . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 13430–13437.
Harvey NL, Butt AJ and Kumar S . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 13134–13139.
Harvey NL, Trapani JA, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Litwack G, Alnemri ES and Kumar S . (1996). Genes Cells, 1, 673–685.
Herr I and Debatin KM . (2001). Blood, 98, 2603–2614.
Kaufmann SH and Earnshaw WC . (2000). Exp. Cell Res., 256, 42–49.
Kharbanda S, Saxena S, Yoshida K, Pandey P, Kaneki M, Wang Q, Cheng K, Chen YN, Campbell A, Sudha T, Yuan ZM, Narula J, Weichselbaum R, Nalin C and Kufe D . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 322–327.
Kobayashi J, Cheng J, Nakamura Y, Ohizumi Y, Hirata Y, Sasaki T, Otha T and Nozoe S . (1988). Tetrahedron Lett., 29, 1177–1180.
Lassus P, Opitz-Araya X and Lazebnik Y . (2002). Science, 297, 1352–1354.
Leist M, Volbracht C, Fava E and Nicotera P . (1998). Mol. Pharmacol., 54, 789–801.
Lindsay BS, Barrows LR and Copp BR . (1995). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 5, 739–742.
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C and Wang X . (1998). Cell, 94, 481–490.
Matsumoto SS, Biggs J, Copp BR, Holden JA and Barrows LR . (2003). Chem. Res. Toxicol., 16, 113–122.
Mendelsohn AR, Hamer JD, Wang ZB and Brent R . (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 6871–6876.
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F and Riccardi C . (1991). J. Immunol. Methods, 139, 271–279.
O'Reilly LA, Ekert P, Harvey N, Marsden V, Cullen L, Vaux DL, Hacker G, Magnusson C, Pakusch M, Cecconi F, Kuida K, Strasser A, Huang DC and Kumar S . (2002). Cell Death Differ., 9, 832–841.
Paroni G, Henderson C, Schneider C and Brancolini C . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 15147–15161.
Read SH, Baliga BC, Ekert PG, Vaux DL and Kumar S . (2002). J. Cell. Biol., 159, 739–745.
Robertson JD, Enoksson M, Suomela M, Zhivotovsky B and Orrenius S . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 29803–29809.
Robertson JD, Gogvadze V, Zhivotovsky B and Orrenius S . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 32438–32443.
Shearwin-Whyatt LM, Harvey NL and Kumar S . (2000). Cell Death Differ., 7, 155–165.
Slee EA, Harte MT, Kluck RM, Wolf BB, Casiano CA, Newmeyer DD, Wang HG, Reed JC, Nicholson DW, Alnemri ES, Green DR and Martin SJ . (1999). J. Cell. Biol., 144, 281–292.
Stefanis L, Troy CM, Qi H, Shelanski ML and Greene LA . (1998). J. Neurosci., 18, 9204–9215.
Walczak H, Bouchon A, Stahl H and Krammer PH . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 3051–3057.
Yamamoto K, Ichijo H and Korsmeyer SJ . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 8469–8478.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Peter H Krammer and Henning Walczak (German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany) as well as Dr Schulze-Osthoff (University of Münster, Germany) for supplying Jurkat T cell clones, and Dr X Wang (University of Texas, Dallas, USA) for providing the anti-Bid antibody. We gratefully acknowledge the excellent lab work of Katharina von Gersdorff.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 369)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dirsch, V., Kirschke, S., Estermeier, M. et al. Apoptosis signaling triggered by the marine alkaloid ascididemin is routed via caspase-2 and JNK to mitochondria. Oncogene 23, 1586–1593 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207281
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207281
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The enigma of caspase-2: the laymen's view
Cell Death & Differentiation (2009)
-
Role of Smac in cephalostatin-induced cell death
Cell Death & Differentiation (2008)
-
Involvement of JNK regulation in oxidative stress-mediated murine liver injury by microcystin-LR
Apoptosis (2008)
-
How do dietary diatoms cause the sex reversal of the shrimp Hippolyte inermis Leach (Crustacea, Decapoda)
Marine Biology (2007)
-
A novel indoloquinoline derivative, IQDMA, induces S-phase arrest and apoptosis in promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells
Cell Biology and Toxicology (2006)